Application of porous carbon nanorod in near-infrared light induced double phototherapy
A near-infrared light and nanorod technology is applied in photodynamic therapy, medical preparations containing active ingredients, wave energy or particle radiation treatment materials, etc. The problem of poor anti-photobleaching ability of the agent can be overcome, and the effects of poor anti-photobleaching ability, single shape and adjustable size can be overcome.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
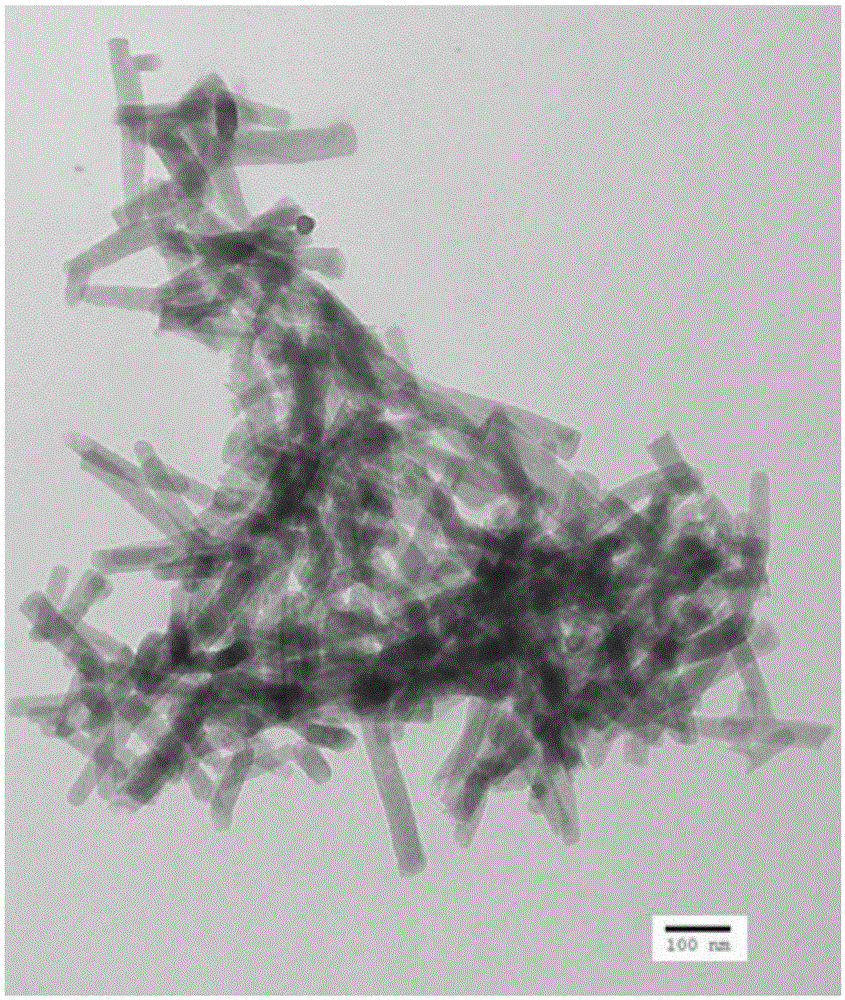
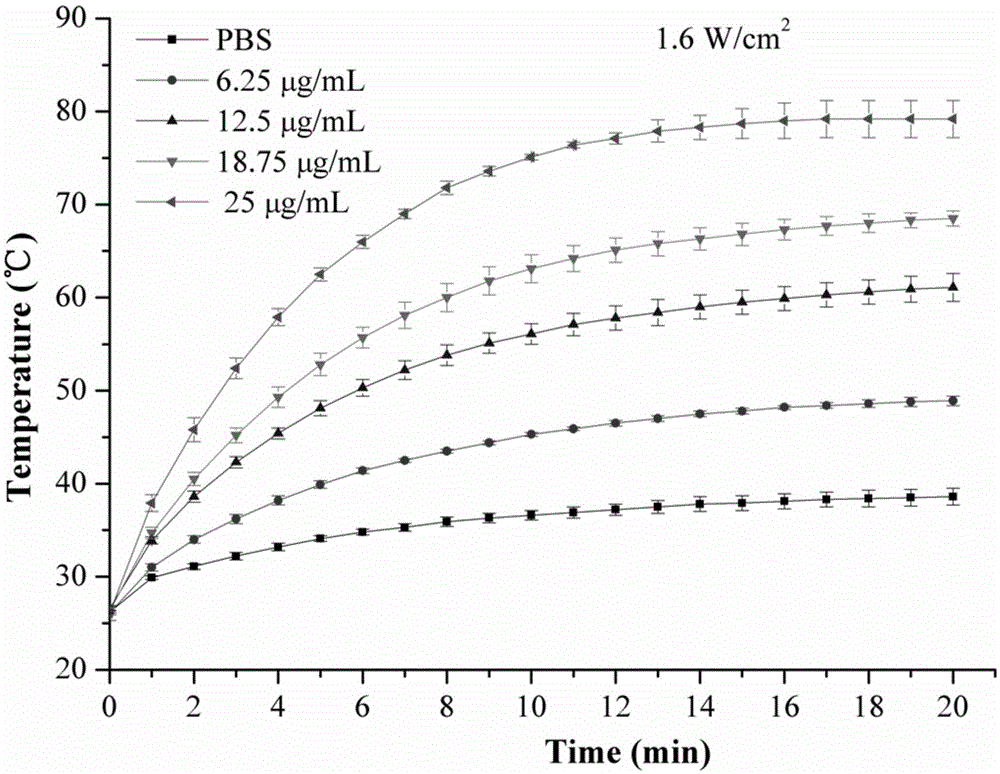
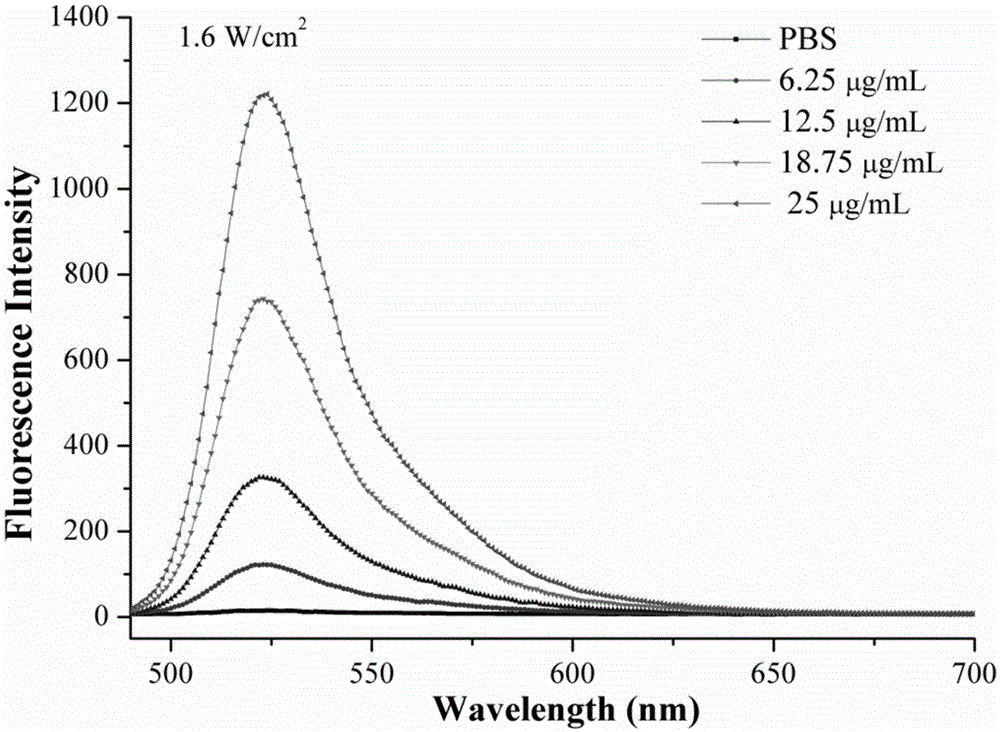
[0023] Dissolve trimesic acid and zinc acetate with a molar ratio of 1:1 respectively, mix with ultrasonic reaction, centrifuge, wash and dry to obtain zinc metal-organic framework material; calcinate at 800°C for 5 hours under nitrogen atmosphere and soak in hydrofluoric acid for 12 hours Metal oxides are removed to obtain porous carbon nanorods. Porous carbon nanorods were ultrasonically dispersed in PBS to prepare material solutions with gradient concentrations. Put the porous carbon nanorod solution under 808nm laser irradiation, the optical power density is 1.6W / cm 2 , the irradiation time was 20min, the interval was 1min, and the temperature change of the material solution was recorded; the ROS indicator DCFH-DA was added to detect the change of the ROS content in the solution.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Dissolve trimesic acid and zinc nitrate with a molar ratio of 1:1 respectively, mix and add triethylamine to react at room temperature, centrifuge, wash, and dry to obtain zinc metal-organic framework materials; calcinate at 800°C for 5 hours under nitrogen atmosphere and use hydrogen Soak in hydrofluoric acid for 12 hours to remove metal oxides to obtain porous carbon nanorods. Porous carbon nanorods were ultrasonically dispersed in PBS to prepare material solutions with gradient concentrations. Put the porous carbon nanorod solution under 808nm laser irradiation, the optical power density is 1.6W / cm 2 , the irradiation time was 20min, the interval was 1min, and the temperature change of the material solution was recorded; the ROS indicator DCFH-DA was added to detect the change of the ROS content in the solution.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Dissolve trimesic acid and zinc acetate with a molar ratio of 1:2 respectively, mix with ultrasonic reaction, centrifuge, wash, and dry to obtain a metal-organic framework material; calcinate at 800°C for 5 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, and soak in hydrofluoric acid for 12 hours to remove metal oxides to obtain porous carbon nanorods. Porous carbon nanorods were ultrasonically dispersed in PBS to prepare material solutions with gradient concentrations. Put the porous carbon nanorod solution under 808nm laser irradiation, the optical power density is 0.8W / cm 2 , the irradiation time was 20min, the interval was 1min, and the temperature change of the material solution was recorded; ROS indicator DCFH-DA was added to detect the change of ROS content in the solution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com