LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) primer group and method for rapidly detecting ditylenchus destructor from complex samples
A technology in D. nematodes and samples, which is applied in the field of LAMP primer sets for rapid detection of D. rottennsis, can solve the problems of requiring several hours, inapplicable to basic-level detection, large-scale screening work, low efficiency, etc., and achieves the effect of good detection effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] Example 1 Establishment and optimization of D. destructor LAMP system
[0089] 1. LAMP primer design
[0090] (1) According to the sequencing results of the ribosomal DNA-28S region of D. destructor, download multiple similar ribosomal DNA-28S gene sequences of other nematodes from the NCBI GenBank database, and perform multiple alignment analysis on the sequences to find 28S sequence fragments The specific sequence fragments in the LAMP primer set are selected for the appropriate specific sequence region and then synthesized. After preliminary screening of specificity and sensitivity experiments, a set of optimal primer sets were obtained for further verification tests.
[0091] This set of primers includes a pair of outer primers F3 / B3, a pair of inner primers FIP / BIP and a loop primer LF, the sequence of which is as follows:
[0092] A pair of outer primers F3 / B3:
[0093] SEQ ID NO.1 (Primer F3): 5'-GGCGCAATGAAAGTAAAGGC-3'
[0094] SEQ ID NO.2 (Primer B3): 5'-AG...
Embodiment 2
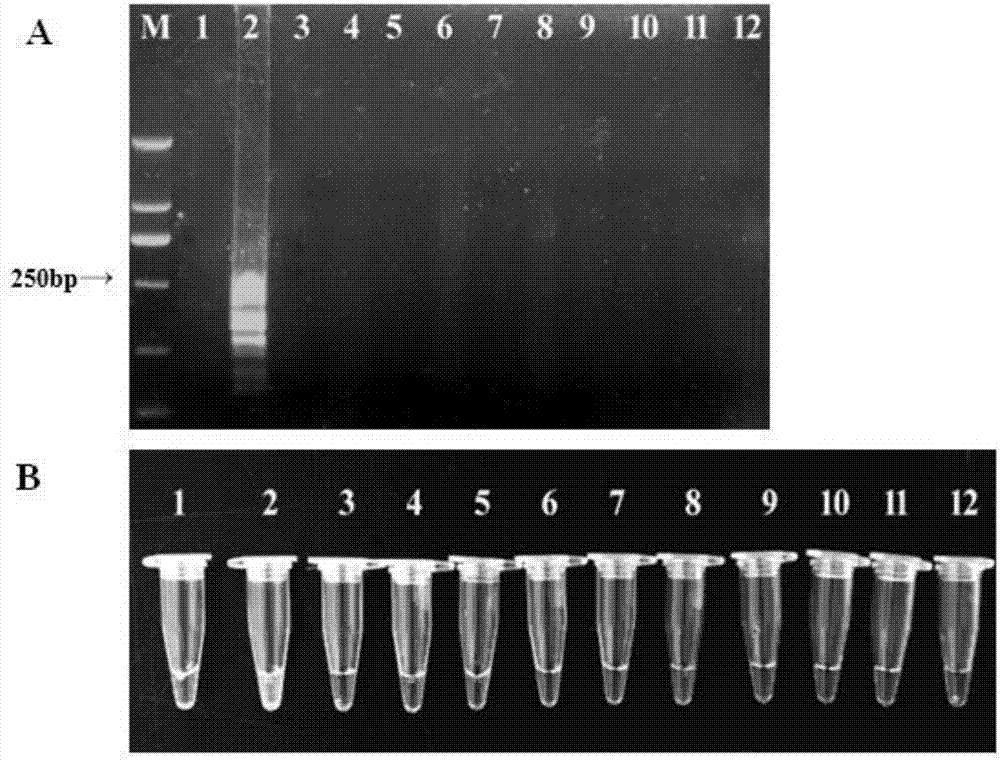
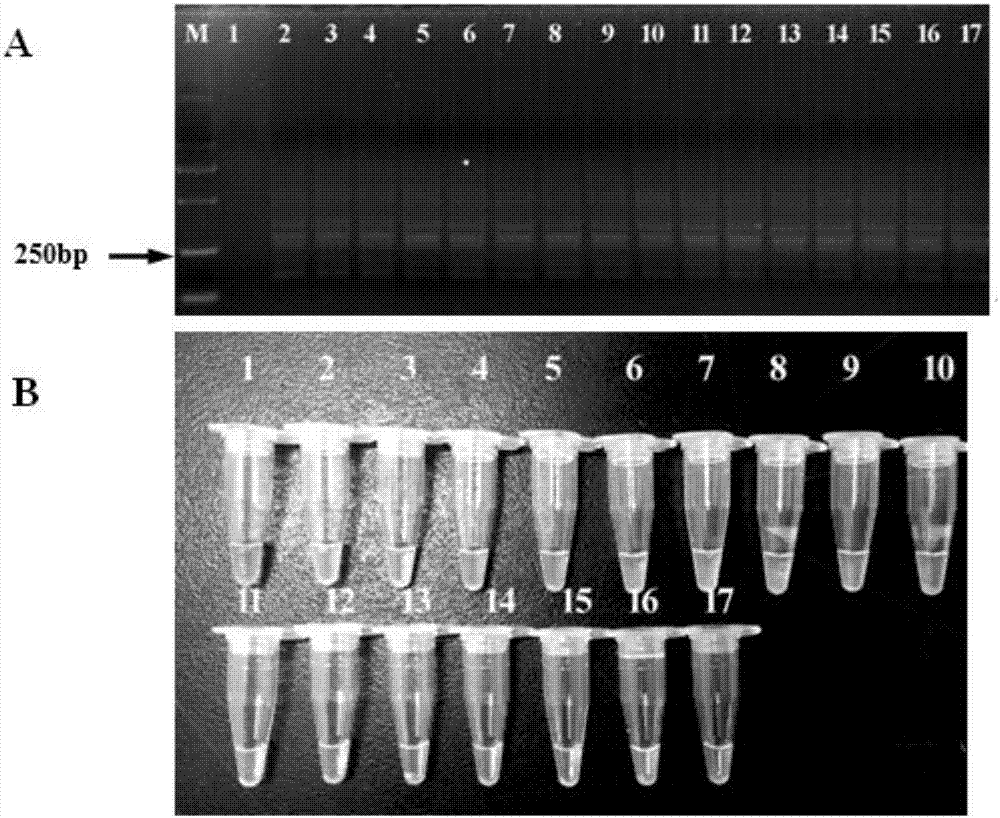
[0125] Example 2 Detection of Primer Specificity and Stability of D. destructor LAMP
[0126] 1. Sample preparation
[0127]The test target nematodes are D. destructor preserved in the laboratory, D. dipsaci, Meloidoglobulina graminaceae, Banana perforator, Chrysanthemum chrysanthemum nematode, New species of smooth blade, short-bodied corn nematode, rice Stem apex nematode, rice root nematode, sarcophagus and small rod nematodes were used as control nematodes to detect the specificity of D. destructor LAMP primers; 16 D. destructor populations (GZ1, SD1 , SD2, HN1, BJ1, LN1, SX2, HB1, AH2, XJ1, TJ1, JS1, SX3, GD1, SX1, YG1) and a single (individual) D. destructor in different stages (egg, larva, female and male) DNA to test the stability of D. destructor LAMP primers.
[0128] The nematodes required for the experiment were all extracted from the DNA of a single worm by the method of Example 1 as a template, and LAMP amplification was carried out according to the reaction sy...
Embodiment 3
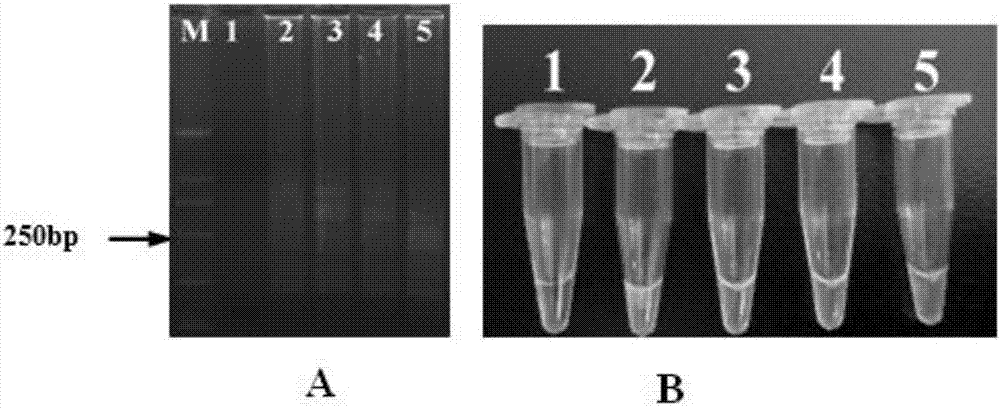
[0136] Example 3 Sensitivity detection of D. destructor LAMP primers
[0137] 1. Sample preparation
[0138] Using the method of Example 1 to extract the DNA of a single worm of D. destructor as a template, dilute the DNA of a single worm according to 10, 50, 100, 200, 1000, 2000, 10000 times, and proceed according to the reaction system and reaction conditions of Example 1 LAMP amplification. Use the electrophoresis detection method in Example 1 and the fluorescent dye visual inspection method in Example 2 to detect the LAMP amplification products.
[0139] 2. Test results
[0140] Using the DNA of D. destructor single worm in gradient dilution as a template, the products amplified by LAMP were electrophoresed and fluorescent dyes were added respectively. The results showed that ( Figure 6 ): The single worm DNA template of D. destructor can still amplify clear electrophoretic bands after diluting 1000 times ( Figure 6 A), after adding SYBR Green I dye, green SYBR Green...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com