Microorganism for producing chitosanase, and plant cultivation composition and cultivation method using same
A technology for chitosan and decomposed products, which is applied to microorganisms producing chitosan decomposing enzymes and plant cultivation compositions and cultivation fields using the same, can solve the problem of difficulty in finding products, insignificant functional effects, and inconvenience to consumers. Trust and other issues, to achieve the effect of increasing the electron-donating capacity and increasing the content of polyphenols and flavonoids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1. Selection of microorganisms
[0033] Prepare colloidal chitosan
[0034] Colloidal chitosan was prepared in the following manner: 400 mL of distilled water was added to 10 g of chitosan, and after stirring, 100 mL of 1 M acetic acid (acetic acid) was added thereto again, and after stirring for one night, filter paper was used. Filter, and after utilizing 1N sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to make filtrate neutralize, under the condition of 6000rpm, centrifuge 20 minutes, only collect precipitate, utilize distilled water to wash 3 times, and in sodium acetate buffer (sodium actetate buffer) (pH 5.5) so as to be suspended at 1%.
[0035] Isolation of strains
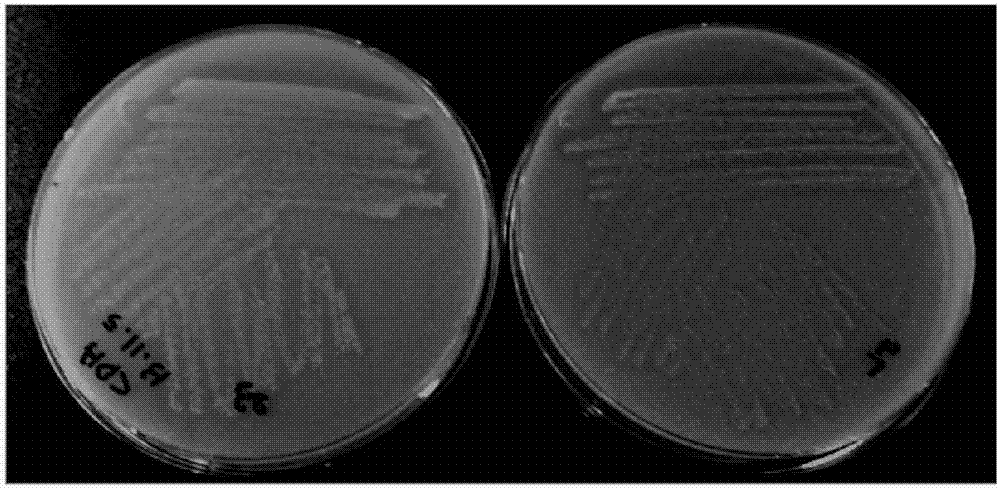
[0036] figure 1 It is a photo of the isolated chitosan decomposing enzyme producing strains C23 and C25 of the present invention.
[0037] In order to isolate chitosan-decomposing enzyme-producing microorganisms, 9 mL of sterilized distilled water was added to 1 g of soil collected in Gyeongbuk, Korea, and...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2. Analysis of effect test by crop growth test - growth promotion
[0050] experimental method
[0051] The lettuce in this experiment uses under totally three kinds of conditions of no treatment group, control group (known microbial preparation sold on the market), C23 and C25 mixed treatment group (mass ratio is 1: 1), cultivated in pots. Lettuce, to investigate fertilizer damage and changes in crops.
[0052] At this time, in the mixed treatment group of C23 and C25, the two microorganisms were diluted 300 times with water for perfusion and foliar fertilization, and used instead of the existing water.
[0053] Fertility promotion experiment results
[0054] According to the survey results of lettuce growth, as shown in Table 1, in the non-treatment group and the control group, the leaf length is 11.6cm, but compared with this, in the treatment group, the leaf length is 12.4cm, which is 12.4cm. High, and in the treatment group, compared with the non-treatme...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3. Analysis of Effect Test by Crop Growth Test - Total Content of Polyphenols
[0059] extraction conditions
[0060] Figure 5 and Figure 6 It is a photo of lettuce extract by ethanol extraction by cultivation time and by treatment group. The lettuce extract was prepared as follows: 1 g of cultivated lettuce was collected, mixed with 50 ml of 80% ethanol, left to extract at room temperature (25°C) for 24 hours, and centrifuged to recover the supernatant .
[0061] Analysis method for the total content of polyphenols
[0062] The total content of polyphenols was determined as follows: according to the Folin-ciocal method, in the prepared 1ml analysis sample, add 1ml of Folin-ciocalteu reagent (SigmaChemical Co., St. .Louis, MO, USA) solution, and at room temperature, after standing for 5 minutes, add 4ml of 75% Na 2 CO 3 The solution was added for an additional reaction for 1 hour, and the absorbance was measured at 756 nm using a Microplate reader (Infi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com