Deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 for regulating and controlling grain shape and leaf color of rice and application thereof
A deubiquitinase, gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The acquisition and phenotype analysis of embodiment 1 mutant
[0032] The rice ubp5 mutant was derived from the mutation produced by EMS mutagenesis of the japonica rice variety Nipponbare, which was obtained in Beijing, China.
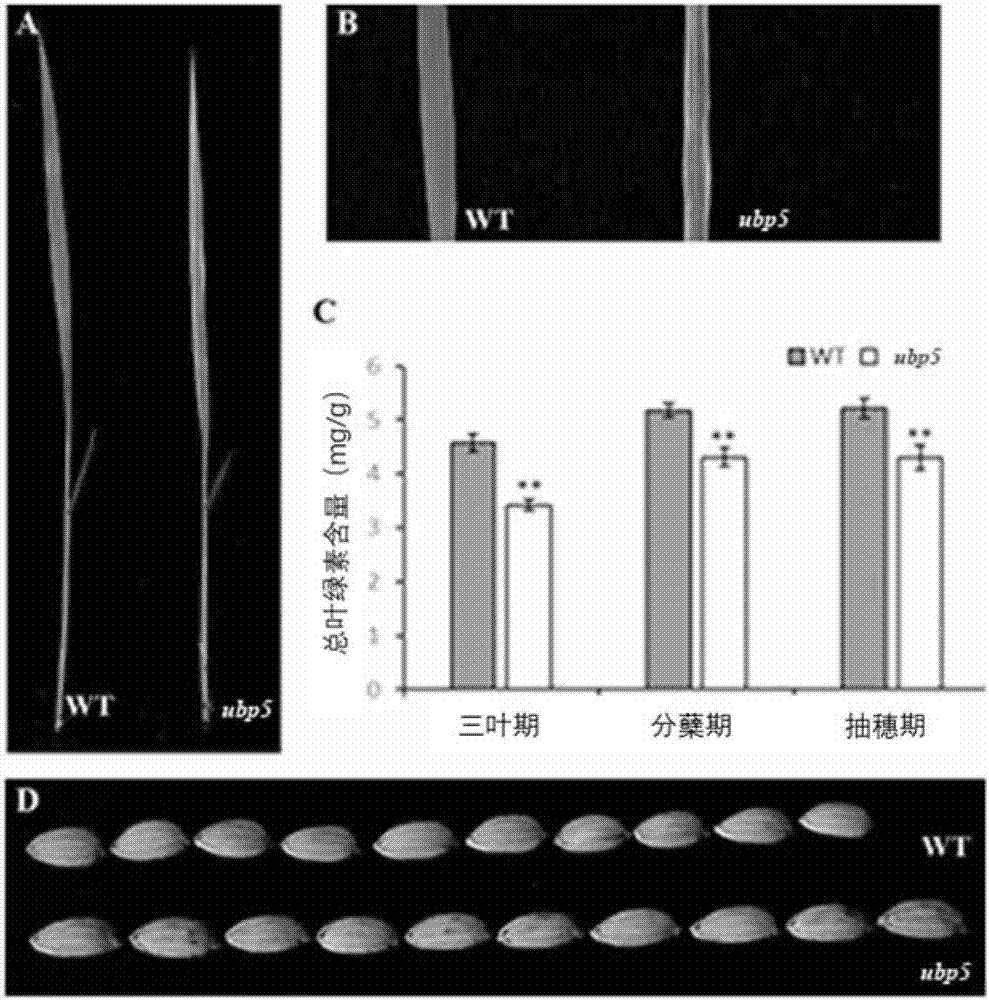
[0033] Under normal sowing conditions, the germination potential of mutant ubp5 seeds was significantly weaker than that of the wild type, and the leaves of the mutant ubp5 showed white stripes after germination; at the tillering and maturity stages, the ubp5 stripe leaf phenotype appeared on some leaves of the plants It is always present and will not disappear in the later stages of childbearing. Compared with the wild type, the chlorophyll content of the mutant decreased in different periods. In addition, the grain length of the mutant increased significantly, while the grain width did not change significantly ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Isolation and cloning of UBP5 gene
[0035] 1. Genetic analysis of ubp5 mutant traits:
[0036] The ubp5 mutant was crossed with its parent Nipponbare to construct the F 2 Populations were isolated for genetic analysis. The analysis results showed that the F 1 The phenotype of the offspring plants was not significantly different from that of the wild type, and in F 2 218 individual plants were randomly selected in the generation population, and the number of individual plants of the wild-type and mutant phenotypes were 168 and 50, respectively. The chi-square test results (χ 2 3:1 =0.391) in line with the segregation ratio of 3:1, indicating that the traits of the mutant are controlled by a single recessive nuclear gene.
[0037] 2. Gene mapping group construction:
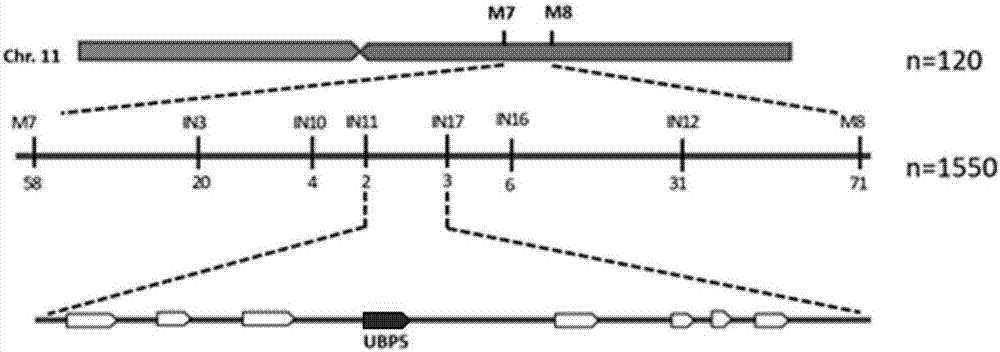
[0038] The ubp5 mutant was crossed with the indica variety Dular, F1 F 2 group. from F 2 1550 ubp5 mutant phenotype plants were selected from the population as the gene mapping population...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 UBP5 and its homologous gene phylogenetic tree analysis
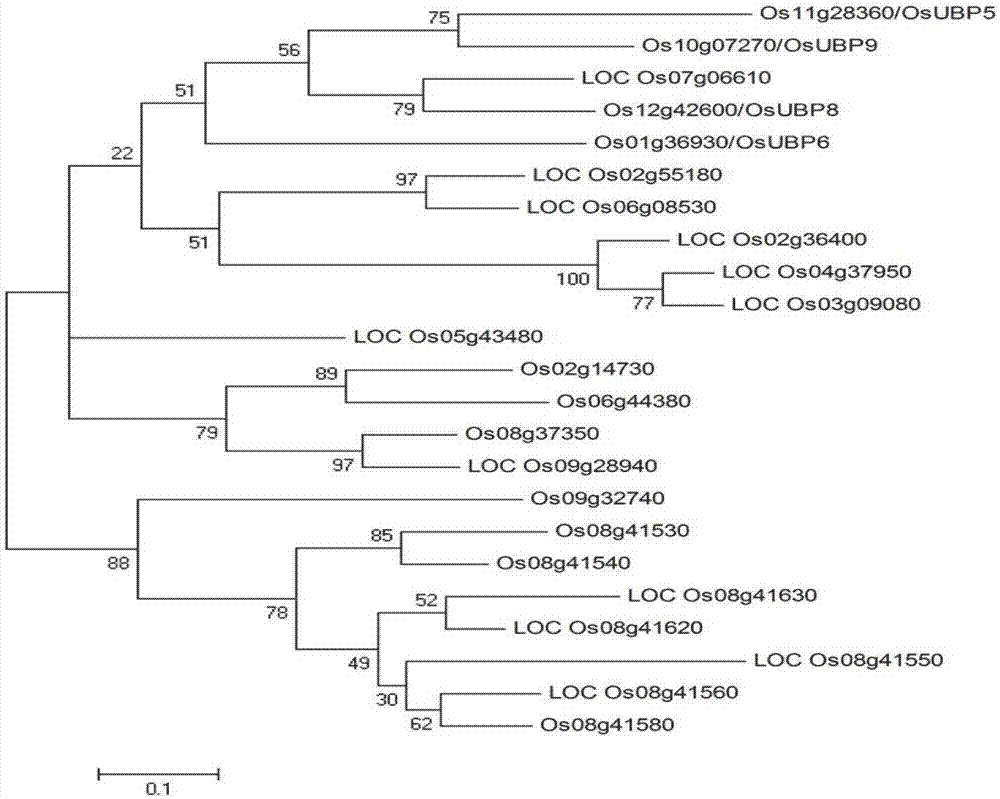
[0046] Deubiquitinases belong to a large gene family, and each species includes a very large number of deubiquitinase genes. For example, Arabidopsis, a model plant for dicotyledon research, contains 27 deubiquitinase genes, and rice contains 23 deubiquitinase genes. In order to study the evolutionary relationship between UBP5 and other rice deubiquitinase proteins, the phylogenetic tree of UBP5 protein and 22 other rice proteins was constructed using MEGA 4.0 software. The results showed that UBP5 and Os10g07270 (UBP9) had the closest relationship and were on the same branch, while Os07g06610 and Os12g42600 at this site were on a large branch ( image 3 ), indicating that the protein family is relatively conserved in structure and closely related in evolution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com