Kit and method for detecting human-derived KRAS gene mutation in excrement
A detection reagent and human-derived technology, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as low detection or detection sensitivity, interference with KRAS gene mutation detection, etc., to achieve the effect of improving detection sensitivity and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1 KRAS gene capture reagent preparation
[0048] For the KRAS gene sequence, specific oligonucleotide probes are designed and synthesized by professional companies. The specific steps of each magnetic bead coating are as follows:
[0049] 1. Invert the magnetic beads up and down or vortex to mix the magnetic beads thoroughly, pipette 20 μl of magnetic beads into a 1.5mL sterilized centrifuge tube;
[0050] 2. Add 1mL magnetic bead rinsing solution, mix by inversion, wash magnetic beads, magnetic field adsorption for 2min, discard supernatant; repeat washing three times;
[0051] 3. Add biotin-labeled specific nucleic acid probes and an equal volume of coupling solution, resuspend the magnetic beads, shake gently, and incubate at room temperature for 10-15 minutes;
[0052] 4. Magnetic field adsorption for 2-3 minutes, discard the supernatant;
[0053] 5. Add 500 μL of magnetic bead washing solution to wash the magnetic beads for 2-3 times, adsorb to the magn...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Stool sample human KRAS gene capture
[0056] 1. Add 1-10ml of fecal cell lysate to 1-5g of fresh feces sample, mix well and lyse, transfer the supernatant to a new clean centrifuge tube by centrifugation at 12000rpm.
[0057] 2. Add a piece of PVPP adsorbent to the supernatant, and vortex to mix the sample thoroughly.
[0058] 3. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2-5min, and transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube.
[0059] 4. Add proteinase K and RNase to the nucleic acid sample obtained after preliminary treatment to completely remove protein and RNA.
[0060] 5. Add the supernatant obtained in the previous step to the binding solution CB, and mix well by inverting up and down.
[0061] 6. Add the prepared gene capture reagent to the above solution, mix by inversion, and incubate at room temperature for 1-2 hours.
[0062] 7. After incubation, transfer the centrifuge tube to the magnetic stand to absorb the magnetic beads, and discard the supernatant....
Embodiment 3
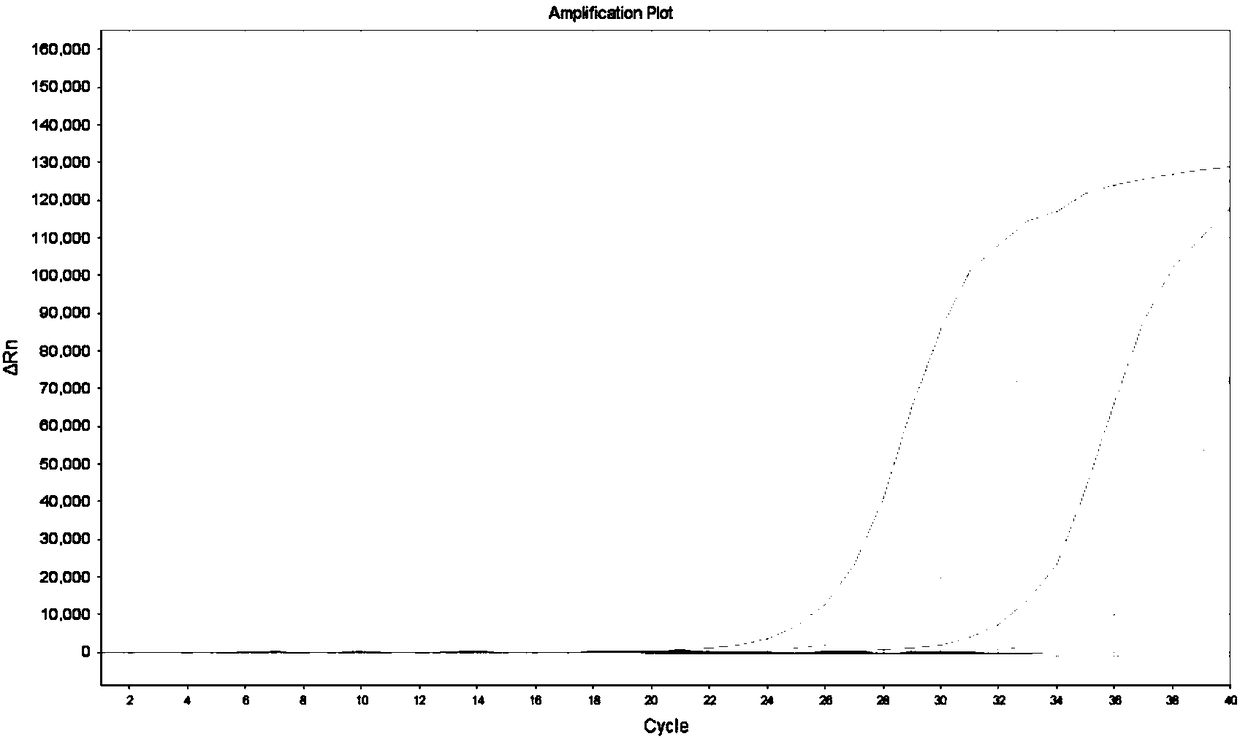
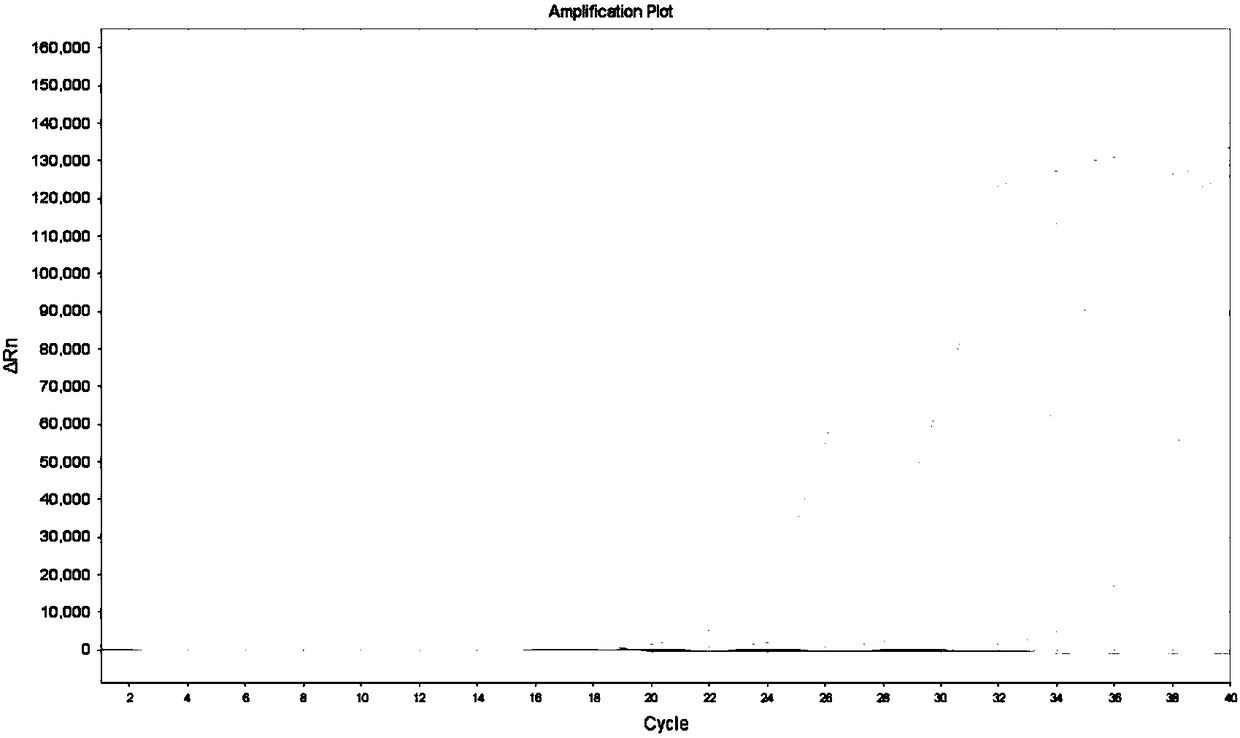
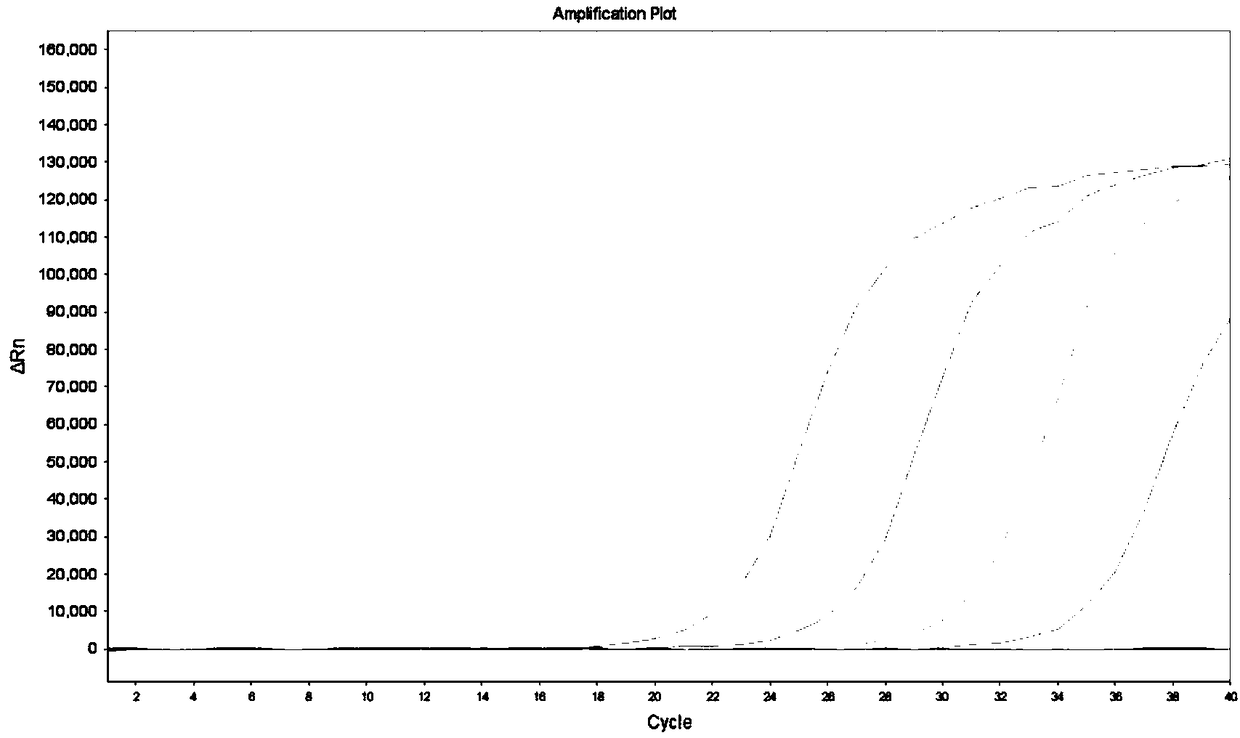
[0067] Embodiment 3, the experiment that detects KRAS gene mutant type in wild-type plasmid
[0068] KRAS gene mutation solutions with different concentration gradients were prepared, and 10 5 Copies / μL of the template contained 100% mutant gene, 10% mutant gene, 1% mutant gene, 0.1% mutant gene and 0% mutant gene in KRAS solution. Taking 34G>A as an example, the preparation method of each concentration is listed as follows:
[0069] (1) KRAS 34G>A 100% mutation solution preparation: 10 5 Copies / μL of 34G>A mutant plasmid
[0070] (2) Preparation of KRAS 34G>A 10% mutation solution: equal volume 2×10 4 Copies / μL KRAS 34G>A gene mutant plasmid with 1.8×10 5 Copies / μL of the wild-type plasmid was mixed evenly, shaken to mix, and centrifuged briefly;
[0071] (3) Preparation of KRAS 34G>A 1% mutation solution: equal volume 2×10 3 Copies / μL KRAS 34G>A gene mutant plasmid with 1.98×10 5 Copies / μL of the wild-type plasmid was mixed evenly, shaken to mix, and centrifuged brief...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com