Macroporous spherical zinc sulfide/ferrous sulfide/carbon negative electrode material and preparation method thereof
A carbon anode material, ferrous sulfide technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Add 2 mmol of iron acetylacetonate, 3 mmol of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 5 mmol of thioacetamide and 2.5 g (13 mmol) of citric acid into 50 mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve to a homogeneous solution;
[0045] (2) Pour the solution obtained in step (1) into a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high-temperature reaction kettle, seal the steel shell, place in a blast oven, heat to 180 °C, react for 16 h, cool naturally to room temperature, filter, The filtrate was cross-washed four times with ethanol and deionized water respectively, and then placed in a blast oven at 60°C for 24 h to obtain a black powder;
[0046] (3) Calcining the black powder obtained in step (2) at 600°C for 3 hours in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and cooling naturally to room temperature to obtain a macroporous spherical zinc sulfide / ferrous sulfide / carbon negative electrode material.
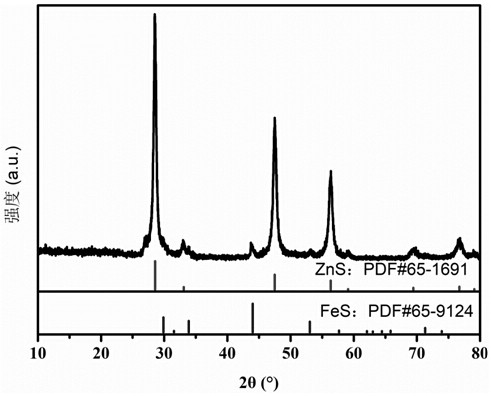
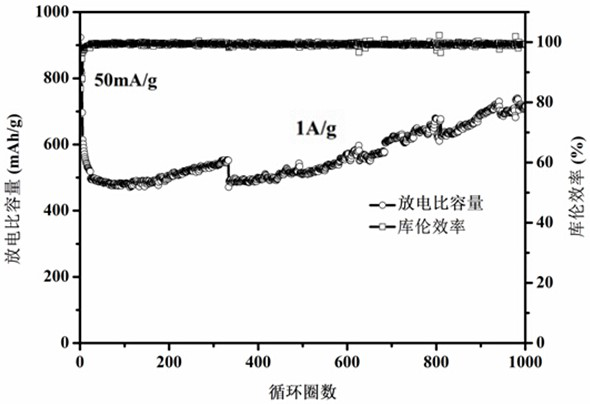
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the zinc sulfide and ferrous sulfide in the macroporous spherical zinc...
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) Add 2 mmol of iron acetylacetonate, 3 mmol of zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 5 mmol of thioacetamide and 2 g (9.52 mmol) of trimesic acid into 50 mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve to a homogeneous solution;
[0053] (2) Pour the solution obtained in step (1) into a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high-temperature reaction kettle, seal the steel shell, place in a blast oven, heat to 200 °C, react for 10 h, cool naturally to room temperature, filter, Wash the filtrate three times successively with ethanol and deionized water, then place it in a blast oven at 100°C, and dry it for 20 h to obtain a black powder;
[0054] (3) Calcining the black powder obtained in step (2) at 450° C. for 5 hours in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and naturally cooling to room temperature to obtain a macroporous spherical zinc sulfide / ferrous sulfide / carbon negative electrode material.
[0055] After testing, the zinc sulfide and ferrous sulfide in the macroporous spherical zinc sulfide / ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] (1) Add 2.5 mmol of ferric citrate, 5 mmol of zinc chloride hexahydrate, 22.5 mmol of thiourea and 1.5 g (7.81 mmol) of citric acid into 50 mL of deionized water, stir and dissolve to a homogeneous solution;
[0062] (2) Pour the solution obtained in step (1) into a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high-temperature reaction kettle, seal the steel shell, place in a blast oven, heat to 160 °C, react for 20 h, cool naturally to room temperature, filter, The filtrate was cross-washed four times with ethanol and deionized water respectively, and then placed in a blast oven at 80°C for 12 h to obtain a black powder;
[0063] (3) The black powder obtained in step (2) was roasted at 500 °C for 4 hours in a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere, and cooled naturally to room temperature to obtain a macroporous spherical zinc sulfide / ferrous sulfide / carbon negative electrode material.
[0064] After testing, the zinc sulfide and ferrous sulfide in the macroporous spherical zinc sulfide / fe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com