Accellular epimatrix and preparation method and application thereof
A decellularization and extramatrix technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve problems such as inability to adapt to repair, inability to completely remove animal-derived DNA components, and damage to active components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a preparation method of decellularized extracellular matrix in one embodiment, comprising the following steps:
[0039] S10. Obtaining tissue precursors after preprocessing mammalian tissues and organs.
[0040] Pretreatment of mammalian tissues and organs is as follows: after preliminary removal of fat, muscle and other appendages from the mammalian tissues and organs by mechanical methods, they are cleaned with pure water (preferably 3 to 5 times). Of these, other organs attached indicate organs other than the pericardium, pleura, diaphragm, peritoneum, and small intestinal submucosa.
[0041] Preferably, the tissues and organs of mammals are those of pigs, cattle or horses.
[0042] Preferably, mammalian tissues and organs include mammalian pericardium, pleura, diaphragm, peritoneum and small intestinal submucosa.
[0043] Particularly preferably, the mammalian tissue is pig peritoneum.
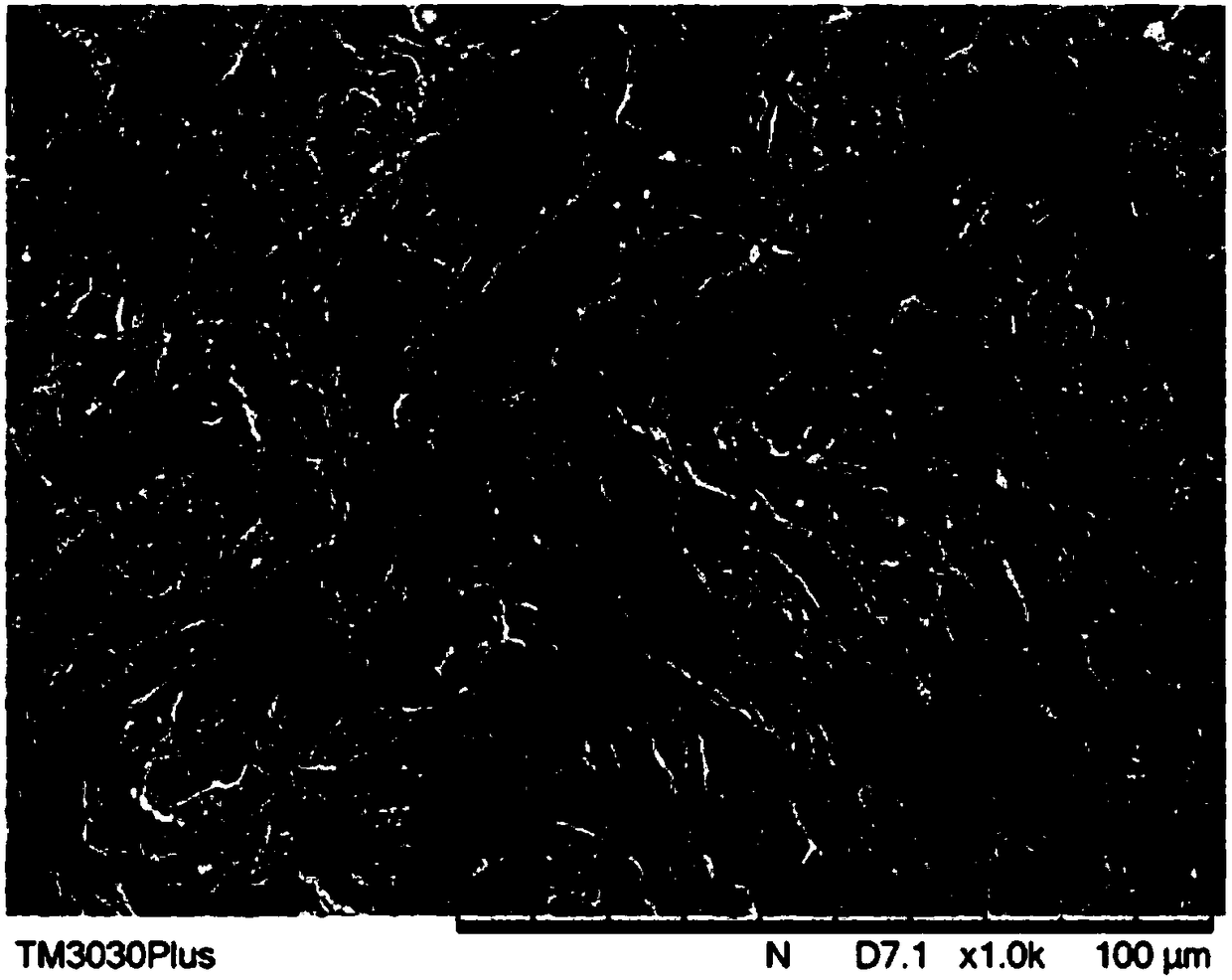
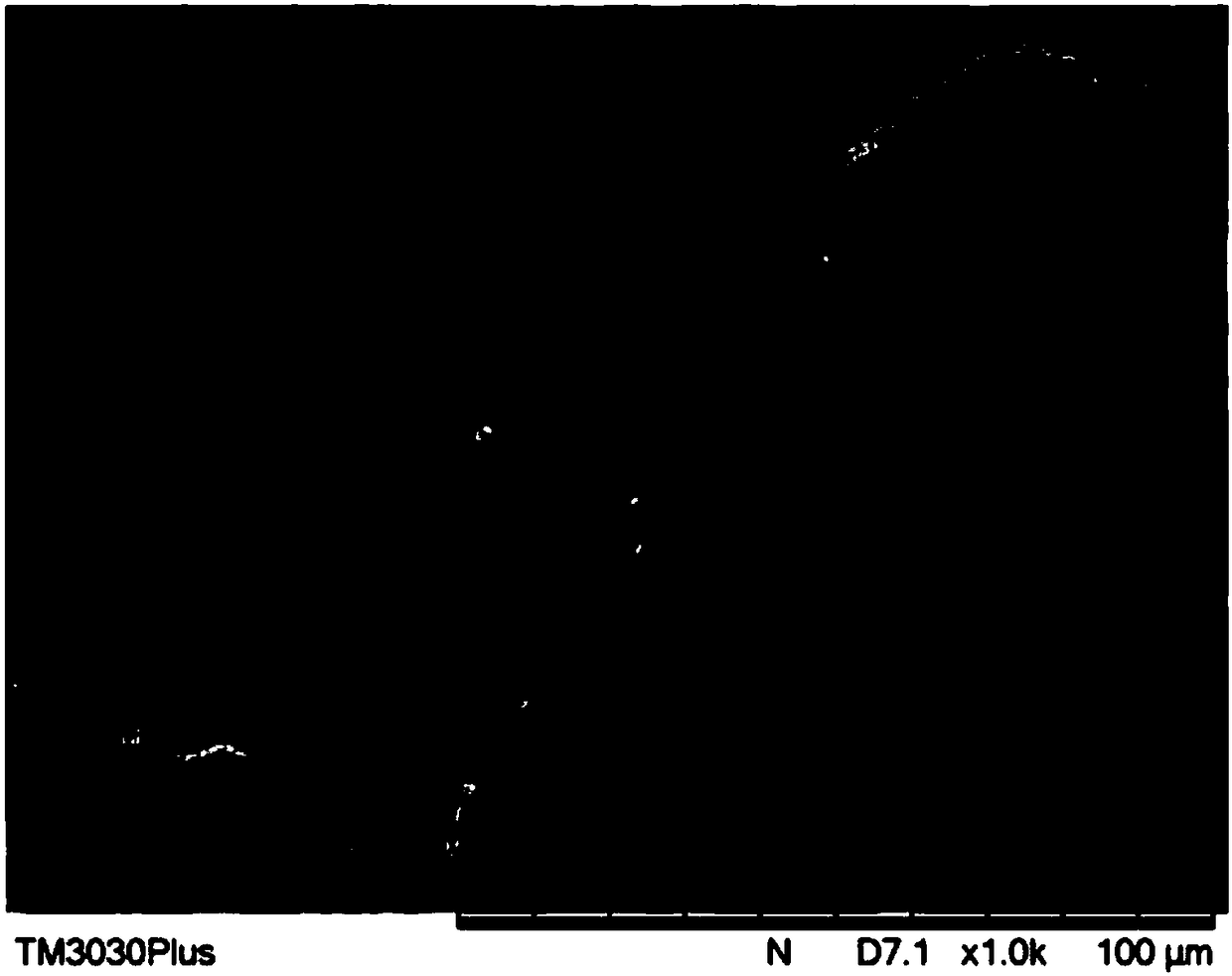
[0044] The tissue p...
Embodiment 1
[0074] Take fresh pig peritoneum tissue, remove fat, muscle and other attached organs from the pig peritoneum by mechanical method, and remove other attached components to make pig peritoneum with a thickness of 0.3mm ~ 1.0mm, and wash it with pure water 4 times , stored at -20°C for later use.
[0075] Soak the pretreated pig peritoneum successively in 2wt% NaOH solution for 12 hours, wash it with pure water for 3 to 5 times, then treat it with 0.5wt% HCl solution for 2 hours, and wash it with pure water for 4 hours. to remove most of the DNA from the animal tissue.
[0076] The pig peritoneum after DNA removal treatment was soaked in 2wt% hydrogen peroxide solution for 3 hours to carry out virus inactivation treatment.
[0077] The inactivated pig peritoneum was soaked in 0.25wt% neutral protease solution for 24 hours, rinsed with pure water and soaked in 1M hypertonic saline for 24 hours to perform decellularization treatment.
[0078] The pig peritoneum was put into n-he...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Take fresh bovine peritoneum tissue, use mechanical method to preliminarily remove fat, muscle and other attached organs, and remove other attached components to make bovine peritoneum with a thickness of 0.3mm ~ 1.0mm, wash it with pure water for 5 times , stored at -20°C for later use.
[0091] Soak the pretreated bovine peritoneum successively in 2wt% NaOH solution for 10 hours, wash 5 times with pure water after treatment, then treat with 0.25wt% HCl solution for 4 hours, wash 5 times with pure water after treatment, to remove most of the DNA from animal tissues.
[0092] The bovine peritoneum after the DNA removal treatment was soaked in a mixed solution of 1 wt% peracetic acid and 50 wt% ethanol for 2 hours to perform virus inactivation treatment.
[0093] The inactivated bovine peritoneum was soaked in 0.25wt% trypsin solution for 12h, rinsed with pure water and soaked in 2M hypertonic saline for 12h for decellularization.
[0094] The bovine peritoneum was put...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com