Method for producing hydrogen and recycling phosphorus through electrolysis of neutral Fenton regulated residual sludge microorganism
A technology of microbial electrolysis and excess sludge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
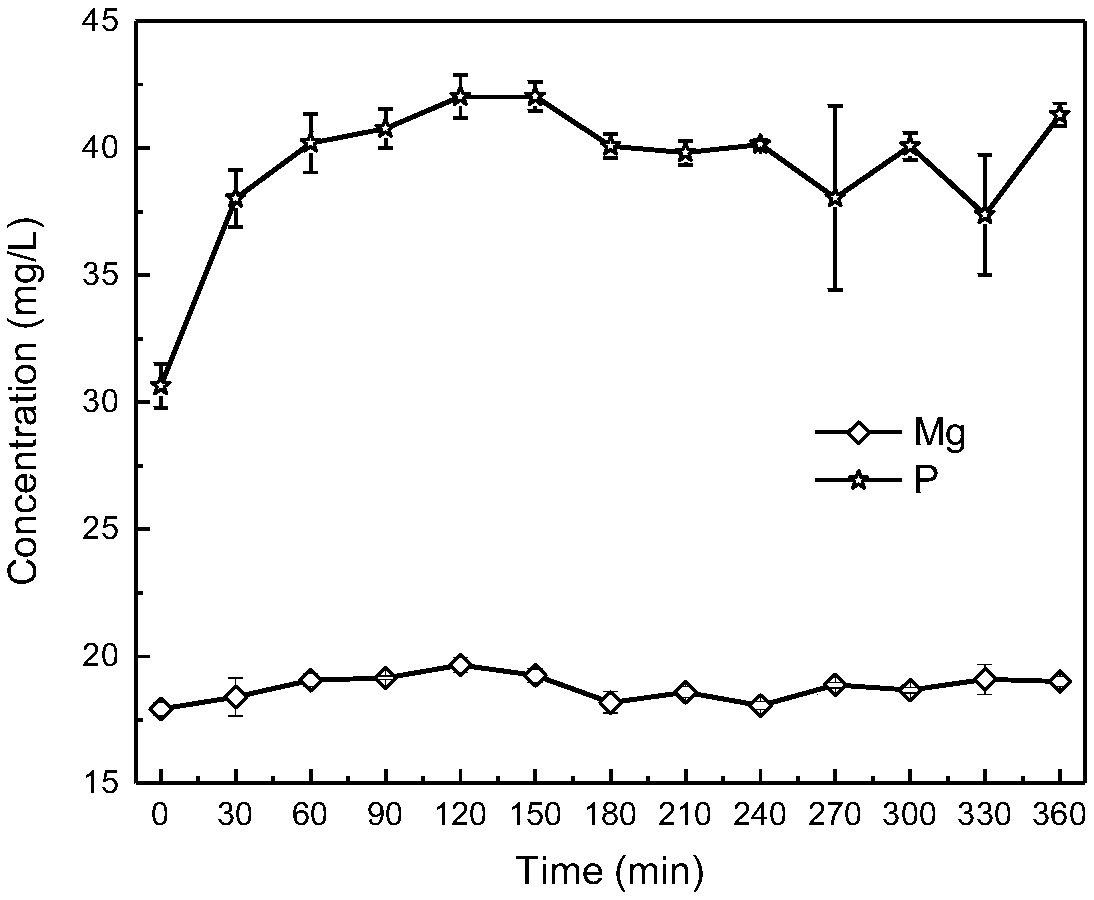
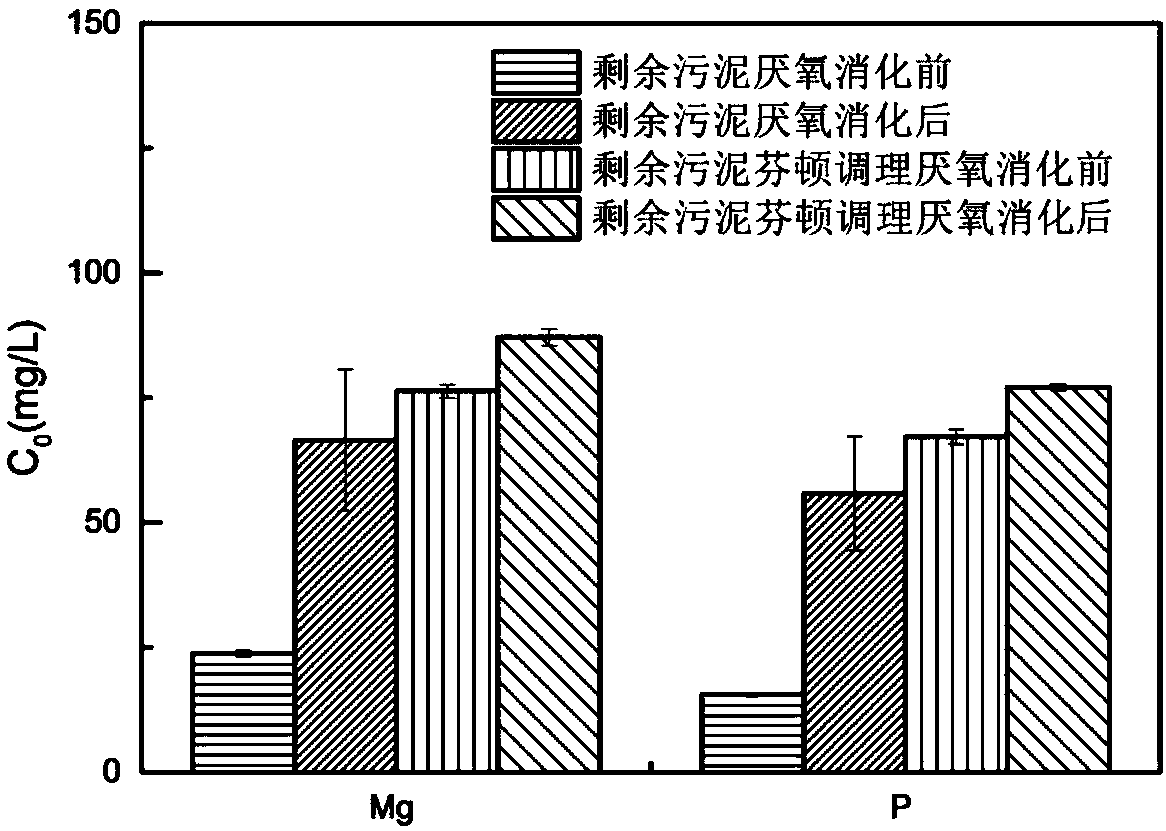
[0040] (I) Neutral Fenton conditioning: take 500mL of TS content of 4.5g / L residual sludge and place it in a beaker, add 3.75mL10mM FeCl 3 Immediately after the solution, add 5.6mL 10mM protocatechuic acid solution (of course, other concentrations can also be used as protocatechuic acid solution), stir rapidly for 30s, and then add 0.4mL 30% H 2 o 2 , stirring rapidly for 30s, then stirring slowly for 2h;
[0041] (II) Anaerobic digestion pretreatment: add 400mL of the pretreated sludge in the step to 100mL of anaerobic granular sludge and mix evenly, the fermentation concentration is 5%, and the fermentation feed liquid is filled with high-purity nitrogen for 15min, and anaerobic digestion is performed at 35°C 3d;
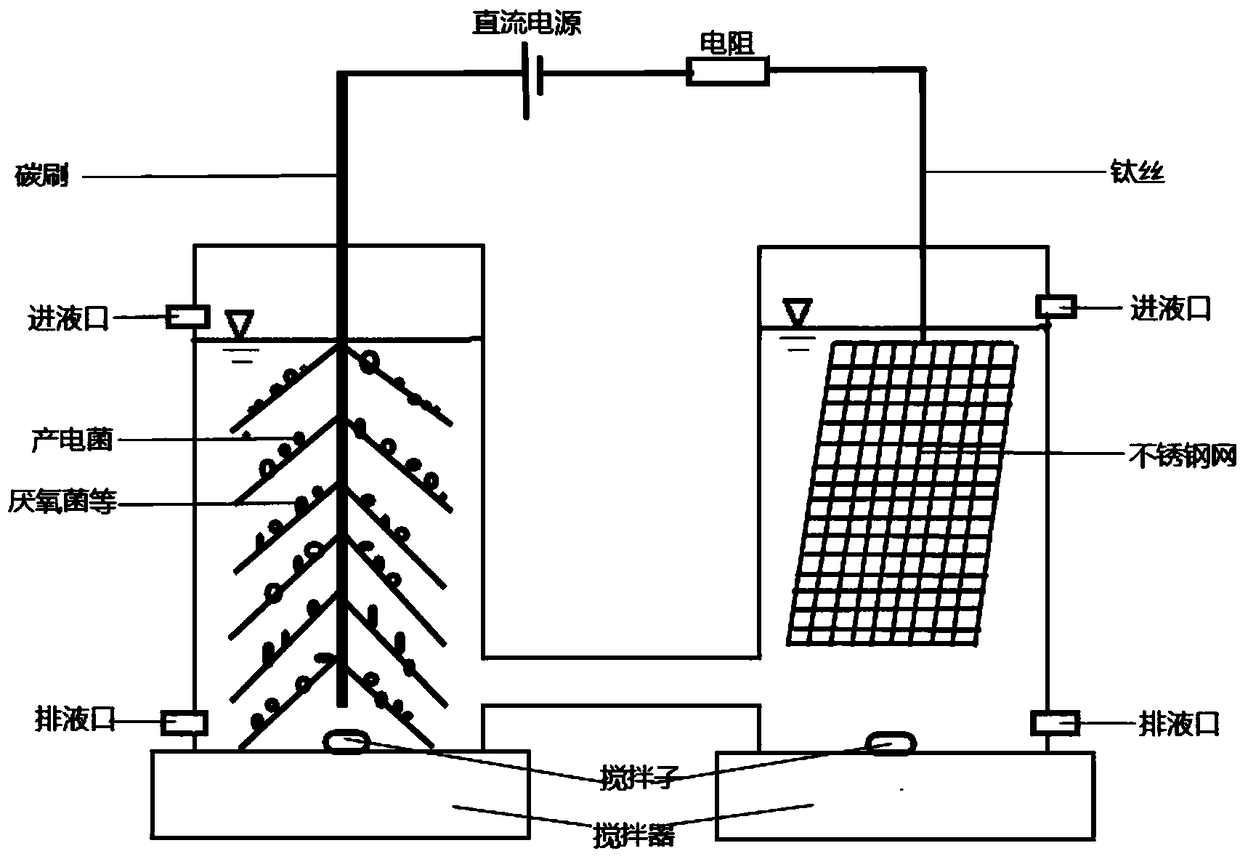
[0042] (Ⅲ) MEC microbial domestication: The total volume of the double-bottle MEC reactor is 600mL and the effective volume is 500mL. The anode of the MEC reactor is a carbon brush, the cathode is made of stainless steel mesh, and the inoculum is effluent from a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (I) Neutral Fenton conditioning: take 500mL of TS content of 5.7g / L residual sludge and place it in a beaker, add 10mM FeCl 3 Add 7.1 mL of 10 mM nitrilotriacetic acid solution immediately after 4.75 mL of the solution (of course, other concentrations of nitrilotriacetic acid solutions can also be used), stir rapidly for 30 seconds, and then add 0.5 mL of 30% H 2 o 2 , stirring rapidly for 30s, then stirring slowly for 2h;
[0047] (II) Anaerobic digestion pretreatment: add 400mL of the pretreated sludge in the step to 100mL of anaerobic granular sludge and mix evenly, the fermentation concentration is 7%, the fermentation feed liquid is filled with high-purity nitrogen for 15min, and anaerobic digestion is performed at 35°C 3d;
[0048] (Ⅲ) MEC microbial domestication: The total volume of the double-bottle MEC reactor is 600mL and the effective volume is 500mL. The anode of the MEC reactor is a carbon brush, the cathode is made of stainless steel mesh, and the inocul...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (I) Neutral Fenton conditioning: take 500mL of TS content of 12.5g / L residual sludge and place it in a beaker, add 10mM FeCl 3 Add 32.5mL of 10mM protocatechuic acid solution immediately after 21mL of the solution, stir rapidly for 60s, then add 2.4mL of 30% H 2 o 2 , stirring rapidly for 30s, then stirring slowly for 2h;
[0053] (II) Anaerobic digestion pretreatment: Add 350mL of pretreated sludge in the step to 150mL of anaerobic granular sludge and mix evenly. The fermentation concentration is 9%. Fill the fermentation feed liquid with high-purity nitrogen for 30 minutes, and perform anaerobic digestion at 35°C. 5d;
[0054] (Ⅲ) MEC microbial domestication: The total volume of the double-bottle MEC reactor is 600mL and the effective volume is 500mL. The anode of the MEC reactor is a carbon brush, the cathode is made of stainless steel mesh, and the inoculum is effluent from a stable MEC. 1.5g / L sodium acetate is used as carbon source, 1.0V voltage is applied, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com