Multi-response type cross-linked polymer and drug-loading nano-micelles as well as preparation methods thereof
A technology of cross-linked polymers and drug-loaded nanometers, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients. Problems such as poor drug loading stability, to avoid poor cycle stability, overcome weak interaction, and improve drug loading stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
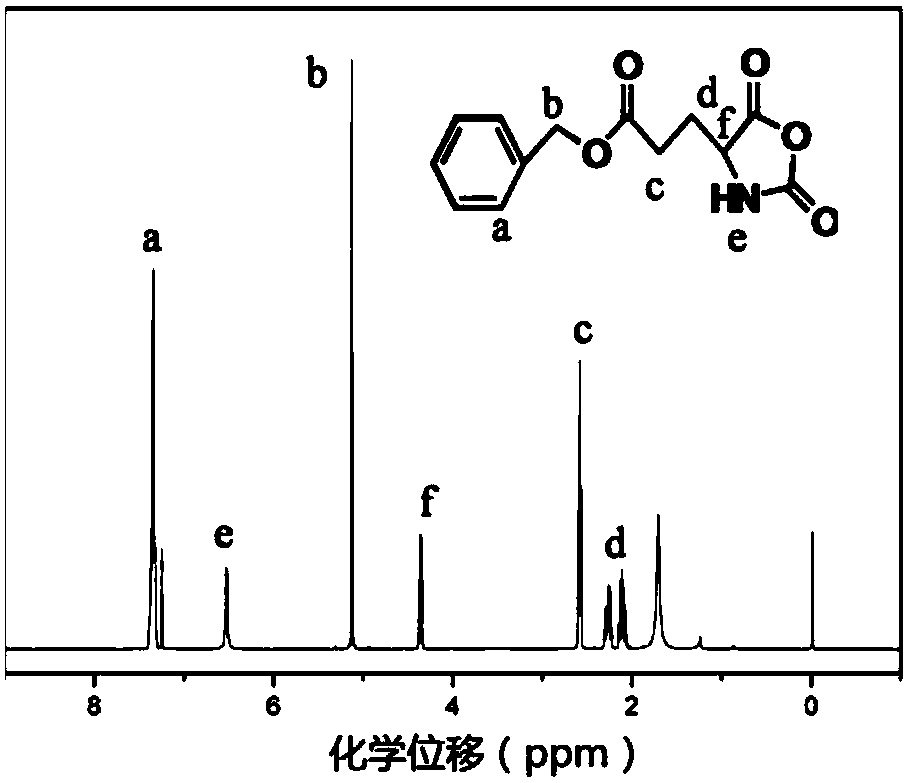
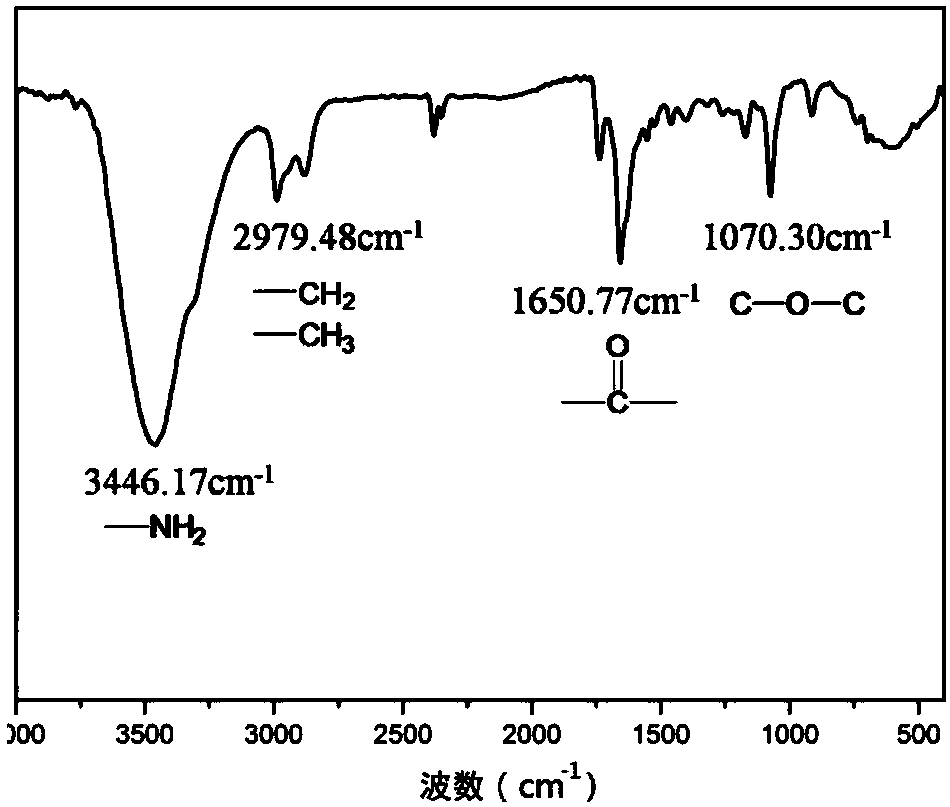
[0057] Benzyl glutamate and triphosgene were dissolved in ethyl acetate at a mass ratio of 1:1 at 0.04 g / mL, then reacted in a reactor at 75 °C for 2 h, washed with water and sodium bicarbonate solution in sequence, and washed with Dry over magnesium sulfate, filter and then rotary evaporate to one-third of the original volume, crystallize in n-hexane, then freeze the product at -20°C for 24h, filter with suction, and dry at 25°C and a vacuum of 0.010MPa for 24h That's it.
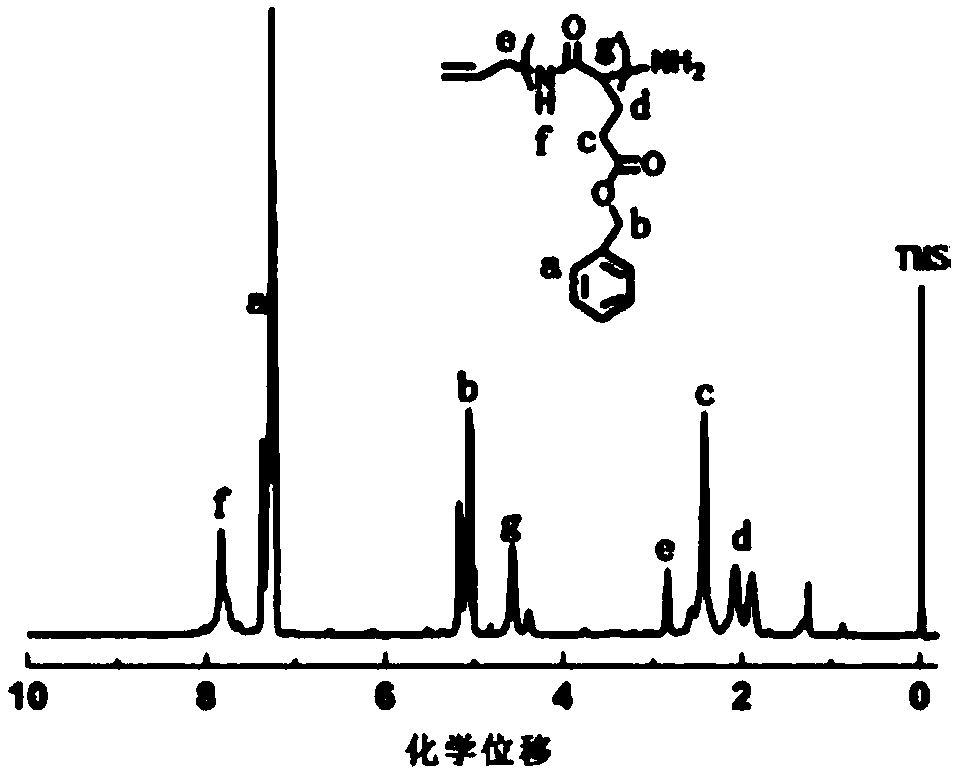
[0058] Dissolve allylamine and the obtained benzyl glutamate cyclic anhydride in THF at a molar ratio of 1:40 to form a 0.25 g / mL solution, react at 25°C for 24 hours, and then use glacial ether for precipitation and suction filtration , and dried at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain polybenzyl glutamate;
[0059] Mix benzyl polyglutamate and N-isopropylacrylamide at a molar ratio of 1:1, dissolve in DMF to make a mixed solution of 0.01g / mL, add benzyl polyglutamate and N-isopropylacrylamide respectively 4% cr...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Benzyl glutamate and triphosgene were dissolved in ethyl acetate at a mass ratio of 2:1 at 0.05 g / mL, then reacted in a reactor at 50 °C for 8 h, washed with water and sodium bicarbonate solution in sequence, and washed with Dry over magnesium sulfate, filter and then rotary evaporate to one-third of the original volume, crystallize in n-hexane, then freeze the product at -20°C for 24h, filter with suction, and dry at 25°C and vacuum 0.012MPa for 24h That's it.
[0063] Allylamine and benzyl glutamic acid anhydride were mixed and dissolved in dichloromethane at a molar ratio of 1:50 to form a 0.52 g / mL solution, reacted in a reactor at 10°C for 36 h, and then cooled with ice Diethyl ether was precipitated, suction filtered, and dried at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain polybenzyl glutamate.
[0064] Mix polybenzyl glutamate and N-isopropylacrylamide at a molar ratio of 1:50, dissolve in DMF to make a mixed solution of 0.02g / mL, add polybenzyl glutamate and N-isopropylacryla...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Benzyl glutamate and triphosgene were dissolved in ethyl acetate at a mass ratio of 3:1 at 0.05 g / mL, then reacted in a reactor at 85°C for 3 h, washed with water and sodium bicarbonate solution in sequence, and washed with Dry over magnesium sulfate, filter and rotary evaporate to one-third of the original volume, crystallize in n-hexane, then freeze the product at -20°C for 24h, filter with suction, and dry at 25°C under a vacuum of 0.014MPa for 16h That's it.
[0068] Allylamine and glutamic acid anhydride were mixed and dissolved in DMSO at a molar ratio of 1:60 to form a 0.30 g / mL solution, reacted at 50°C for 48 hours, and then precipitated with glacial ether, suction filtered, and dissolved at 60 Dry at ℃ for 24h to obtain polybenzyl glutamate.
[0069] Mix benzyl polyglutamate and N-isopropylacrylamide at a molar ratio of 1:20, dissolve in DMSO to form a mixed solution of 0.05g / mL, add benzyl polyglutamate and N-isopropylacrylamide respectively 5% cross-linkin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com