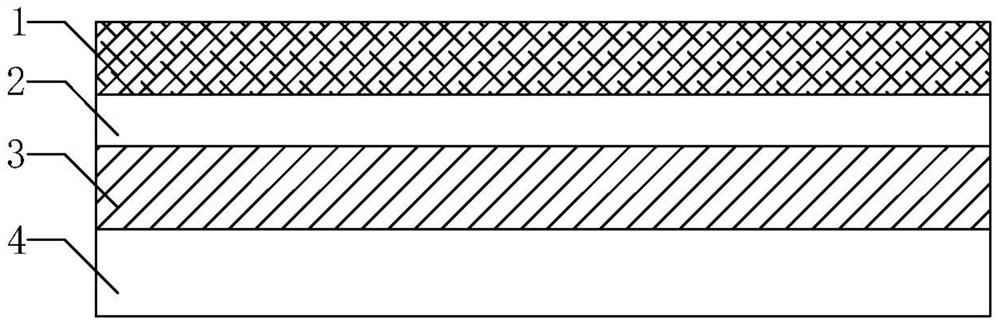
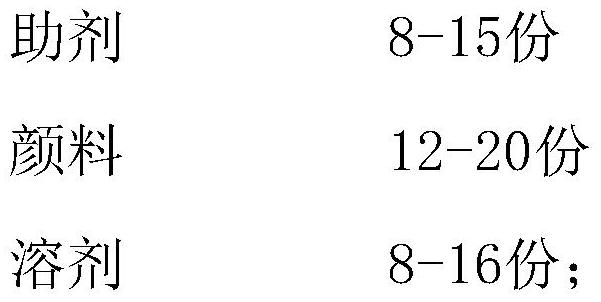A kind of two-dimensional code film and its preparation process
A preparation process and two-dimensional code technology, applied in the field of two-dimensional code film and its preparation process, can solve the problems of roughness, high hardness of the two-dimensional code layer, low adhesion force of the two-dimensional code, etc. The effect of high yield and excellent line definition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A preparation process for a two-dimensional code film, comprising the steps of:
[0045] A. Spraying ink: take the substrate film, spray two-dimensional code ink on the surface of the substrate film, and cure by UV light to obtain two-dimensional code coating;
[0046] B. Gluing: Coating the adhesive on the back of the substrate film, and curing it by heat to obtain the adhesive layer.
[0047] In the step A, UV light curing adopts a UV lamp, the distance between the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 30mm, and the angle between the light of the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 90°, and the UV The light source temperature of the lamp was 120°C.
[0048] In the step A, the two-dimensional code ink includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Wherein, the auxiliary agent is a mixture of thixotropic agent, slip agent and defoamer in a weight ratio of 1:2.5:1.8.
[0052] The curing resin is epoxy ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The difference between this embodiment and above-mentioned embodiment 1 is:
[0064] In the step A, the UV light curing adopts a UV lamp, the distance between the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 35mm, and the angle between the light of the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 87°, and the UV The light source temperature of the lamp was 128°C.
[0065] In the step A, the two-dimensional code ink includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0066]
[0067] Wherein, the auxiliary agent is a mixture of thixotropic agent, slip agent and defoamer in a weight ratio of 1:2.8:1.6.
[0068] The curing resin is polyester acrylate or polyether acrylate; the linking material is triglyceride or ethyl cellulose; and the photosensitizer is benzoin dimethyl ether.
[0069] The pigment is permanent orange or toluidine red; the diluent A is castor oil polyglycidyl ether; and the solvent is methylated ethanol.
[0070] The thixotropic agent ...
Embodiment 3
[0078] The difference between this embodiment and above-mentioned embodiment 1 is:
[0079] In the step A, the UV light curing adopts a UV lamp, the distance between the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 40mm, and the angle between the light of the UV lamp and the surface of the substrate film is 83°, and the UV The light source temperature of the lamp was 135°C.
[0080] In the step A, the two-dimensional code ink includes the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0081]
[0082]
[0083] Wherein, the auxiliary agent is a mixture of thixotropic agent, slip agent and defoamer in a weight ratio of 1:3:1.5.
[0084] The curing resin is urethane acrylate; the linking material is linseed oil or polyol rosin resin; the photosensitizer is benzoin ethyl ether or 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl ketone.
[0085] The pigment is carbon black; the diluent A is cresyl glycidyl ether; and the solvent is isopropyl acetate or isopropanol.
[0086] The thixotropic age...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com