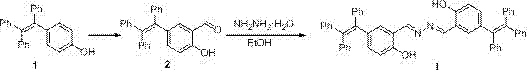Aggregation-induced emission-based copper ion detection probe and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of aggregation-induced luminescence and copper ion detection, applied in the field of chemical analysis and detection, to achieve the effect of sensitive identification, strong specificity and low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Synthesis of fluorescent probes of the present invention
[0046] The preparation route of fluorescent probe of the present invention is as follows:
[0047]
[0048] (1) Preparation of intermediate compound 2
[0049]
[0050] Dissolve compound 1 and hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) in trifluoroacetic acid, the ratio of the amount of compound 1 to HMTA is 1:1, heat and stir for 5 hours, after the reaction of the raw materials is completed, rotary evaporation under reduced pressure The solvent was removed, and the crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain compound 2 as a yellow solid;
[0051] (2) Preparation of fluorescent probe I
[0052]
[0053] Get compound 2, the hydrazine hydrate that mass fraction is 80% is dissolved in dehydrated alcohol, and the ratio of the amount of described compound 2 and hydrazine hydrate substance is 2:1,60 o Stirred under the condition of C for 2 hours, the solid was completely precipitated, filtered, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Molecular Working Curve
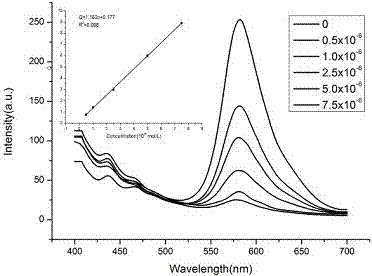
[0057] Take 2 mL of the prepared water-dispersed solution of ratiometric fluorescent probe molecules, add 20 μL of copper sulfate aqueous solution with different concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 μmol / L), and let it stand for 60 minutes , Fluorescence spectrometer recorded the change of fluorescence intensity at 581nm respectively. Taking the fluorescence intensity as the ordinate and the copper ion concentration as the abscissa, the working curve of the ratio fluorescent probe molecule is obtained by fitting. In the present embodiment, the ratiometric fluorescent probe is used to measure the concentration of copper ions. Under the excitation of 380nm excitation light, the relationship between the fluorescence intensity and the concentration of copper ions is as follows: figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Fluorescent Probe Molecular Cation Selectivity Determination
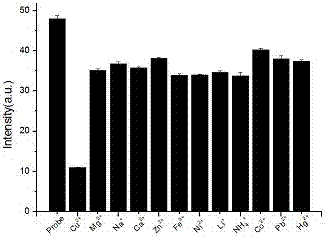
[0060] Take 2mL of the water-dispersed solution of the ratio fluorescent probe molecule prepared in Example 2, and add 20 μL of Ag with a concentration of 0.01M + , Ba 2+ , Ca 2+ , Li + , Mg 2+ , NH 4 + , Ni 2+ , Zn 2+ , Pb 2+ , Co 3+ , Hg 2+ After the aqueous solution was left for 60 minutes, the fluorescence spectrometer recorded the changes of the fluorescence intensity at 581nm respectively. Experimental results show that, except for copper ions, other particles do not cause obvious changes in fluorescence, indicating that the probe molecules of the present invention have good selectivity. In the present embodiment, the molecular selectivity of the fluorescent probe is measured, and the relationship diagram of the fluorescence intensity changing with the concentration of copper ions under the excitation of 380nm excitation light is as follows figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com