Separation and purification method and molecular identification method of potato scab pathogens
A potato scab, separation and purification technology, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of complicated operation, high cost, and long time consumption, and achieve the effects of simplifying experimental steps, improving efficiency, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The separation and purification of embodiment 1 potato scab pathogenic bacteria
[0058] The present embodiment provides a kind of method for the isolation and purification of potato scab pathogenic bacteria, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0059] Step (a): Wash the collected potato scab diseased potato with clean water, and wash it with ddH 2 O Rinse once, put it on a clean absorbent paper towel to absorb the surface water dry, use a sterilized scalpel blade to remove the surface layer of the scab and lesion in the sterilized ultra-clean workbench, and cut out the scab with a length and width of about 1 cm and a thickness of about 1 cm. 1-2mm lesion tissue block; use sterilized forceps to soak the tissue block in 75% medical alcohol for 30 s, then use sterile ddH 2 O rinse 3 times; then put in a sterile 1.5mL EP tube, add 200 μL sterile ddHO 2 O, simply chop the tissue block with a scalpel blade, fully grind it with a sterilized plastic grinding rod, an...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 Molecular Identification of Potato Scab Pathogenic Bacteria
[0063] The present embodiment provides a kind of method for the molecular identification of potato scab pathogen, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0064] Step (A): After picking up the single bacterium provided by Example 1 of the present invention with an inoculation needle or a 10 μL pipette tip, stir several times in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube containing 600 μL ISP I liquid medium, and wait until the inoculation needle or pipette After the colony on the tip of the liquid gun is mixed into the culture medium, place it on a shaker at 28°C and shake at 200rpm for 24-36h;
[0065] Step (B): The above-mentioned bacterial liquid is directly used for bacterial liquid PCR to amplify the 16S rDNA sequence. The specific method is as follows:
[0066] Amplification primers using Streptomyces 16S rDNA sequence amplification primers:
[0067] name
serial number
Primer sequence (5...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3 Molecular Identification of Potato Scab Pathogenic Bacteria
[0075] The present embodiment provides a kind of method for the molecular identification of potato scab pathogen, and the difference with embodiment 2 is in step (C), also includes:
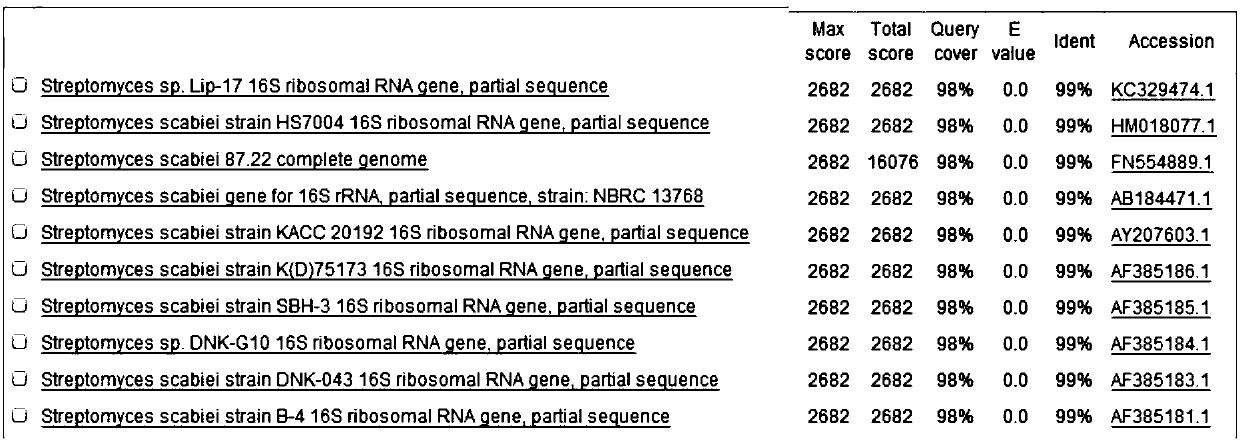
[0076] After the PCR amplification reaction was completed, 5 μL of the reaction product was taken to detect the amplification result by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. If the amplified band matches the target band, recover the target gene fragment and connect it to the cloning vector pMD18-T, transform the ligated product into Escherichia coli DH5α by heat shock method, and spread the Amp resistance plate; the bacterial solution is positive The colonies were sent to Huada Gene Company for sequencing, and the sequencing results were compared in the NCBI database to determine whether the isolated Streptomyces was the causative bacterium of potato scab.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com