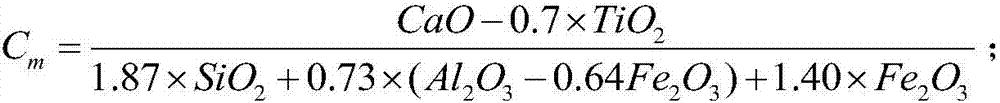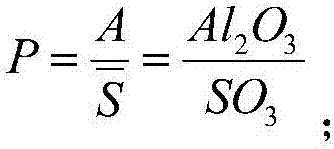System and method for preparing building 3D printing material by using municipal waste and industrial solid waste
A 3D printing and industrial solid waste technology, applied in the direction of solid waste management, sustainable waste treatment, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of high investment in sludge dewatering equipment, high operation and maintenance costs, and environmental pollution caused by odorous gas, achieving Effect of eliminating dehydration process, reducing dehydration cost and energy consumption, and reducing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
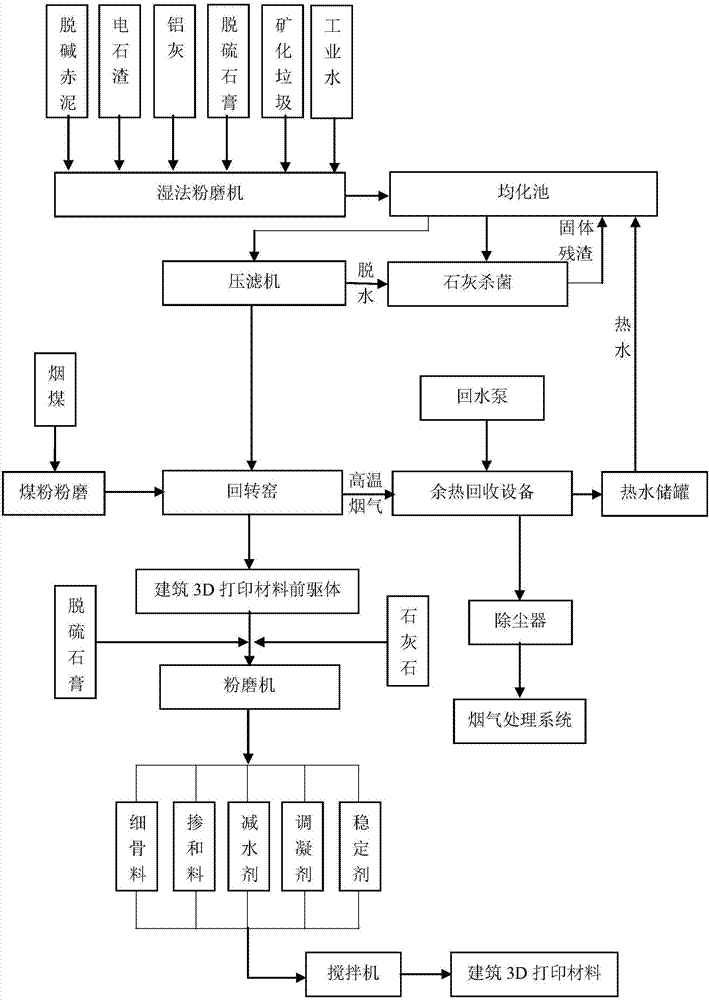
[0115] The above system and process are used for preparation, and the specific parameters, calculation results and detection are as follows: based on the mass of solid-liquid mixture after mixing and matching, the dry weight ratio of wet sludge, mineralized waste, red mud, desulfurized gypsum and calcium carbide slag 8:12:25:15:40. The mechanically dehydrated raw meal is directly transported into the rotary kiln for calcination. The calcination temperature is 1310°C and the calcination time is 60 minutes. At this time, toxic and harmful substances such as dioxin can be well eliminated. Then the flue gas passes through the waste heat recovery equipment to recover the heat. Finally, dust removal and flue gas treatment are carried out on the flue gas, and no harmful substances such as dioxins are found in the treated flue gas after testing. The obtained product is tested by the cement mortar strength test method (GB / T 17671-1999), and the 2h compressive strength is 15.4MPa, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0117] The above system and process are used for preparation, and the specific parameters, calculation results and detection are as follows: based on the mass of solid-liquid mixture after mixing and matching, the dry weight ratio of wet sludge, mineralized waste, red mud, desulfurized gypsum and calcium carbide slag 8:15:20:12:45. The mechanically dehydrated raw meal is directly transported into the rotary kiln for calcination, the calcination temperature is 1280°C, and the calcination time is 60 minutes. No harmful substances such as dioxins were found in the treated flue gas after testing. According to the cement mortar strength test method, the 2h compressive strength is 14.2MPa, and the 3-day and 28-day compressive strengths are 41.5MPa and 54.5MPa respectively. The initial setting time is 24 minutes, and the final setting time is 35 minutes. It meets the requirements for the use of architectural 3D printing materials.
Embodiment 3
[0119] The above system and process are used for preparation, and the specific parameters, calculation results and detection are as follows: based on the mass of solid-liquid mixture after mixing and matching, the dry weight ratio of wet sludge, mineralized waste, red mud, desulfurized gypsum and calcium carbide slag 8:10:18:10:54. The mechanically dehydrated raw meal is directly transported into the rotary kiln for calcination, the calcination temperature is 1300°C, and the calcination time is 45 minutes. No harmful substances such as dioxins were found in the treated flue gas after testing. According to the cement mortar strength test method, the 2h compressive strength is 13.4MPa, and the 3day and 28day compressive strength are 39.6MPa and 51.8MPa respectively. The initial setting time is 30 minutes, and the final setting time is 42 minutes. It meets the requirements for the use of architectural 3D printing materials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com