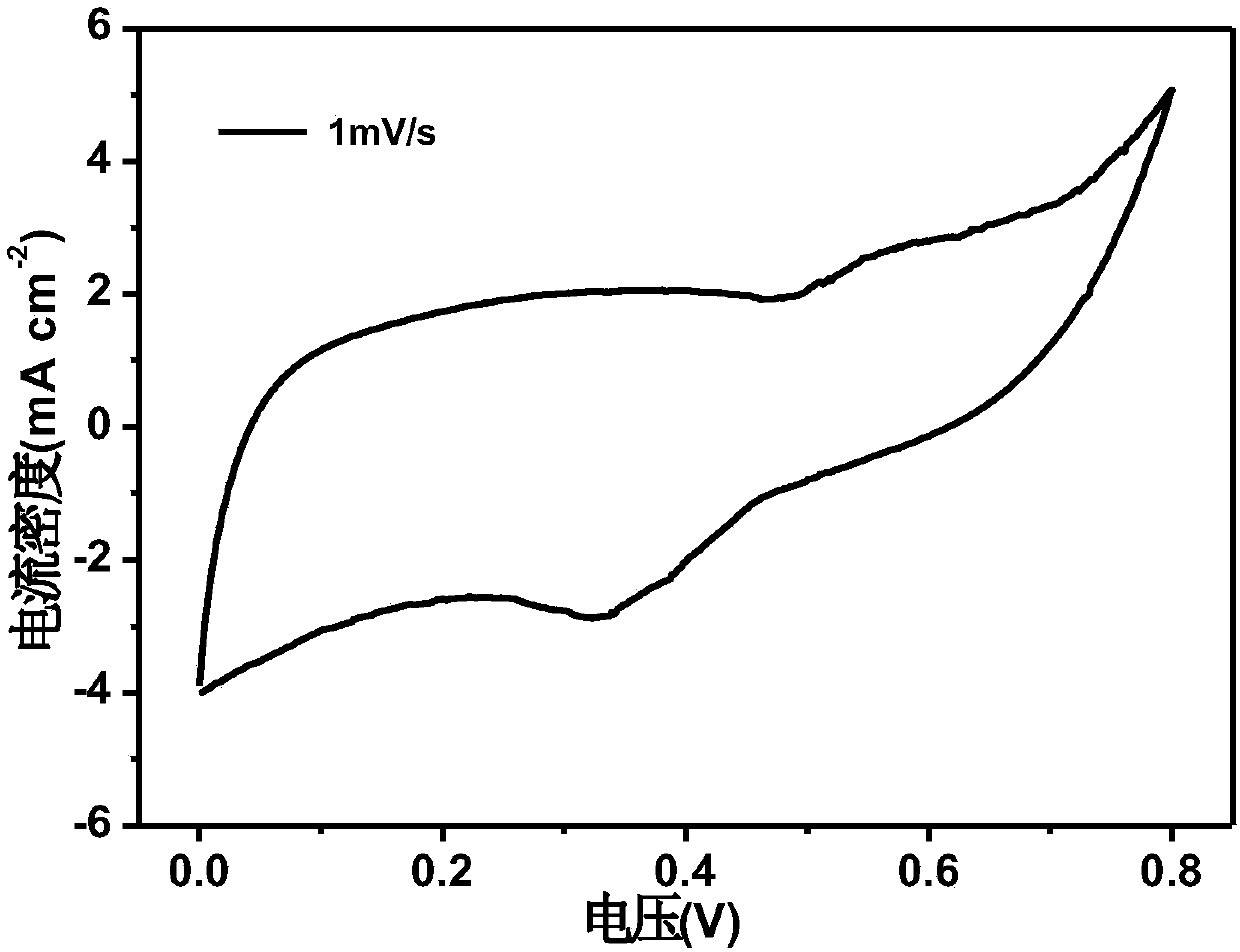
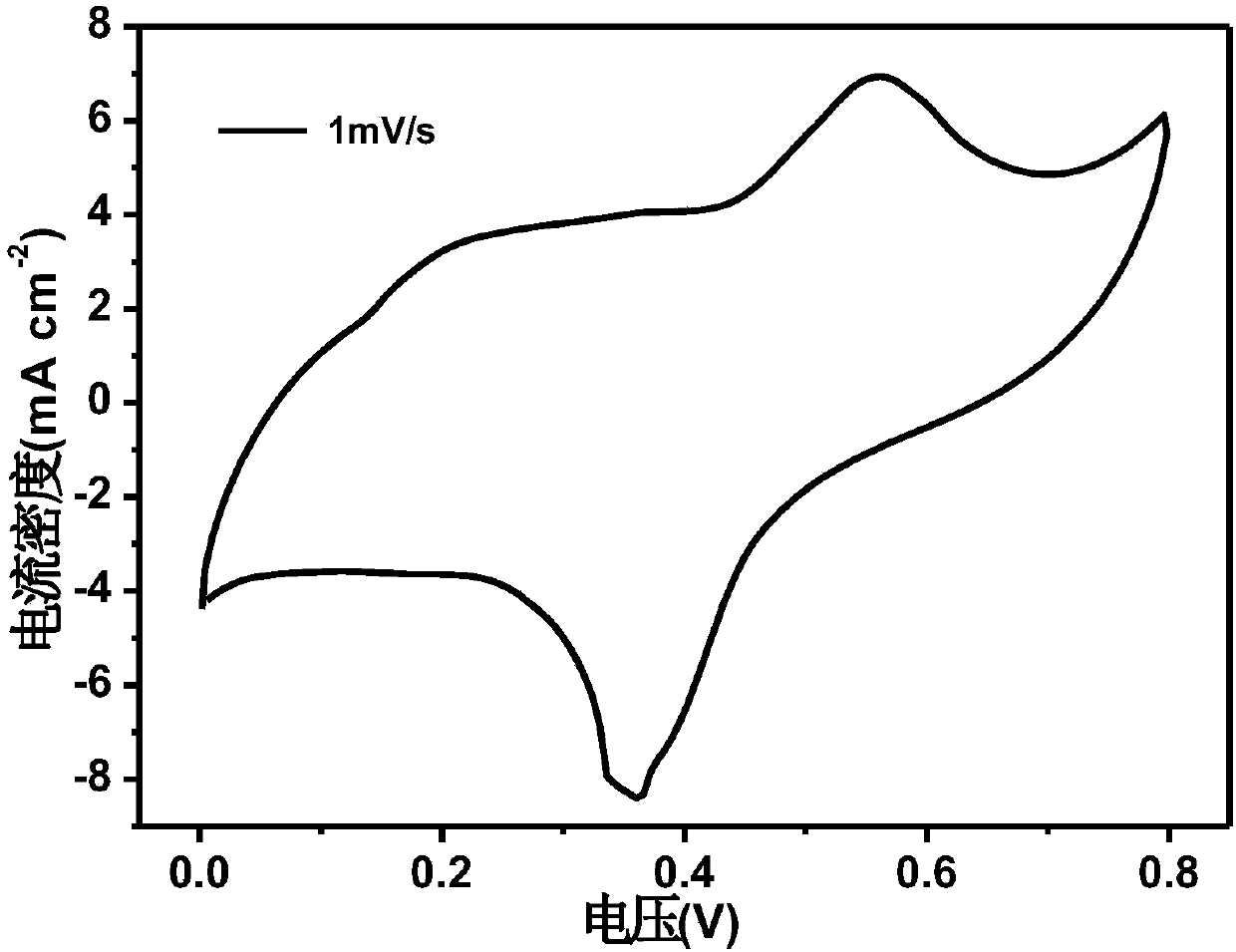
Wood base compounding electrode material and preparing method thereof
A composite electrode, wood-based technology, used in hybrid capacitor electrodes, hybrid/electric double-layer capacitor manufacturing, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of decreased electrochemical performance, prone to cracking, and inability to fully utilize the cavity structure of wood cells. , to achieve the effect of reducing brittleness, improving flexibility, and improving flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
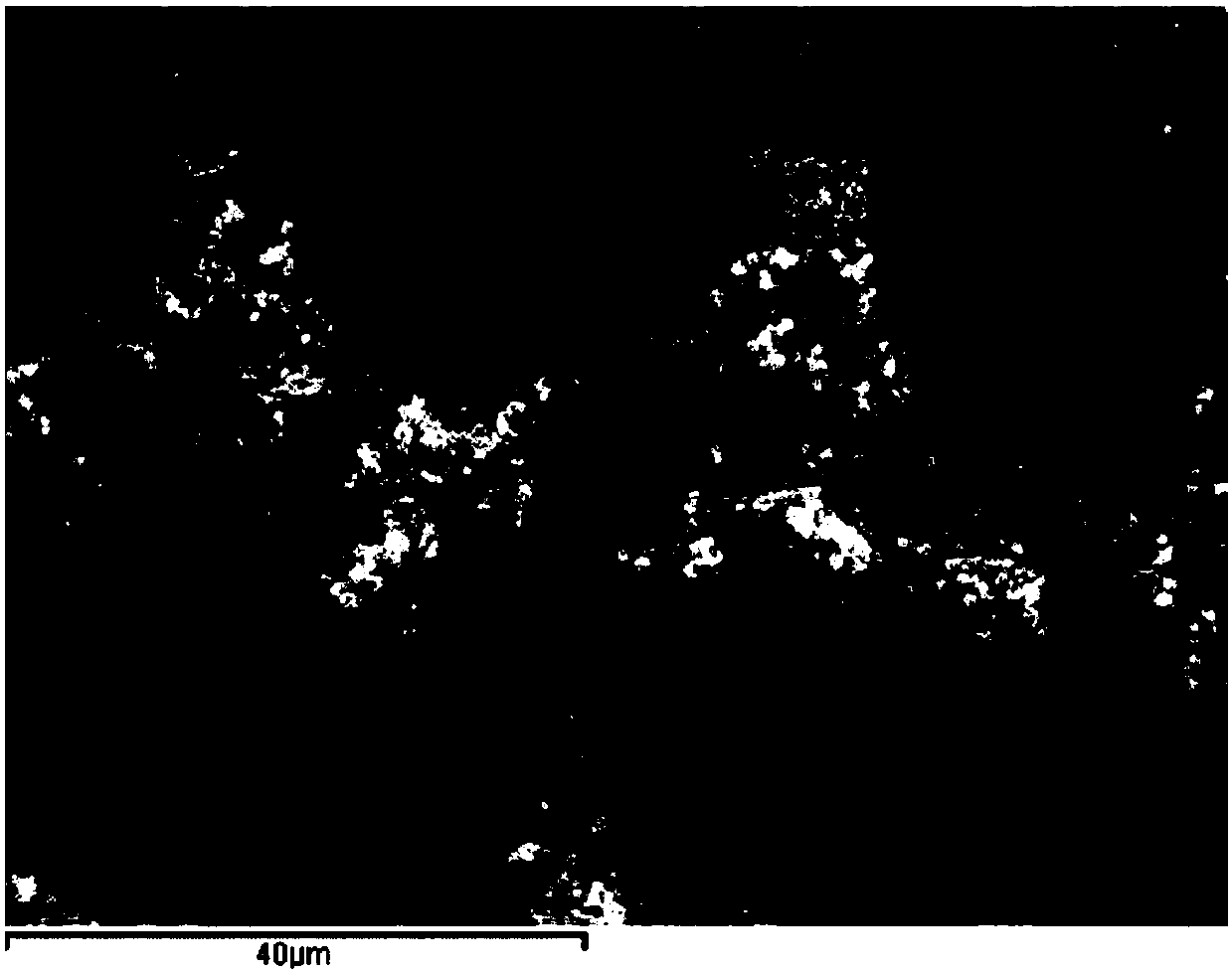
[0035] 1) slice the fir sapwood along the direction perpendicular to the axial direction to obtain a wood slice with a thickness of 180 μm and a length and width of 2cm×1cm;
[0036] 2) Put 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.1 g) obtained in step 1) into a mixed solution consisting of 5 g of concentrated nitric acid and 5 g of dichloromethane, and keep at 6° C. for 1 minute;
[0037] 3) Take out the 10 pieces of wood flakes obtained in step 2), and quickly immerse them in boiling water at 100°C for 5 minutes;
[0038] 4) Take out the 10 wood flakes obtained in step 3), dry them naturally, and then soak them in 1 mg / mL graphene oxide dispersion for 2 hours;
[0039] 5) Take out the 10 wood slices obtained in step 4), freeze them with liquid nitrogen for 1 minute, and then freeze-dry them for 2 days;
[0040] 6) Take out 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.15g) obtained in step 5), immerse them in a hydrothermal reaction kettle filled with 5g of hydrazine hydrate and 10g of ammoni...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 1) slice the cedar sapwood along the direction perpendicular to the axial direction to obtain a wood slice with a thickness of 180 μm and a length and width of 2 cm×1 cm;
[0047] 2) Put 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.1 g) obtained in step 1) into a mixture of 5 g of concentrated nitric acid and 10 g of dichloromethane, and keep at 6° C. for 1 minute;
[0048] 3) Take out the 10 pieces of wood flakes obtained in step 2), and quickly immerse them in boiling water at 100°C for 5 minutes;
[0049] 4) Take out the 10 wood flakes obtained in step 3), dry them naturally, and then soak them in 1.5 mg / mL graphene oxide dispersion for 2 hours;
[0050] 5) Take out the 10 wood slices obtained in step 4), freeze them with liquid nitrogen for 1 minute, and then freeze-dry them for 2 days;
[0051] 6) Take out 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.15g) obtained in step 5), immerse them in a hydrothermal reaction kettle filled with 4.5g of hydrazine hydrate and 18g of ammonia water, ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1) Slice the basswood sapwood along a direction perpendicular to the axial direction to obtain a thin slice of wood with a thickness of 240 μm and a length and width of 2 cm × 1 cm;
[0058] 2) Put 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.15g) obtained in step 1) into a mixture composed of 7.5g of concentrated nitric acid and 22.5g of dichloromethane, and keep at 8°C for 1 minute;
[0059] 3) Take out the 10 pieces of wood flakes obtained in step 2), and quickly immerse them in boiling water at 100°C for 8 minutes;
[0060] 4) Take out the 10 wood flakes obtained in step 3), dry them naturally, and then soak them in 2.0 mg / mL graphene oxide dispersion for 2 hours;
[0061] 5) Take out the 10 wood slices obtained in step 4), freeze them with liquid nitrogen for 1 minute, and then freeze-dry them for 2 days;
[0062] 6) Take out 10 pieces of wood flakes (about 0.25g) obtained in step 5), immerse them in a hydrothermal reaction kettle filled with 7.14g of hydrazine hydrate and 4...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com