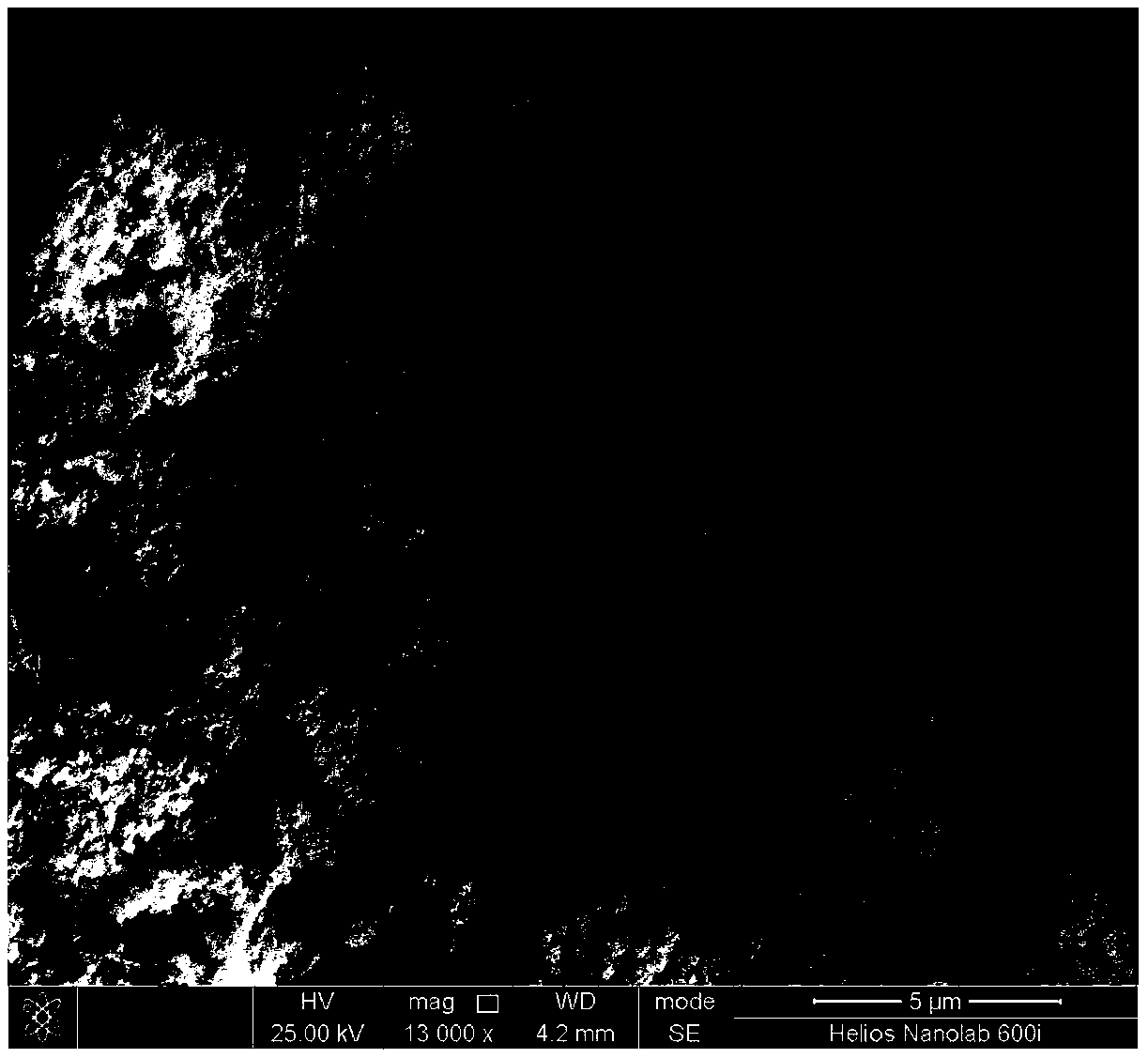
High temperature-resistant, heat-insulation and wave-permeable ceramic-based composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material and high-temperature-resistant technology, which is applied to ceramic products, other household appliances, applications, etc., can solve the problems of low heat-resistant temperature and non-oxidation resistance, achieve low dielectric constant, reduce production energy consumption, and shorten the preparation cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a high-temperature-resistant, heat-insulating, and wave-transmitting ceramic-based composite material, which is characterized in that it includes the following steps:
[0033] The first step: put kaolin, alumina, and industrial aluminum sol with a mass of 100g, 52g, and 154g respectively in a mixing tank, and simultaneously add mineralizers with a mass of 7.5g and 5g of anhydrous aluminum fluoride and a mass of 5g Molybdenum trioxide as a sintering aid, and then add 400g of alumina balls and 150ml of absolute ethanol as grinding medium, after continuous mixing for 24 hours, dry in an oven at 60°C and sieve to obtain mixed powder A;
[0034] The second step: put the mixed powder A and the pore-forming agent PS microspheres in the first step with a mass ratio of 1:0.5 in the mixing tank, add 200g of alumina balls and 150ml of absolute ethanol as the ball milling medium, wet Mix for 2 hours, dry in an oven at 60°C and pass th...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the mass ratio of the mixed powder A to the pore-forming agent PS microspheres in the second step is 1:0.35; the preparation method of the aluminum sol in the seventh step is as follows: , obtained by diluting commercially available industrial aluminum sol with a solid content of 25% to a solution with a solid content of 3%.
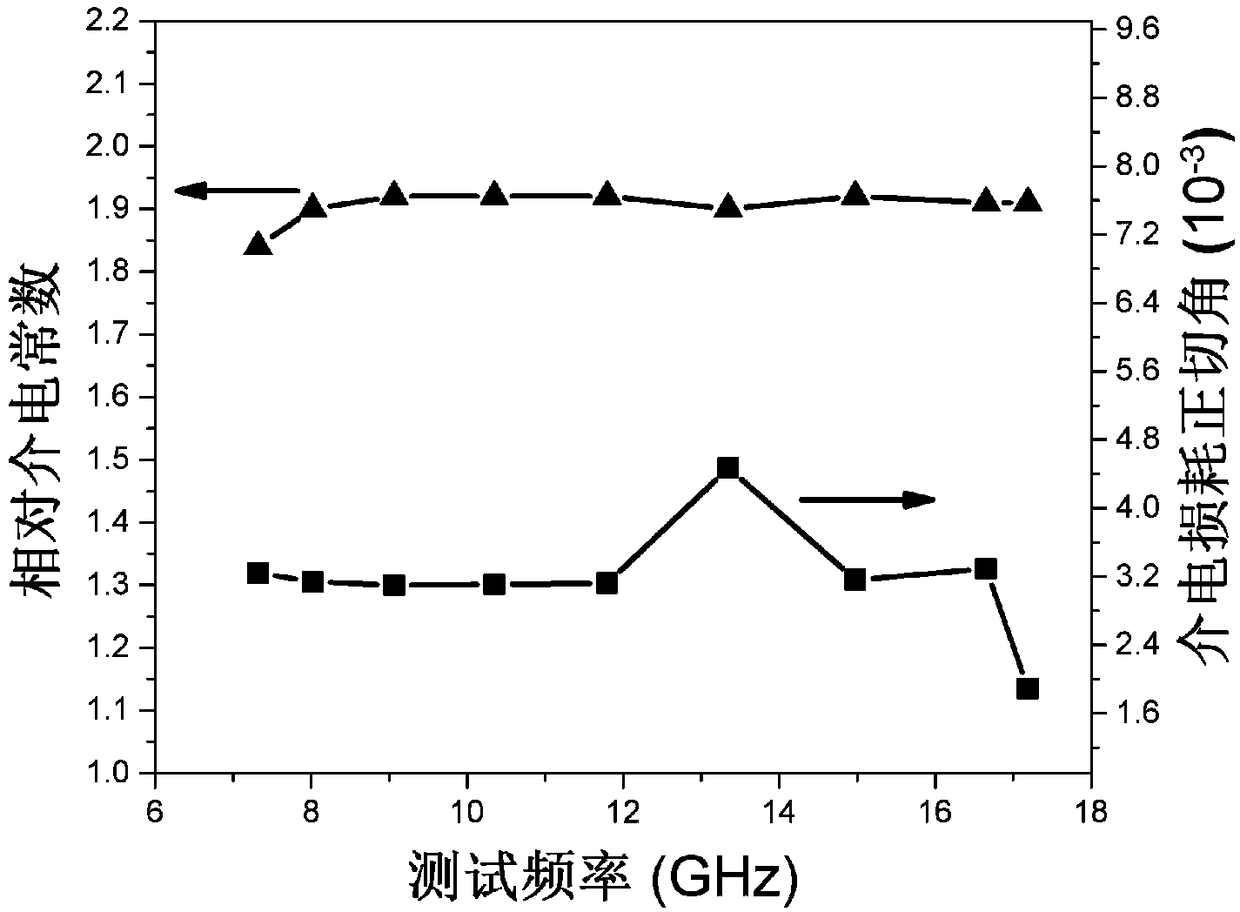
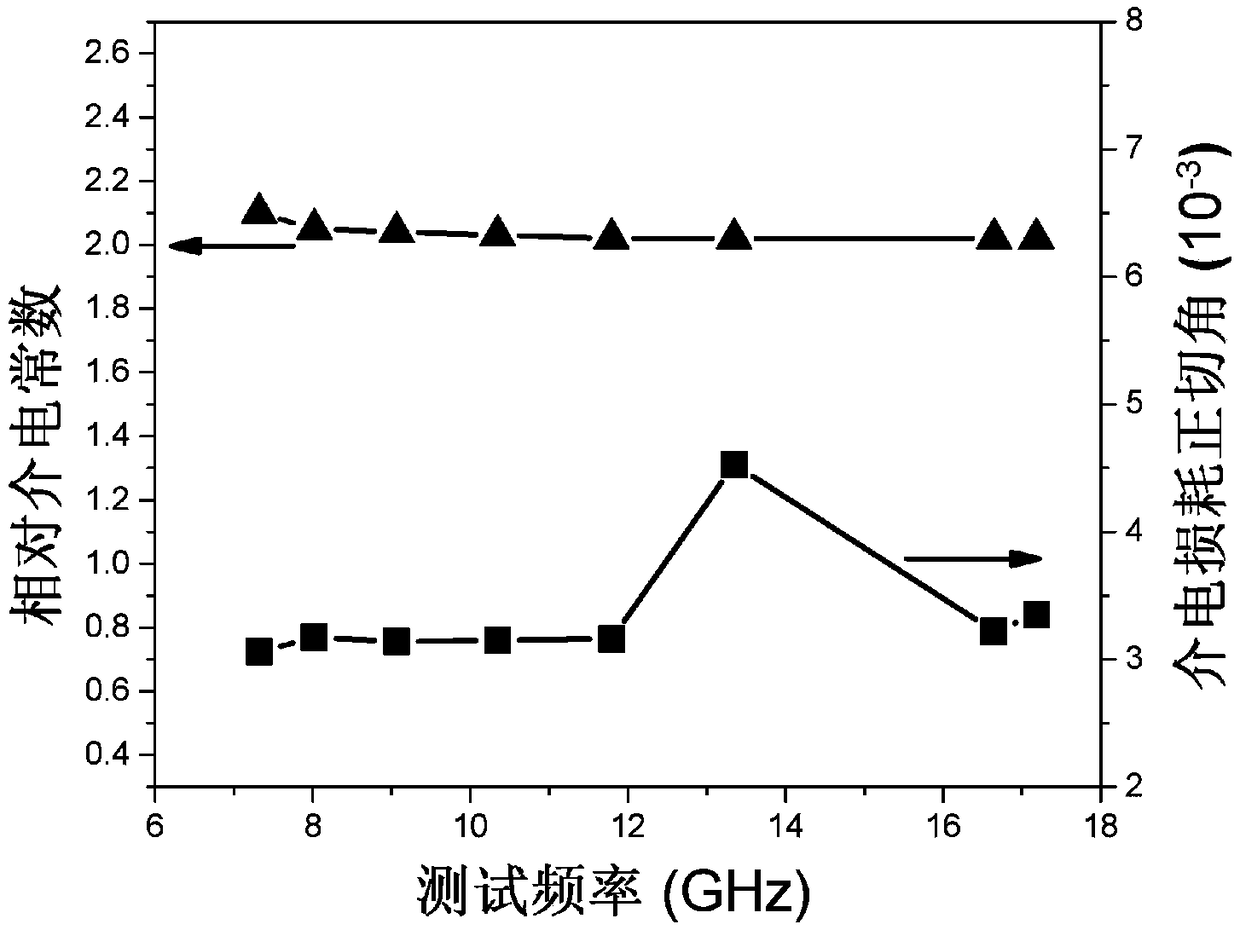
[0049] See image 3 ,
[0050] image 3 It is the dielectric constant and dielectric loss diagram of a high-temperature-resistant, heat-insulating, and wave-transmitting ceramic matrix composite material prepared in this example.
[0051] pass image 3 It can be seen that the average dielectric constant of a high-temperature-resistant, heat-insulating, and wave-transmitting ceramic matrix composite material prepared in this example is 2.02, and the dielectric loss tangent value is less than 5×10 -3 .
[0052] Therefore, in this embodiment, by adjusting the content of the pore-forming a...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the pore-forming agent in the second step is replaced by PMMA microspheres, and the mass ratio of the ceramic powder A to the pore-forming agent is 1:0.7, wherein the The average particle size of the pore-forming agent is less than 5 μm: and the third step is debinding and sintering in a muffle furnace. The process is replaced by heating up to 650 °C at a rate of 4 °C / min, holding for 2 hours, and then heating at 4 °C / min rate, the temperature was raised to 1200°C and kept for 2 hours to obtain porous mullite.
[0055] In this example, except that the type and content of the pore-forming agent are different, a composite material with lower thermal conductivity (0.11 W / m / K) is obtained by adopting a low sintering temperature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com