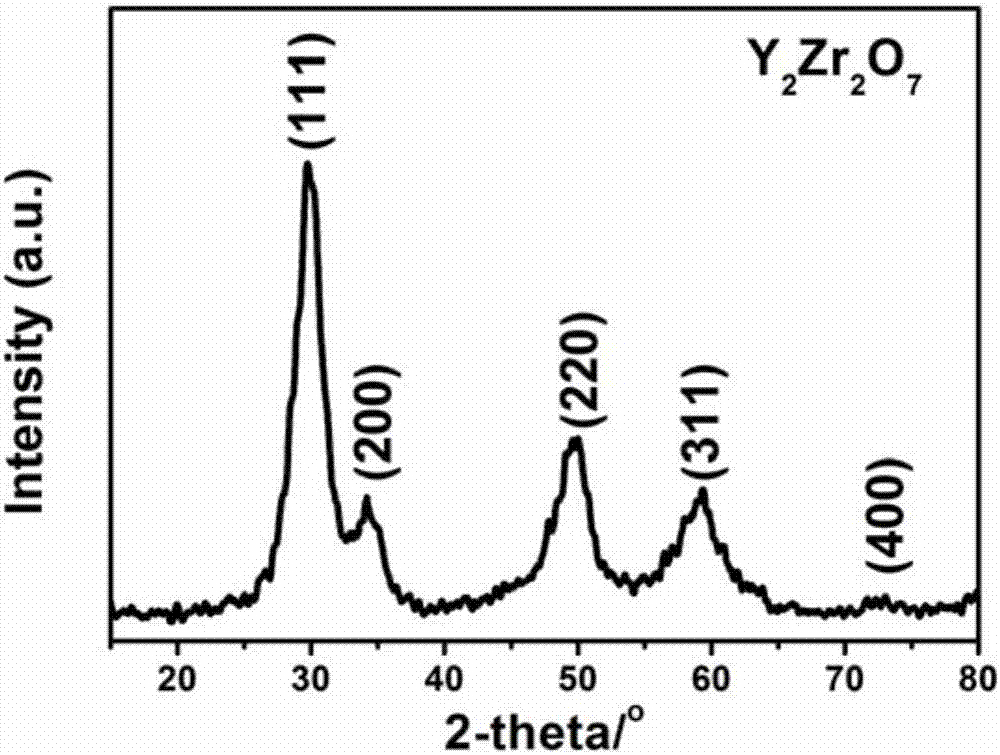
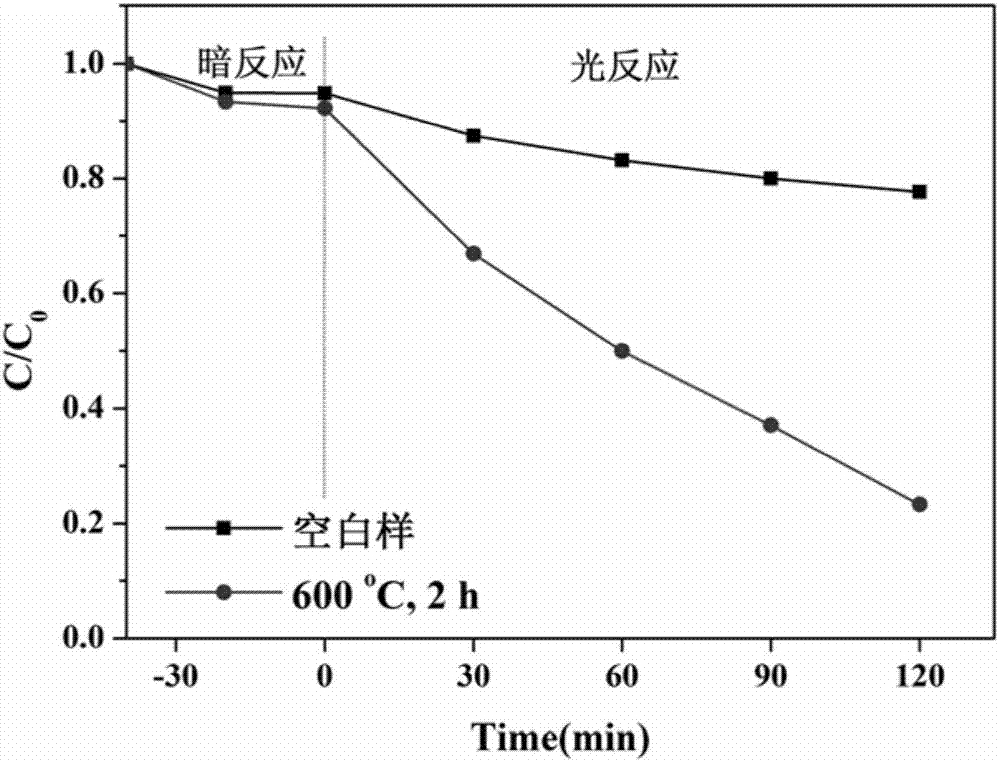
Method for preparing zirconate yttrium through tartaric acid-nitrate combustion method
A technology of tartaric acid and nitrate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, zirconium compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high temperature of reactants, large size of products, and loss of stoichiometry, so as to promote low-temperature rapid synthesis and product Less loss rate and lower synthesis temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1) Weigh 2mmol of analytically pure Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and ZrO(NO 3 ) 2 ·H 2 O, placed in an agate mortar and ground thoroughly to obtain a mixed powder.
[0028] 2) According to the molar ratio of tartaric acid: EDTA = 1: 1, take quantitative analysis of pure tartaric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), prepare a compound complexing agent with a tartaric acid concentration of 0.2mol / L, and adjust it with concentrated ammonia water Composite complexing agent pH=7, obtains complex complexing agent solution; Wherein, tartaric acid and Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 The molar ratio of O is 2:1.
[0029] 3) After stirring with a magnetic stirrer at a speed of 350 rpm for 12 hours, add the complex complexing agent solution drop by drop into the mortar containing the mixed powder, grind while adding, and continue grinding for 15 minutes after the addition is completed , to obtain a pasty viscous intermediate.
[0030] 4) The obtained paste-like viscous intermediate w...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Weigh 3mmol of analytically pure Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and ZrO(NO 3 ) 2 ·H 2 O, placed in an agate mortar and ground thoroughly to obtain a mixed powder.
[0034] 2) According to the molar ratio of tartaric acid: EDTA = 1: 1, take quantitative analysis of pure tartaric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), prepare a compound complexing agent with a tartaric acid concentration of 0.2mol / L, and adjust it with concentrated ammonia water Composite complexing agent pH=6, obtains complex complexing agent solution; Wherein, tartaric acid and Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 The molar ratio of O is 2:1.
[0035] 3) After stirring with a magnetic stirrer at a speed of 400 rpm for 8 hours, add the complex complexing agent solution drop by drop into the mortar containing the mixed powder, grind while adding, and continue grinding for 20 minutes after the addition is completed , to obtain a pasty viscous intermediate.
[0036] 4) The obtained paste-like viscous intermediate wa...
Embodiment 3
[0042] 1) Weigh 5mmol of analytically pure Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and ZrO(NO 3 ) 2 ·H 2 O, placed in an agate mortar and ground thoroughly to obtain a mixed powder.
[0043] 2) According to the molar ratio of tartaric acid: EDTA = 1: 2, take quantitative analysis of pure tartaric acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), prepare a compound complexing agent whose tartaric acid concentration is 0.2mol / L, and adjust it with concentrated ammonia water Composite complexing agent pH=5, obtains complex complexing agent solution; Wherein, tartaric acid and Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 The molar ratio of O is 2:1.
[0044] 3) After stirring with a magnetic stirrer at a speed of 450 rpm for 8 hours, add the complex complexing agent solution drop by drop into the mortar containing the mixed powder, grind while adding, and continue grinding for 25 minutes after the addition is completed , to obtain a pasty viscous intermediate.
[0045] 4) The obtained paste-like viscous intermediate was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com