Method for producing cellulase from cornstalk furfural residues through fermentation via mixed fungi
The technology of corn stalk and cellulase is applied in the field of producing cellulase by fermenting corn stalk furfural residue with mixed bacteria, and can solve the problems of unfavorable Trichoderma reesei production of cellulase, decreased enzyme activity of filter paper, low enzyme activity of filter paper, etc. Achieve good economic and social benefits, high substrate concentration and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
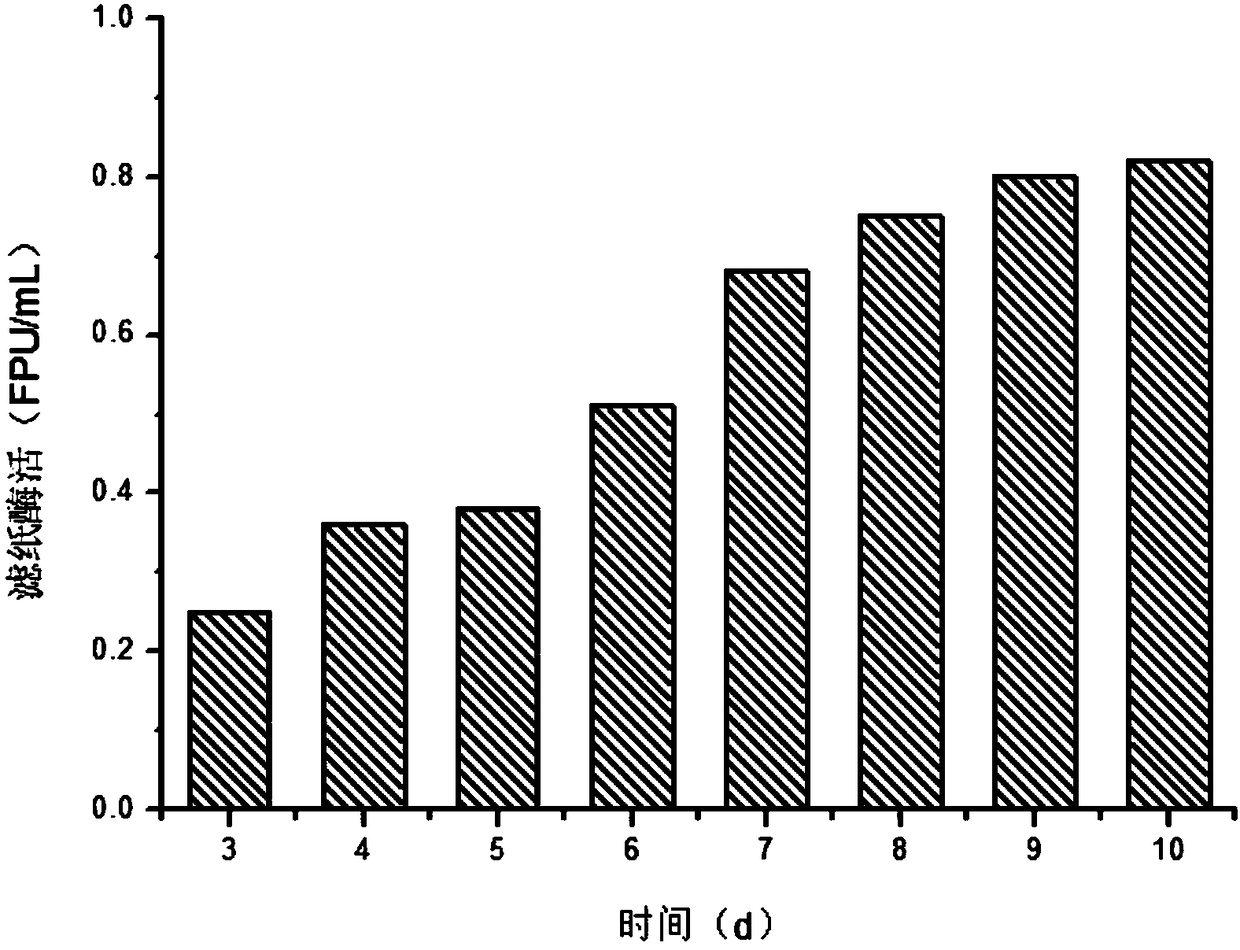
[0043] Cellulase produced by mixed bacteria fermentation
[0044] The Trichoderma reesei CICC13052 and CICC40360 preserved on the slant were respectively activated, transferred from the spore suspension to the seed culture solution with a 5% inoculation amount, and cultured on a shaker at 28° C. and 180 rpm for 24-48 hours. Then transfer it to the enzyme-producing medium containing 50g / L furfural slag at an inoculation ratio of 1:1 and a total inoculation amount of 5%, and take samples at regular intervals to determine the enzyme activity. The result is as figure 1 It was shown that the cellulase activity of the mixed bacteria could reach 0.82 FPU / mL when 50 g / L corn stalk furfural residue was used as the induced carbon source.
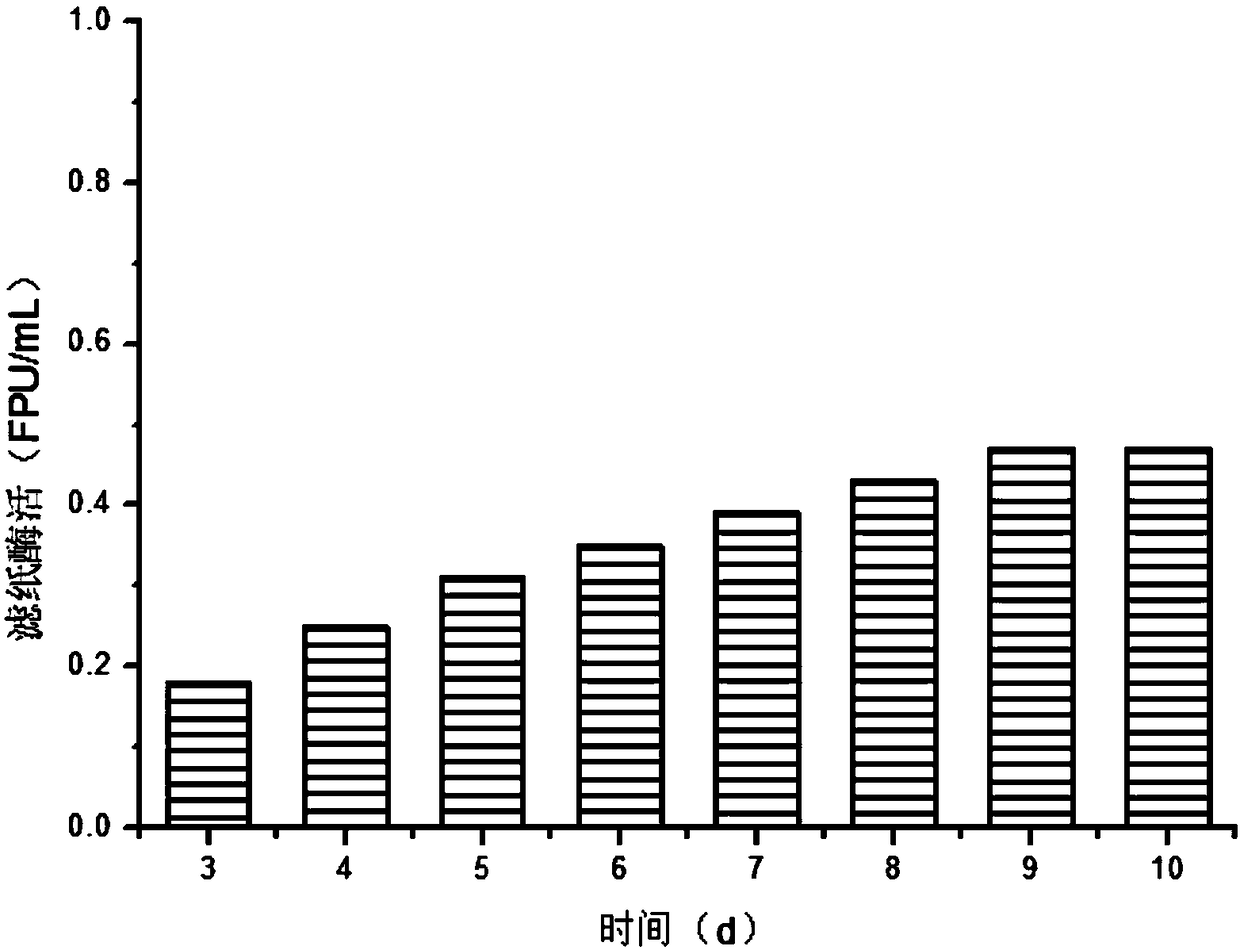
Embodiment 2
[0052] Effects of Different Substrate Concentrations on Enzyme Production by Mixed Bacteria Fermentation
[0053] According to the method described in Example 1, the mixed bacteria were transferred to the enzyme-producing medium with different concentrations of furfural slag at an inoculation ratio of 1:1 and a total inoculation amount of 5%, and samples were taken at regular intervals to determine the enzyme activity to explore its optimal carbon source. content and enzyme production. The result is as Figure 4 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the mixed bacteria have better substrate tolerance, even at the concentration of 200g / L furfural residue, they can also ferment and produce enzymes. When 100g / L furfural residue is used as the induced carbon source, the cellulose The maximum enzyme activity can reach 0.87FPU / mL, so the substrate concentration in subsequent tests is preferably 100g / L.
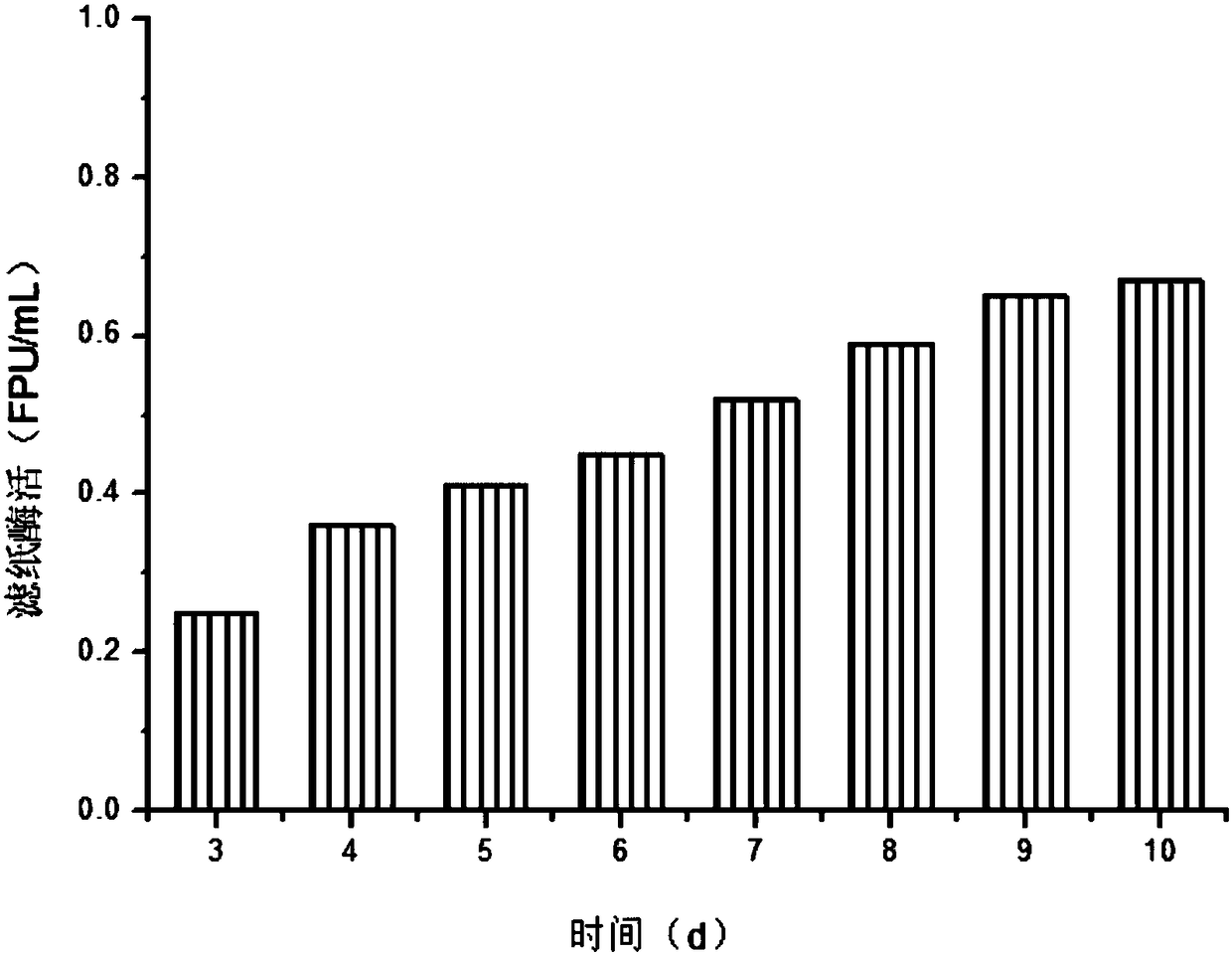
Embodiment 3
[0055] Effects of Different Initial pH on Enzyme Production by Mixed Bacteria Fermentation
[0056] The pH of the medium is closely related to the growth and reproduction of cells and the production of enzymes by fermentation. During the fermentation process, with the growth and reproduction of cells and the accumulation of metabolic products, the pH of the medium often changes, so this experiment only controls the initial pH .
[0057] According to the method described in Example 2, the mixed bacteria are transferred to the product containing 100g / L furfural slag with an initial pH of 2.80, 4.32, 4.80, 6.00, 7.00, 8.00 with an inoculation ratio of 1:1 and a total inoculation amount of 5%. Fermentation was carried out in the enzyme medium, samples were taken regularly to measure the enzyme activity, the effect of the initial pH on the enzyme production of the mixed bacteria fermentation was observed, and the optimal initial pH and enzyme production were explored. The result i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com