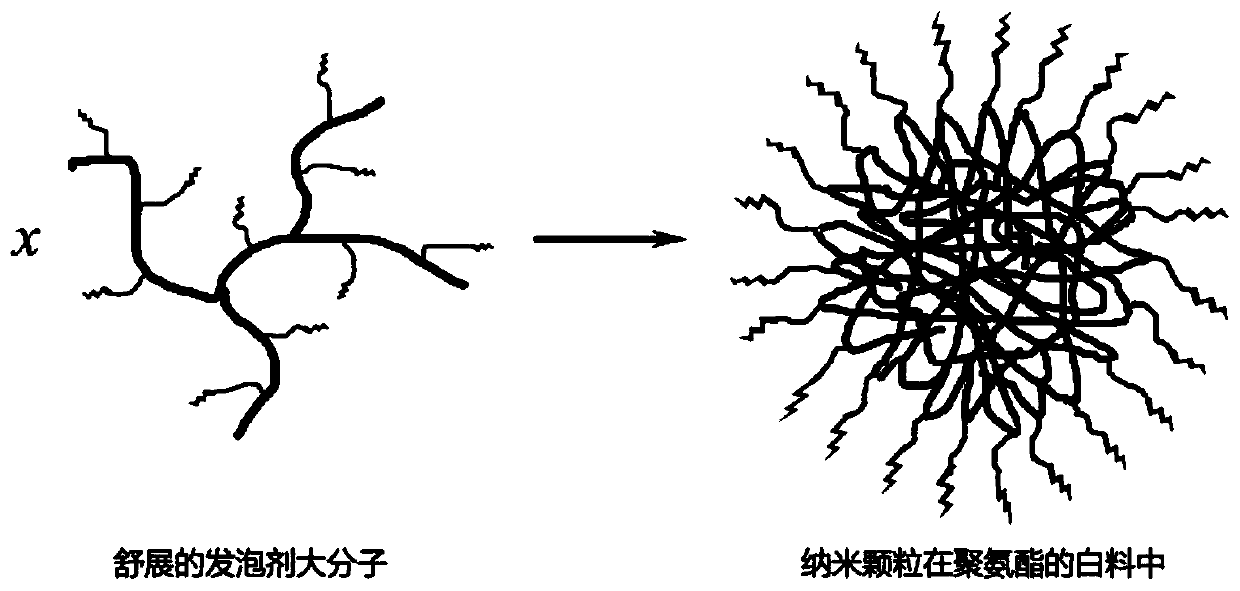
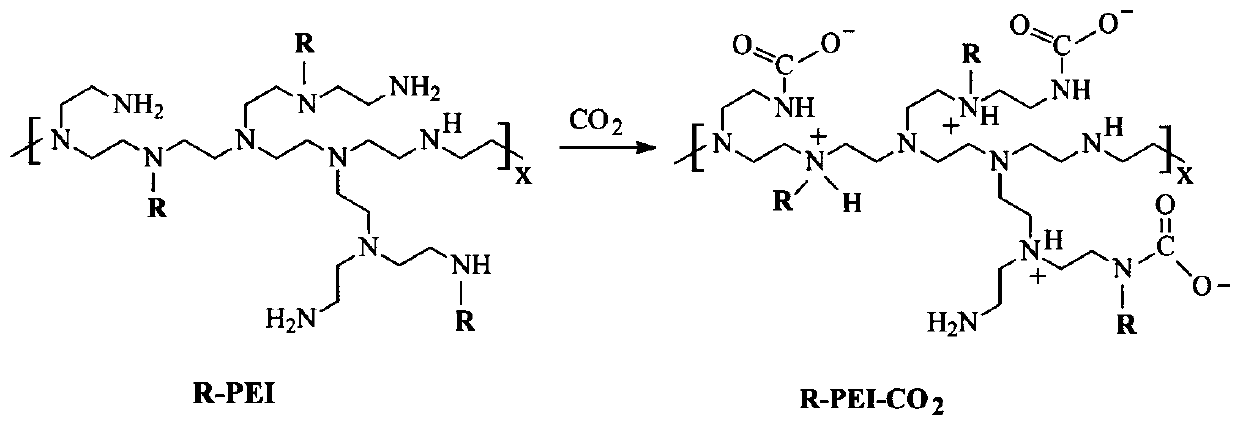
Hydrophobic Modified Polyethyleneimine Foaming Agent
A polyethyleneimine and foaming agent technology, applied in the foaming agent and its preparation and application fields, can solve the problems of acid pollution, elimination, damage to the ecological environment, etc., and achieve the improvement of CO2 content, foaming) capacity improvement and expansion Application-wide effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-20
[0040] This group is to use the glycidyl ether group (i.e. epoxy group) of the glycidyl ether compound containing polypropylene oxide repeating units to react with the amine group in polyethyleneimine to generate hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine. the embodiment. The structure of the glycidyl ether compound is (The parameters such as m and n are shown in Table 1). The hydrophobic side chain and the main link group of the hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine obtained by this group are Q1:
[0041] Table 1
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] The above-mentioned hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine is prepared by the following method: polyethyleneimine (PEI) is added in the reactor, and ethanol is added in the reactor so that the mass concentration of PEI is about 5%. The PEI was completely dissolved under low temperature, then glycidyl ether compounds were added, and the reaction was stirred at 50°C for 15 hours, and then the ethanol was removed by rotary...
Embodiment 21-40
[0052] This group is an example of using hydrophobically modified PEI as a raw material to prepare a hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine blowing agent capable of releasing carbon dioxide. Apply the hydrophobically modified PEI prepared in Table 1 evenly on the wall of the autoclave, then fill the autoclave with carbon dioxide gas with a pressure of 0.5 MPa and keep the pressure, react at room temperature for 2 days, and take it out to obtain the hydrophobic Chain-modified polyethyleneimine CO 2 Adduct blowing agent. Table 2 shows the hydrophobic chain content and CO of each blowing agent 2 content. of which CO 2 The content is obtained from the thermal weight loss test (the percentage of thermal weight loss in the range of 50°C to 150°C is CO 2 mass percent content). Theoretical CO 2 The content is based on the absorption of 1 molecule of CO by two PEI repeat units 2 calculated.
[0053] Table 2
[0054]
Embodiment 41-50
[0061] This group of embodiments first synthesizes the hydrophobic chain halogenated hydrocarbon, and its structural formula is (see Table 3 for parameters such as m and n) Then carry out alkylation reaction with the amine group of branched polyethyleneimine (molecular weight 25000), obtain hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine, and the connecting group between its main chain and side chain is Q2: (corresponding to iodohydrocarbon, embodiment 41-45) or Q3: (corresponding to brominated hydrocarbons, embodiment 46-50); finally the gained hydrophobically modified polyethyleneimine and CO 2 The reaction yielded the CO of hydrophobic chain-modified PEI 2 Adduct blowing agent.
[0062] table 3
[0063]
[0064]
[0065] Note: The values in brackets in the column of grafting ratio of hydrophobic chains are the theoretical grafting ratios given according to the feeding ratio.
[0066] The specific synthesis process is as follows: For Examples 41-45, take 1 mole par...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com