Phthalic acid di(2-ethyl) hexyl ester degrading bacterium as well as culture method and application thereof
A technology of phthalate di- and culture method, which is applied in the field of dihexyl phthalate-degrading bacteria, can solve DEHP pollution and other problems, and achieve strong substrate specificity, rapid growth and remarkable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: The bis(2-ethyl)hexyl phthalate degrading bacterium of this embodiment is Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1, which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, The date of deposit is June 8, 2017, and the deposit number is CCTCC No: M 2017315.
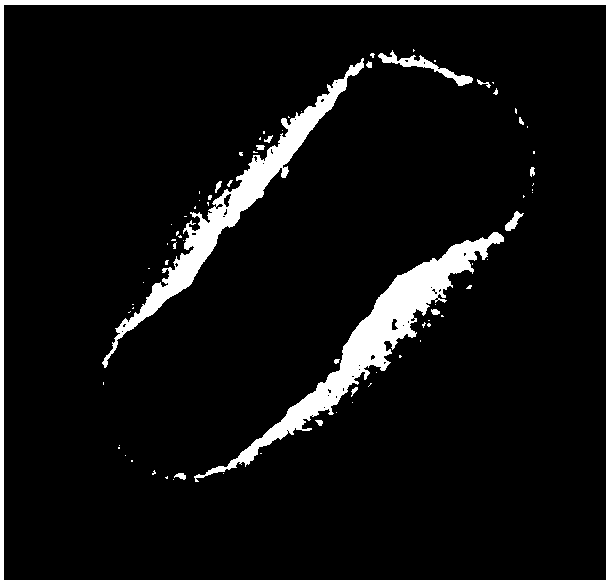
[0032] In this example, Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 is a Gram-positive bacterium, and the colony is milky white and shiny, with a wet surface and a bulge in the middle, and neat edges. The transmission electron microscope photo of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 is as follows figure 1 with figure 2 shown.
[0033] Physiological and biochemical identification of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 with reference to the eighth edition of "Berger's Bacteria Identification Manual" and "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual": the urease test, glycolysis test, methyl Red test, citrate utilization test, indole test are all positive, starch hydrolysis test, V-P te...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Domestication and isolation of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1
[0037] In this example, Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 was isolated from the soil of an abandoned and polluted facility in Harbin. The separation method is carried out according to the following steps: 1. Take 500 g of the soil surface sample of 0-20 cm, put it in a sterilized waterproof paper bag, and store it in a refrigerator at 4°C. 2. Add a small amount of plastic debris to the retrieved soil, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for enrichment and cultivation for 2 weeks. 3. Take 3 soil samples after enrichment culture, each weighing 5g, put them into a triangular flask containing 90mL sterilized water and 5-8 glass beads and seal them with a sealing film. Shake in a constant temperature shaking incubator for 30 minutes, then let stand for 30 minutes.
[0038] Take 10mL supernatant and add it into 100mL basic inorganic salt culture medium containing DEHP for cultivation. First, the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Molecular characterization of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1
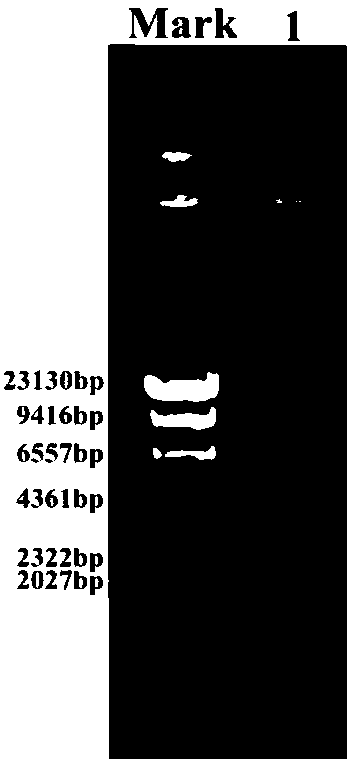
[0041] The molecular identification of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 obtained by isolation and screening was carried out according to the following steps: extract the total DNA of the strain, use bacterial 16S rDNA general primers 27f and 1522r, and use genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification. Then use the gel recovery kit to recover and purify the PCR product; after that, carry out cloning and transformation, screen the colony of positive clones, and sequence them after expansion and cultivation. The electrophoresis results of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 genomic DNA are as follows image 3 . The PCR amplification result of Arthrobactersp.DNEH-S1 16S rDNA sequence is as follows Figure 4 .
[0042] The 16S rDNA sequence of Arthrobacter sp.DNEH-S1 was submitted to GenBank and the sequence number obtained was KC874838. The sequence result was compared with the 16S rDNA sequence in GenBank. The phylogeneti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com