Material for generating calcium phytate in situ to seal dentin lumen and application thereof
A technology of dentinal tubules and dentin, used in dentistry, dental preparations, dental prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of uneven texture, poor adaptability of root canal walls, and inability to accurately control the length of gutta-percha tip entry.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
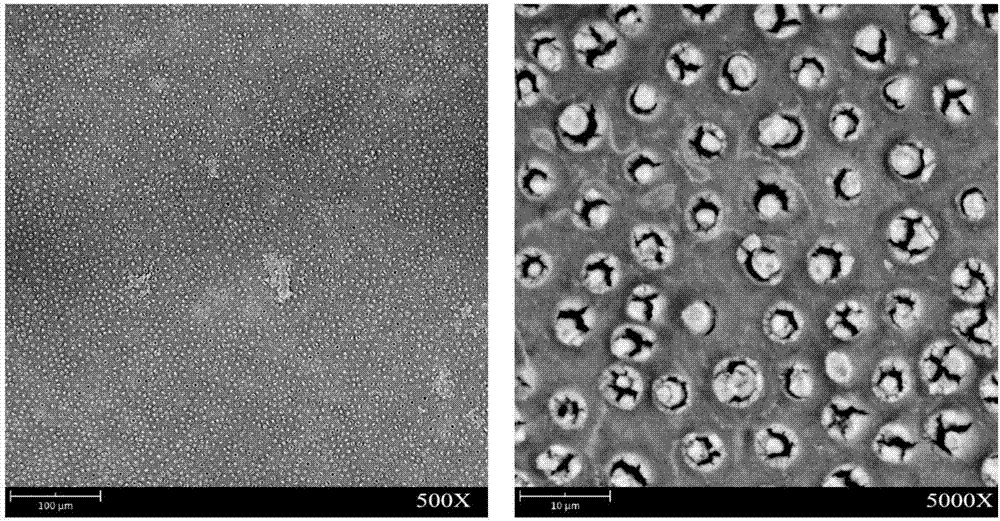
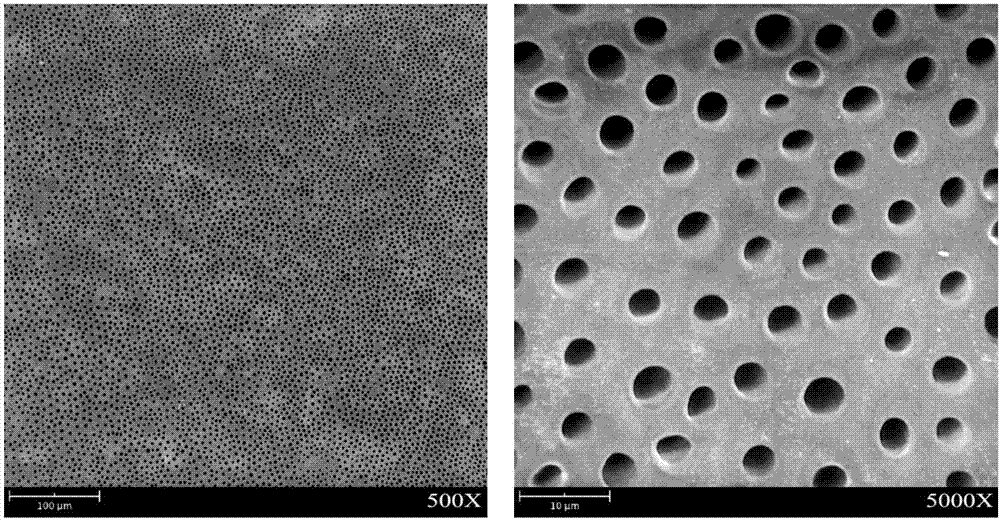
[0022] figure 2 The SEM figure of coating the reagent after the dentin acid etching of embodiment 1;
[0023] image 3 Dentin tubule section SEM figure after using the reagent in embodiment 1;
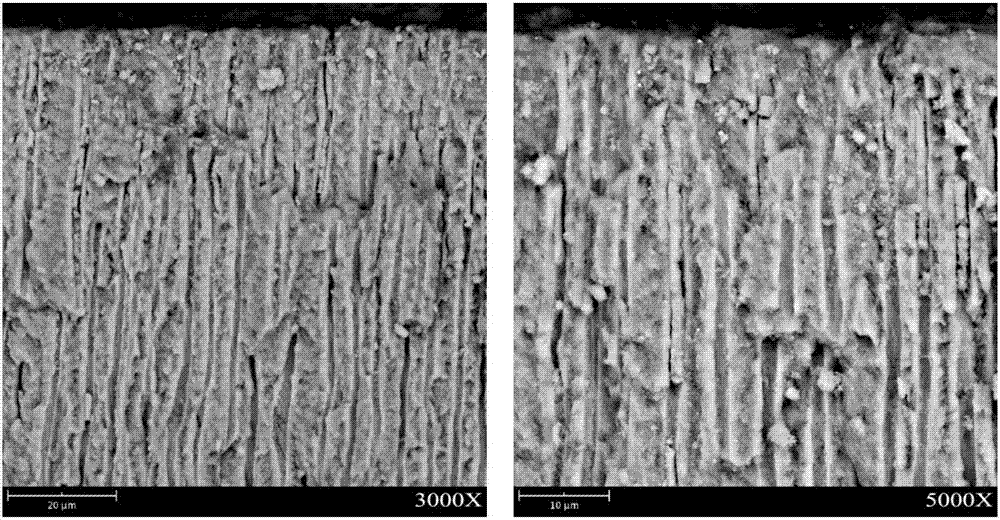
[0024] Figure 4 The dentin of embodiment 1 uses the SEM picture of described coating reagent 7 days
[0025] in Figure 1-4 The left and right pictures are pictures of different scales.
[0026] Figure 5 It is a light microscope (left) SEM (right) picture of the reagent embedded in the root canal of Example 2.
[0027] Specific experimental example
[0028] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
[0029] Example 1: Occlusion of dentin tubules (tubules invisible to the naked eye)
[0030] Methods: 6 human premolars with intact crowns, no caries and cracks were selected from the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery of the School of Stomatology, Capital ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Apical foramen closure (canal visible to the naked eye)
[0038] Methods: 3 human premolars with intact crowns, no caries and cracks were selected from the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery of the School of Stomatology, Capital Medical University, freshly extracted for orthodontics (the patient gave informed consent, and the residual soft tissue on the root surface was removed with a curette after extraction, 4 ℃ physiological saline for storage, the time shall not exceed 4 weeks), and it shall be used as a test piece for future use.
[0039] Equipment: scanning electron microscope (Phenom proX, Phenom-World B.V., Netherlands), metallographic sample pre-grinding machine (YM-2A, Shanghai Metallographic Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd.), low-speed cutting machine (Isomet 4000Linear Precision Saw, Buehler, USA) ;
[0040] Materials: self-curing methyl methacrylate base resin (Shanghai Medical Instrument Co., Ltd. Dental Material Factory, referred to as se...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Dentin tubules blocked by adding ethanol to the reagent A in Example 3
[0045] Steps: Prepare reagent A: dissolve calcium phytate in deionized water, adjust the pH value between 3.5-4 with hydrochloric acid, and add 95% ethanol with a volume percentage of 0.5% at the same time; prepare reagent B: dissolve sodium hydroxide for deionization Prepare sodium hydroxide solution in water, adjust the pH value to 8-10, and add 95% ethanol with a volume percentage of 0.5% at the same time.
[0046] Before use, the dentin samples were etched with 37% phosphoric acid for 30 seconds, rinsed for 10 seconds, and then dried naturally to fully expose the dentin tubules for electron microscope observation. Apply reagent A on the surface of the dentin sample, let it dry naturally for 1 minute, then apply reagent B, let it dry naturally for 10 minutes, clean the tooth surface with deionized water, remove excess substances, etc., and observe with an electron microscope. Soak in artificial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com