Organic light-emitting display device
A light-emitting display device, an organic technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high requirements for the main material, comparable, and failure to reach the commercialization of OLEDs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
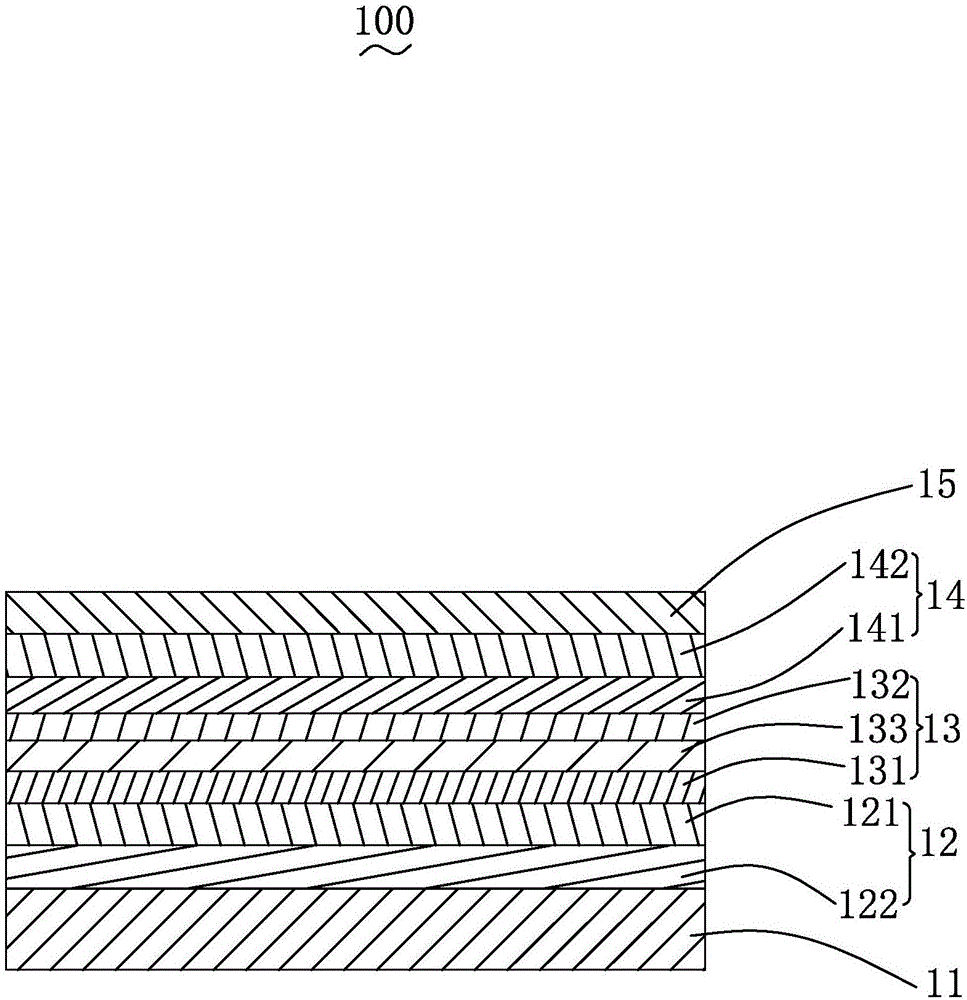
[0089] see figure 1 , is a schematic structural view of Embodiments 1-4 of the organic light-emitting display device provided by the present invention. The organic light emitting display device 100 includes a first conductive layer 11 , a hole transport part 12 , a light emitting layer 13 , an electron transport part 14 and a second conductive layer 15 which are sequentially deposited.
[0090] The first conductive layer 11 is an anode, and its material is ITO, IGZO, IZO, graphene, nano-silver wire, carbon nanotube and other materials; preferably ITO. The second conductive layer 15 is a cathode, and its material is a low work function metal or metal alloy, such as Al, Mg:Ag alloy or Ag, preferably Al.
[0091] The hole transport portion 12 includes a hole injection layer 121 and a hole transport layer 122 deposited on the hole injection layer 121, and the hole injection layer 121 is disposed between the first conductive layer 11 and the Between the hole transport layer 122. ...
Embodiment 2
[0155] combine figure 1 And the specific materials of each layer structure,
[0156] The structure of Example 2 is: ITO / NPB / TCTA / TCTA:PdN3N:DCM1 / TCTA / TCTA:PdN3N:DCM1 / TPBi / Bphen / LiF / Al.
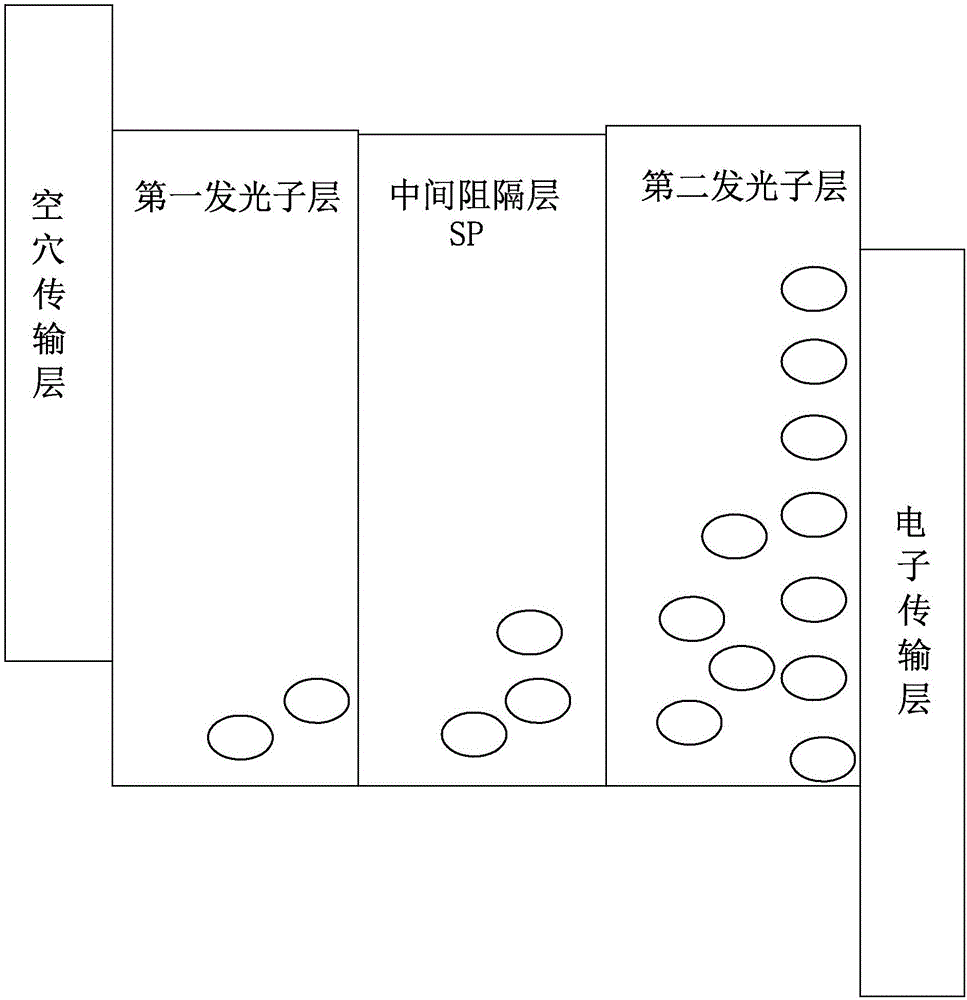
[0157] Both the first luminescent sublayer 131 and the second luminescent sublayer 132 are formed by doping a metal-assisted delayed fluorescence sensitizer, a host material, and a fluorescent guest material. The first luminescent sublayer 131 and the second luminescent sublayer 131 The middle barrier layer 133 is formed between the luminescent sub-layers 132 .
[0158] In the first luminescent sublayer 131 and the second luminescent sublayer, PdN3N is used as a metal-assisted delayed fluorescence sensitizer, TCTA is used as a host material, and DCM1 is used as a fluorescent guest material, which belongs to a red fluorescent material with a CIE (0.64 , 0.34).
[0159] Please refer to Figure 6 , Figure 7 ,in Figure 6 It is the absorption spectrum and emission spectrum diagram of PdN3N;...
Embodiment 3
[0165] combine figure 1 And the specific materials of each layer structure,
[0166] The structure of Example 3 is: ITO / NPB / TCTA / TCTA:PdN3N:DCJTB / TCTA / TCTA:PdN3N:DCJTB / TPBi / Bphen / LiF / Al.
[0167] Both the first luminescent sublayer 131 and the second luminescent sublayer 132 are formed by doping a metal-assisted delayed fluorescence sensitizer, a host material, and a fluorescent guest material. The first luminescent sublayer 131 and the second luminescent sublayer 131 The middle barrier layer 133 is formed between the luminescent sub-layers 132 .
[0168] Please combine Figure 6 and Figure 9 ,in Figure 9 It is the absorption spectrum figure of DCJTB, wherein curve a represents the fluorescence intensity curve of Alq (Alq represents 3,8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum), curve b represents the absorption intensity curve of DCJTB, and curve c represents the absorption intensity curve of QAD (QAD represents quinoline Acridine (two) ketone), curve d represents the fluorescence in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com