Edible mushroom cultivation method with reed substituting for cottonseed hull
A technology of edible mushrooms and cottonseed hulls, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, fertilizers made of biological waste, etc., can solve the problems of high cottonseedhull prices, loss of mushroom farmers, low economic benefits, etc., to avoid pesticide residues Effect of high content, increase of carbon dioxide content, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
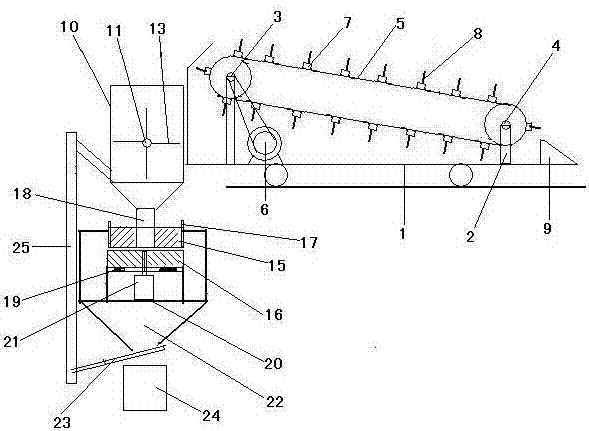
[0020] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with a specific embodiment. Firstly, a reed crushing device is introduced.
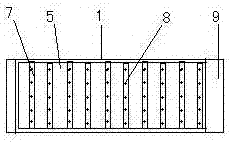
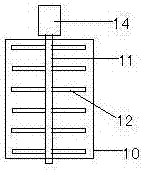
[0021] This reed crushing device includes a reed conveying part, a cutting machine and a grinder, and is characterized in that the reed conveying part includes an unmanned remote-controlled electric vehicle 1, and a belt rack 2 is installed on the bottom plate of the remote-controlled electric vehicle 1. The driving roller 3 and the driven roller 4 are equipped with a conveying belt 5 on the driving roller 3 and the driven roller 4. The conveying belt 5 is installed obliquely with the front low and the rear high. The belt motor 6 connected with the driving roller 3 is installed on the remote control electric motor. On the bottom plate of the car 1, a horizontal bar 7 is evenly fixed on the working surface of the conveyor belt 5, and a grab bar 8 perpendicular to the conveyor belt is uniformly fixed on the bar 7, and the grab b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com