RNA polymerase mutants that can utilize chemically modified nucleotides
A technology of polymerase and mutant, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low efficiency of chemical modification of nucleotides, low synthesis efficiency, low synthesis efficiency and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Design of Amino Acid Exchange Mutations in T7 RNA Polymerase Polypeptides
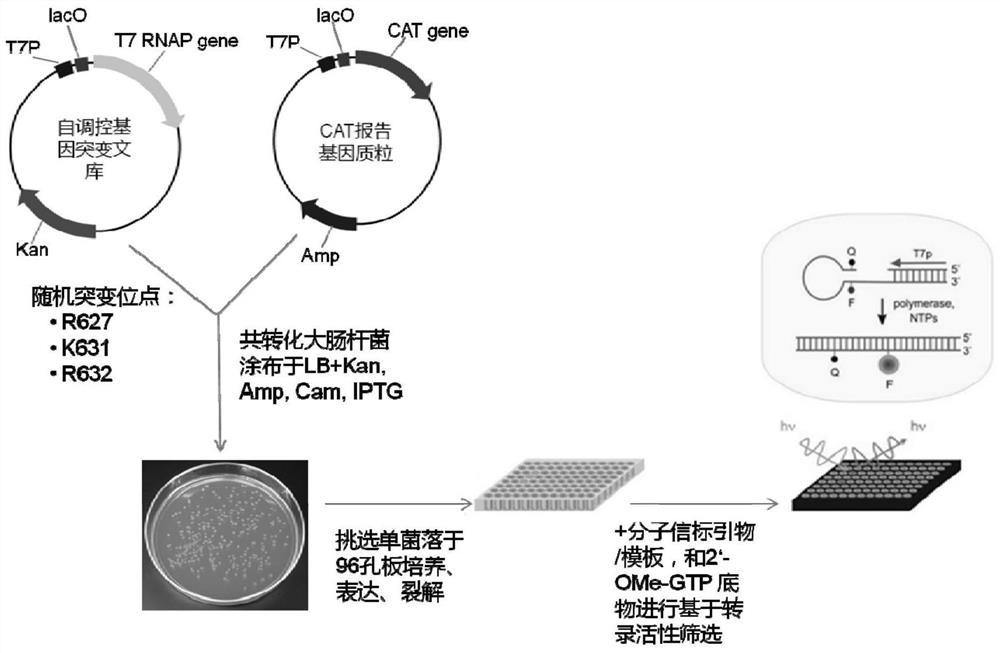
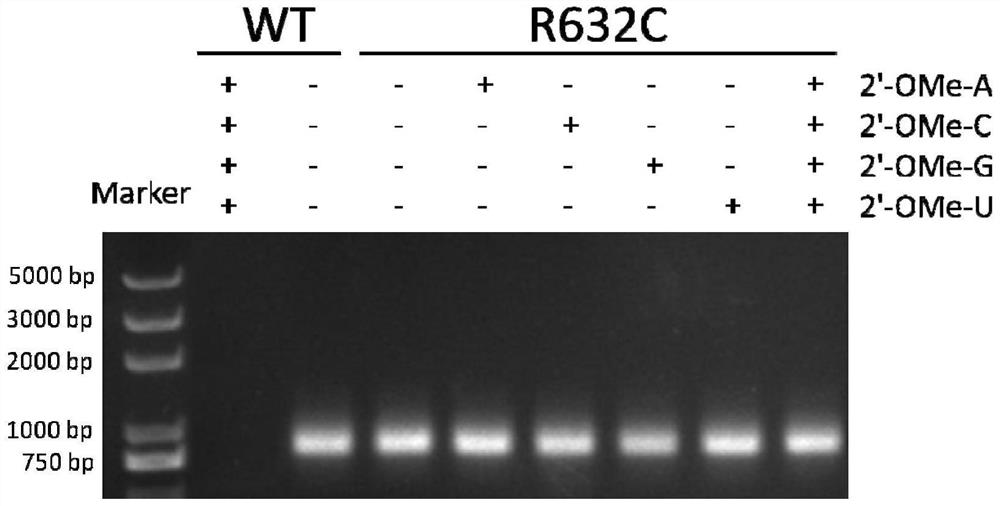
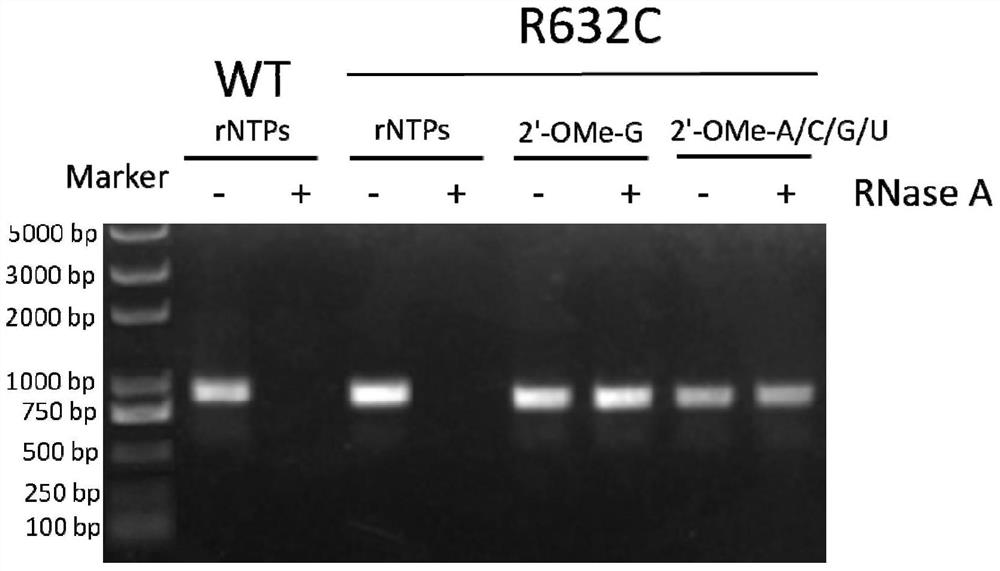
[0050] According to literature reports, amino acid residues R425, R632 and H811 are responsible for the interaction with the first initiating nucleotide 3-dGTP-(1), while the second initiating nucleotide 3-dGTP-(2) interacts with K441, R425 , R627, K631, H784 and D812 residues interact. Since K441, R425, and Y639 residues have been reported to be associated with increased 2'-O-methyl nucleotide incorporation capabilities, we chose to randomly mutate R627, K631, and R632 sites to construct the T7 self-regulated gene library , to discover new mutant enzymes with improved 2'-OMe GTP catalytic activity. The polymerase mutant library was cloned downstream of the T7 promoter and introduced into E. coli cells together with a vector carrying a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene also controlled by the T7 promoter. After the mutant library transformed cells containing the r...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Construction of wild-type T7 RNA polymerase self-regulating gene carrier, random mutation library and reporter gene plasmid
[0052] 2.1 Materials
[0053] Escherichia coli DH5α and BL21(DE3) competent cells and rapid plasmid extraction reagents were purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.;
[0054] pET28a+ was purchased from Novagen, the reporter plasmid pCAT3-promoter was purchased from Promaga; Phusion high-fidelity DNA polymerase;
[0055] Restriction enzymes Nde I, BamH I, Nhe I, Xho I, and DpnI; RNase A and lysozyme were purchased from New England Biolabs;
[0056] IPTG, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, kanamycin, tryptone, yeast extract, agar powder, NaCl, Tris–HCl, EDTA, DTT, MgCl2, spermidine, salmon sperm DNA, agarose, and ethidium bromide, etc., were purchased from Shanghai Sangong;
[0057] Ni-NTA Agarose was purchased from Qiagen, and the Quick Start Bradford protein assay kit was purchased from Bio-Rad;
[0058] All 2'-...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3: Active T7 RNA polymerase mutant screening:
[0070]Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells were co-transformed with self-regulating random mutant T7 RNA polymerase gene library and CAT reporter gene vector pCATT7. The transformed library was first recovered in liquid LB medium without antibiotics, then 25 mg / ml kanamycin and 100 mg / ml ampicillin were added to the medium, and cultured at 37°C for 2 hours. The culture was induced by adding 30 mg / ml chloramphenicol and 1 mM IPTG. Cells were incubated at 37°C for 6 hours. The saturated culture was spread on LB plates containing 25mg / ml kanamycin, 1mM IPTG, and 100mg / ml ampicillin, and different concentrations (50, 100, and 200mg / ml) of chloramphenicol, and cultured at 37°C for 16 Hour. It can be observed that the plate with higher concentration of chloramphenicol grows fewer colonies, and the size of the colonies varies. Colonies were picked from each plate and used for viability-based screening. As a negat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com