Method and application for preparing magnetic Sm2Co17/Al-Ni-Co composite through spark plasma sintering
A discharge plasma and composite material technology, applied in the field of composite material preparation, can solve the problems of restricting industrialization development, complex sintering process, inclusion and fouling, etc., and achieves the effect of solving poor magnetic properties, simple process and stable structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
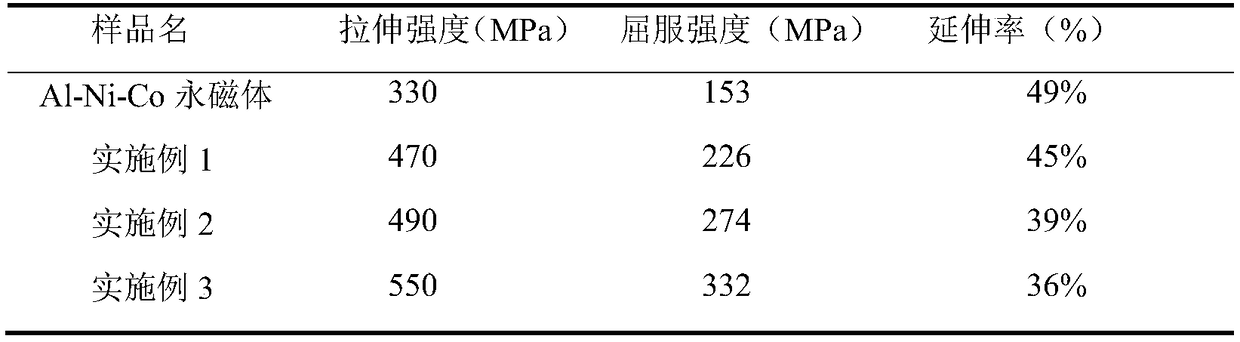
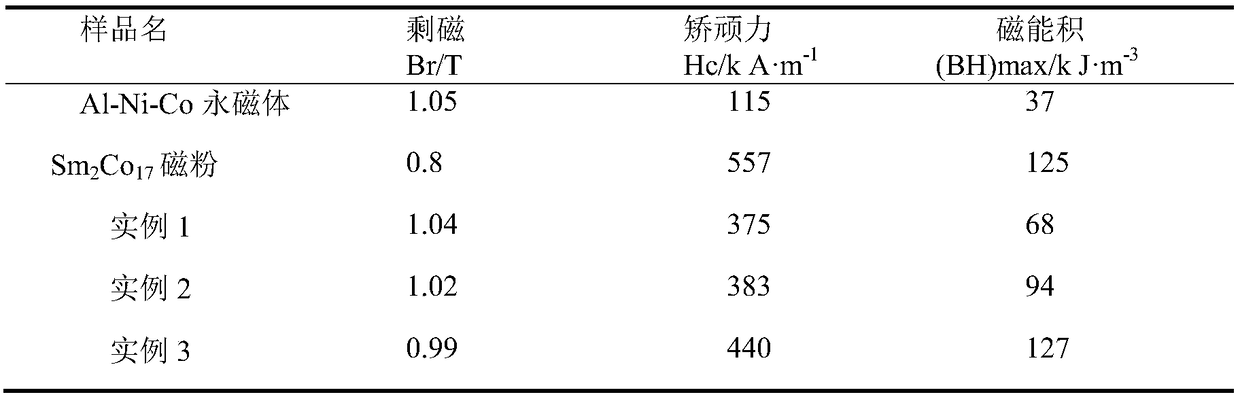
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Milling:
[0028] The aluminum powder used in the experiment is 99.85% pure powder with an average particle size of 10 μm; general-purpose cobalt powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; nickel powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; industrial production 2:17 type Sm-Co permanent magnet material (Sm 2 co 17 Magnetic powder), the average particle size after powder making is about 5 μm;
[0029] (2) Ball milling:
[0030] Weigh 18gSm 2 co 17 Magnetic powder, 18g aluminum powder, 18g cobalt powder, 18g nickel powder, mix the above powders, add ethanol, make the ethanol cover the above mixed powder, wet mill in planetary ball mill for 12h, put the powder after ball milling into a vacuum oven for drying dry to obtain mixed powder;
[0031] (3) Compression molding:
[0032] The mixed powder after drying is compressed by cold isostatic pressing, pressurized at 90MPa, and kept under pressure for 5min to obtain a compact composite billet;
[0033] (4) Spar...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Milling:
[0039] The aluminum powder used in the experiment is 99.85% pure powder with an average particle size of 10 μm; general-purpose cobalt powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; nickel powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; industrial production 2:17 type Sm-Co permanent magnet material (Sm 2 co 17 Magnetic powder), the average particle size after powder making is about 5 μm;
[0040] (2) Ball milling:
[0041] Weigh 25gSm 2 co 17Magnetic powder, 15g aluminum powder, 15g cobalt powder, 15g nickel powder, mix the above powders, add ethanol, make the ethanol cover the above mixed powder, wet mill in a planetary ball mill for 10h, put the ball milled powder into a vacuum drying oven and dry dry to obtain mixed powder;
[0042] (3) Compression molding:
[0043] The dried mixed powder is compressed by cold isostatic pressing, pressurized at 100MPa, and kept under pressure for 2min to obtain a dense composite billet;
[0044] (4) Spark plasma s...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Milling:
[0050] The aluminum powder used in the experiment is 99.85% pure powder with an average particle size of 10 μm; general-purpose cobalt powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; nickel powder with an average particle size of 2 μm; industrial production 2:17 type Sm-Co permanent magnet material (Sm 2 co 17 Magnetic powder), the average particle size after powder making is about 5 μm;
[0051] (2) Ball milling:
[0052] Weigh 36gSm 2 co 17 Magnetic powder, 12g aluminum powder, 12g cobalt powder, 12g nickel powder, mix the above powders, add ethanol, make the ethanol cover the above mixed powder, wet grind in planetary ball mill for 11h, put the ball milled powder into vacuum drying oven and dry dry to obtain mixed powder;
[0053] (3) Compression molding:
[0054] The mixed powder after drying is compressed by cold isostatic pressing, pressurized at 95MPa, and kept under pressure for 3min to obtain a compact composite billet;
[0055] (4) Spark pl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com