Process and system for treating waste salt slurry produced in production of sodium chlorate
A treatment process and treatment system technology, applied in the field of waste salt mud treatment process and system in sodium chlorate production, can solve the problems of excessive chromium content in waste salt mud, hard particles of waste salt mud, hidden safety hazards, etc., and achieve high Social and economic benefits, scientific and reasonable system design, no secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
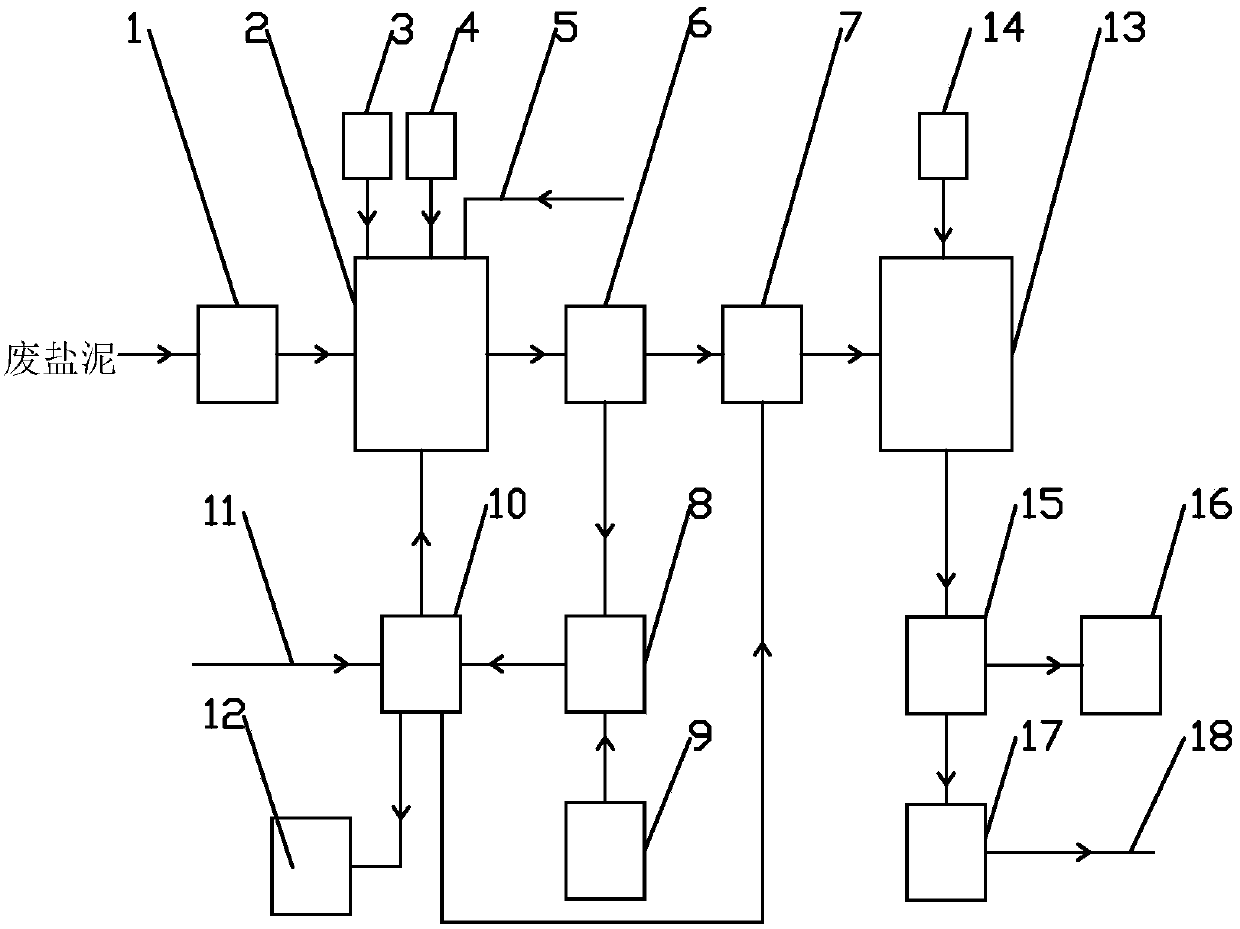
[0027] Such as figure 1 Shown, the processing system of waste salt mud in the production of sodium chlorate, it comprises grinder 1, oxidation stripping system, washing system, reduction system and waste water regulating tank 17, the outlet of grinder 1 and the oxidation stripping of oxidation stripping system The feed port of the reaction tank 2 is connected, the outlet of the water receiving tank 7 of the oxidation dissolution system is connected with the inlet of the reduction reaction tank 13 of the reduction system, and the liquid outlet of the reduction centrifuge 15 of the reduction system is connected with the water inlet of the waste water regulating tank 17 , the outlet of the wastewater regulating tank 17 is communicated with the incoming water pipeline 18 of the wastewater plant, the slag outlet of the oxidative dissolution centrifuge 6 of the oxidative dissolution system is communicated with the feed port of the slag collection tank 8 of the washing system, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Utilize the processing technology of waste salt mud in the sodium chlorate production that embodiment 1 carries out, it comprises the steps: (1) waste salt mud grinding, (2) oxidation, (3) chromium ion stripping, (4) washing, (5) ) reduction; among them,
[0039] (1) Grinding of waste salt mud: Grinding the waste salt mud to 50 meshes to obtain abrasives; the purpose of grinding is to fully release the chromium ions wrapped in the waste salt mud to improve the efficiency of subsequent oxidation, dissolution and reduction.
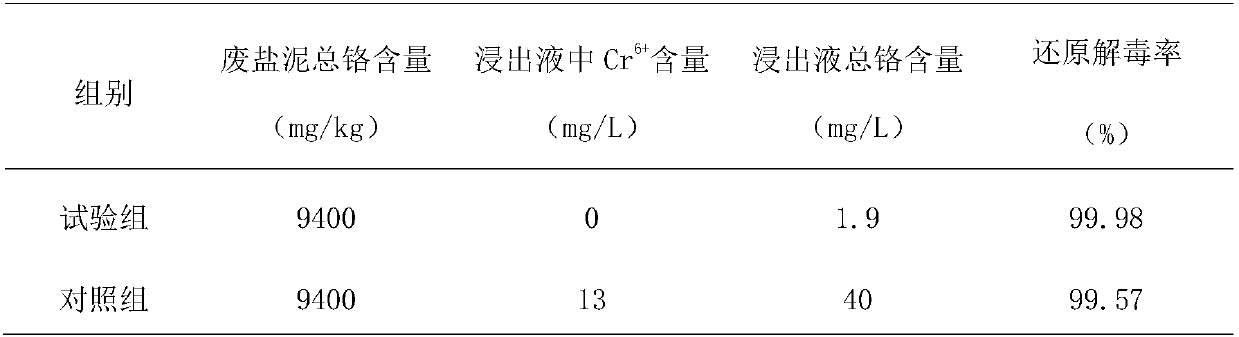
[0040] (2) Oxidation: (1) After the waste salt mud is ground, mix the grinding material with water at a mass ratio of 1:0.5. Carry out the oxidation reaction under the conditions, the oxidant is permanganate, the mass ratio of the oxidant and the abrasive is 1:15, the oxidation reaction time is 2h, after the oxidation reaction ends, the oxidation slurry is obtained; the effect of oxidation is to convert the trivalent chromium ion The oxidant is oxid...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Utilize the processing technology of waste salt mud in the sodium chlorate production that embodiment 1 carries out, it comprises the steps: (1) waste salt mud grinding, (2) oxidation, (3) chromium ion stripping, (4) washing, (5) ) reduction; among them,
[0047] (1) Waste salt mud grinding: Grind the waste salt mud to 100 meshes to obtain abrasives; the purpose of grinding is to fully release the chromium ions wrapped in the waste salt mud to improve the efficiency of subsequent oxidation, dissolution and reduction.
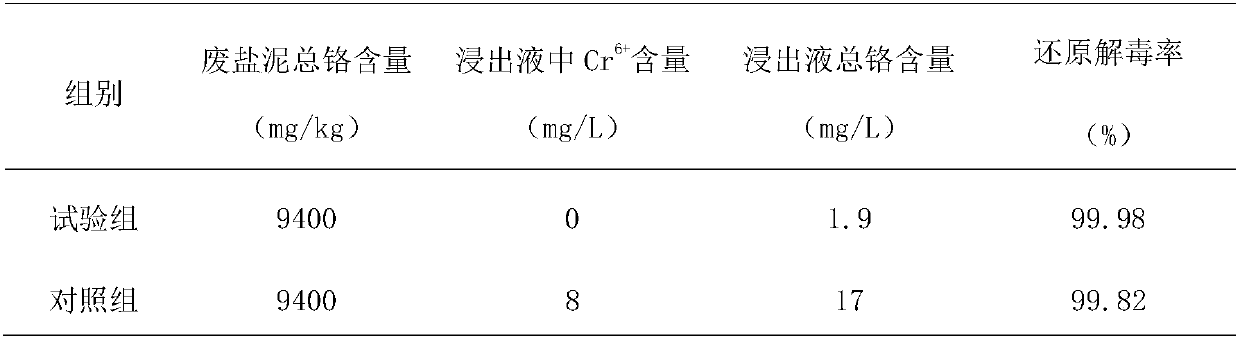
[0048] (2) Oxidation: (1) After the waste salt mud is ground, mix the grinding material with water at a mass ratio of 1:1. The oxidation reaction is carried out under the conditions, the mass ratio of the oxidizing agent to the abrasive is 1:25, the oxidation reaction time is 0.5h, and the oxidizing agent is sodium peroxide. After the oxidation reaction is completed, the oxidation slurry is obtained; The oxidant is oxidized to hexavalent chromium ions, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com