3D-printing wound dressing material based on silk microsphere bio-ink and preparation method thereof
A technology of bio-ink and three-dimensional printing, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, microcapsules, drug delivery, etc., can solve the problems of low strength of fiber membranes, and achieve the effects of ensuring air permeability, wound coating, and uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Centrifuge the aqueous solution of aspirin-coated silk protein microspheres with a particle size of 1-5 μm, remove the supernatant, add the aqueous solution of silk protein, stir ultrasonically, and mix uniformly to obtain a silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, wherein The mass fraction of the aspirin-coated fibroin microspheres is 3%, and the mass fraction of the silk protein is 5%.
[0034] (2) Add 1wt% ultraviolet photoinitiator Irgacure I-2959 and 3wt% polyvinyl alcohol ester to the silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, and mix evenly to obtain silk microsphere bio-ink.
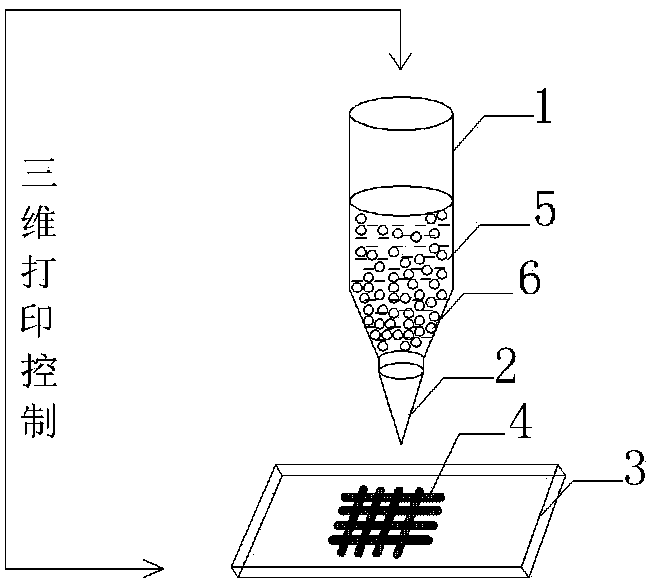
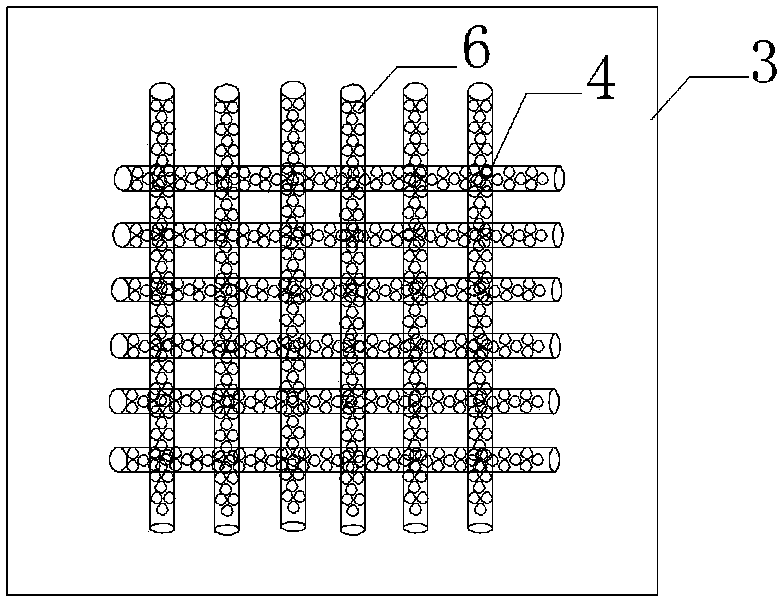
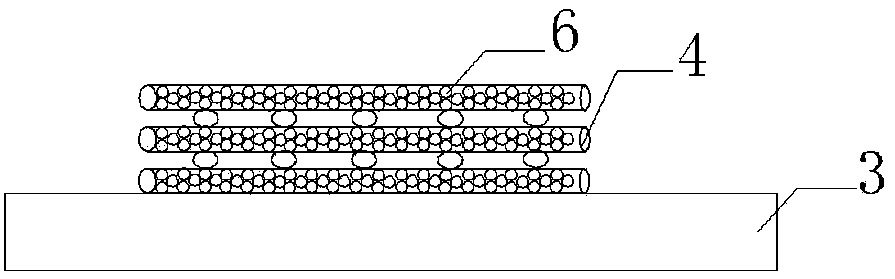
[0035] (3) Transfer the silk microsphere bio-ink to the syringe of the 3D printer, use cotton gauze as the base cloth for printing, establish a cyclical cross network structure scaffold model in MIMICS software, and adjust the needle cylinder pillow and cotton gauze The distance is 0.5mm, and the silk microsphere bio-ink is printed on the surface of ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Centrifuge the aqueous solution of aspirin-coated silk protein microspheres with a particle size of 1-5 μm, remove the supernatant, add the aqueous solution of silk protein, stir ultrasonically, and mix uniformly to obtain a silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, wherein The mass fraction of the aspirin-coated fibroin microspheres is 5%, and the mass fraction of the silk protein is 5%.
[0038] (2) Add 1wt% ultraviolet photoinitiator Irgacure I-2959 and 3wt% polyvinyl alcohol ester to the silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, and mix evenly to obtain silk microsphere bio-ink.
[0039] (3) The silk microsphere bio-ink was transferred to the syringe of the 3D printer, and cotton gauze was used as the base, and the bracket model of the cycled cross network structure was established in the MIMICS software, and the distance between the syringe pillow and the cotton gauze was adjusted as 0.5mm, the silk microsphere bio-ink was pr...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Centrifuge the aqueous solution of aspirin-coated silk protein microspheres with a particle size of 1-5 μm, remove the supernatant, add the aqueous solution of silk protein, stir ultrasonically, and mix uniformly to obtain a silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, wherein The mass fraction of the aspirin-coated fibroin microspheres is 4%, and the mass fraction of the silk protein is 5%.
[0042] (2) Add 1wt% ultraviolet photoinitiator Irgacure I-2959 and 3wt% polyvinyl alcohol ester to the silk protein solution containing silk protein microspheres, and mix evenly to obtain silk microsphere bio-ink.
[0043] (3) The silk microsphere bio-ink was transferred to the syringe of the 3D printer, and cotton gauze was used as the base, and the bracket model of the cycled cross network structure was established in the MIMICS software, and the distance between the syringe pillow and the cotton gauze was adjusted as 0.5mm, the silk microsphere bio-ink is pri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com