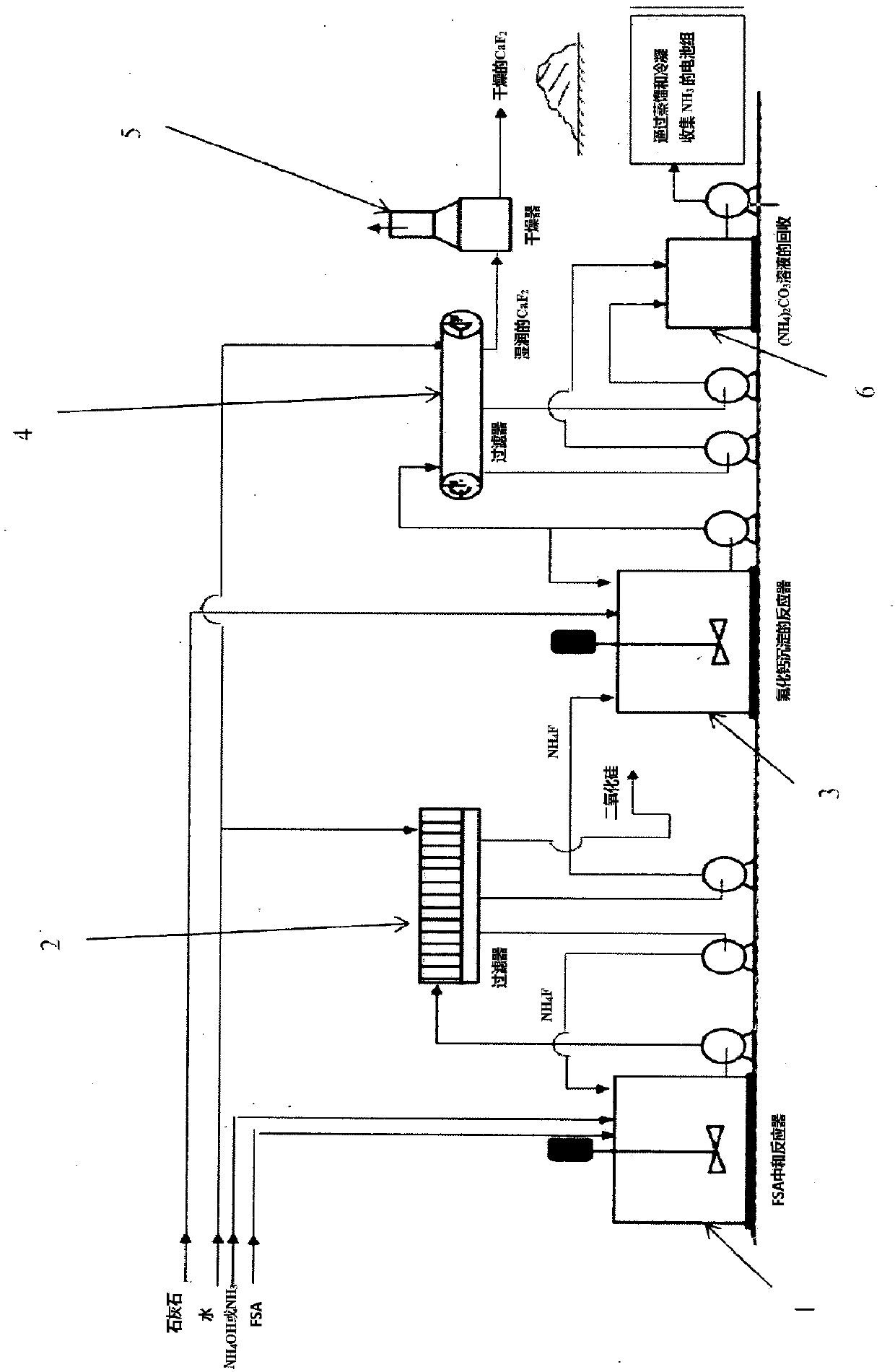
Process for preparing calcium fluoride from fluosilicic acid
A technology of fluorosilicic acid and calcium fluoride, applied in chemical instruments and methods, silicon compounds, chemical methods for reacting liquids and gaseous media, etc., can solve the huge loss of fluorine and ammonia, long reaction time, and difficulty in ammonia recovery And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0108] 252 grams of a solution of fluorosilicic acid at a concentration of 32% by weight, which is commercial fluorosilicic acid, was fed into a 1 liter stirred reaction vessel. The solution in the reaction vessel was stirred at a speed of 250 rpm. During stirring, will be like NH 3 A solution of 380 g of ammonium hydroxide having a concentration of 25% by weight is injected just below the liquid surface. The residence time of the reaction mixture was about 60 minutes, the final pH was about 8.3, and the temperature dropped from 61°C to 28°C. The reaction mixture was then filtered, and the resulting filter cake was washed with distilled water and dried at 110°C. Under these conditions, the neutralization yield of fluorine was 81.24%. Chemical analysis and X-ray diffraction measurements of the dried cake indicated that ammonium fluorosilicide was produced instead of reactive silica.
Embodiment 2
[0112] 80 g of ammonium fluoride having a concentration of 8.47% by weight recovered from the fluorosilicic acid neutralization step was supplied to a reaction vessel provided with a stirrer. The solution in the reaction vessel was stirred at a speed of 250 rpm. During stirring, 71.4 g of calcium hydroxide (concentration of 74.16% by weight) suspension (19.5% by weight) was supplied to make the NH 4 The F / CaO weight ratio is equal to 2.1. The residence time of the reaction mixture was about 30 minutes, the final pH was about 10, and the temperature dropped from 21°C to 16°C. The reaction mixture was then filtered, and the resulting filter cake was washed with distilled water and dried at 110°C. Under these conditions, the precipitation yield of fluorine was 87.62%. Chemical analysis and X-ray diffraction measurements of the dried cake indicated that calcium fluoride was obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0118] 200 g of a fluorosilicic acid solution having a concentration of 23% by weight, prepared by diluting 32% by weight of commercially available fluorosilicic acid, was supplied to a 1-liter reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer. The solution in the reaction vessel was stirred at a speed of 250 rpm. During stirring, will be like NH 3 A solution of 308 grams of ammonium hydroxide having a concentration of 25% by weight was injected just below the surface layer of the liquid surface. The residence time of the reaction mixture was about 60 minutes, the final pH was about 9.6, and the temperature was decreased from 54°C to 20°C. The reaction mixture was then filtered, and the resulting filter cake was washed with distilled water and dried at 110°C. Under these conditions, depending on the silica morphology and filtration parameters of the method, the maximum neutralization yield of fluorine was 98.22%. Chemical analysis showed that the active silica obtained had a high sil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com