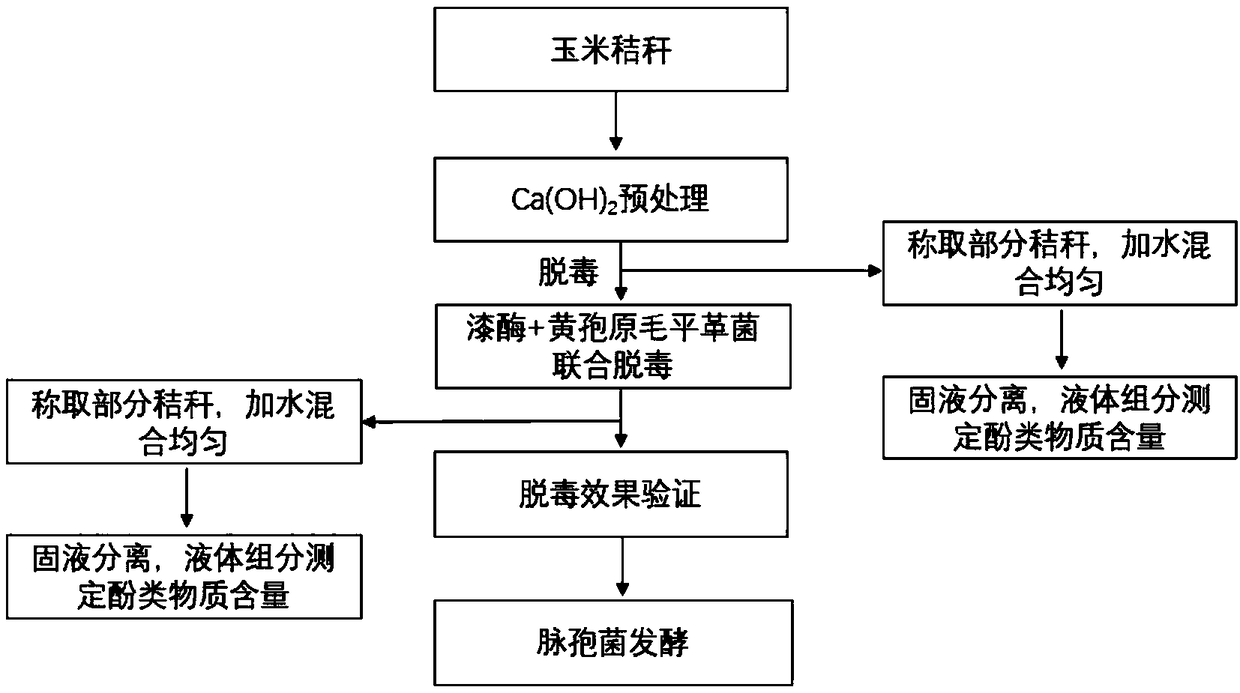
Pretreatment method of straw biological feed raw material
A straw biological feed and pretreatment technology, which is applied to the pretreatment of straw biological feed raw materials, the preparation of biological feed raw materials that produce true protein by fermentation, straw alkali treatment, and the field of biological detoxification, which can solve the problem that the extraction is not necessarily complete and the cost is high. , flammability and other issues, to achieve the effect of increasing nutritional value, low price, and reducing concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A pretreatment method for straw biological feed raw materials, the method comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) Crush: Crush the corn stalks into 0.1mm particles;
[0035] (2) Add Ca(OH) according to the mass ratio of straw to calcium hydroxide 10:1 (g:g) 2 , with a water content of 80%, stir well, and treat at 80°C for 2 hours. Weighed part of the semi-solid straw and dissolved it in water, extracted with dichloromethane to determine the phenolic substances in it, see the chromatographic peak diagram in the attached figure 2 , it can be seen from the figure that vanillin, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde and ferulic acid were released to a large extent after the straw was treated with alkali at 80°C.
[0036] (3) Adjust the pH of the straw mixture to 5.0;
[0037] (4) Cu in straw mixture 2+ The final concentration is 30mg / L, Mn 2+ The final concentration is 30mg / L, the amount of laccase added is 0.1%, the activity is 10000U / mL, the detoxification temperature of laccase ...
Embodiment 2
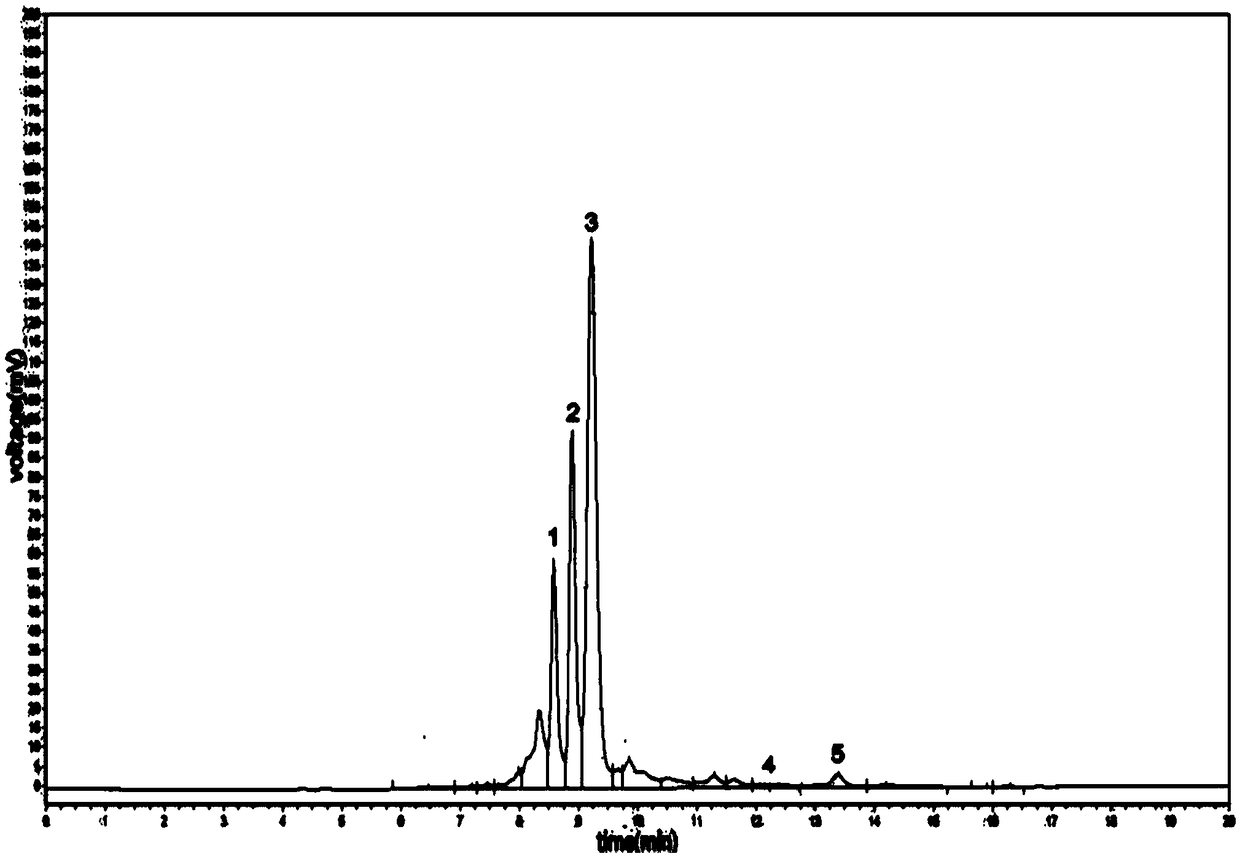
[0042] Using the same conditions as in Example 1, the detoxification time of Phanerochaete chrysosporium was extended to 36 hours during the detoxification process. After detoxification, the content of phenolic inhibitors was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The results showed that the degradation rates of vanillin, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, ferulic acid, 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol and salicylic acid were respectively 90.12%, 88.73%, 98.85%, 86.37%, 78.33%. The peak diagram of phenolic substances in the liquid components is shown in the appendix Figure 4 . It can be seen from the figure that vanillin, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde and ferulic acid have all been converted to a large extent, indicating that further extending the detoxification time of Phanerochaete chrysosporium can achieve a better detoxification effect.
[0043] The fungal fermentation conditions were the same as Example 1, and the true protein content increased by 2.64 times after Neurospora ferment...
Embodiment 3
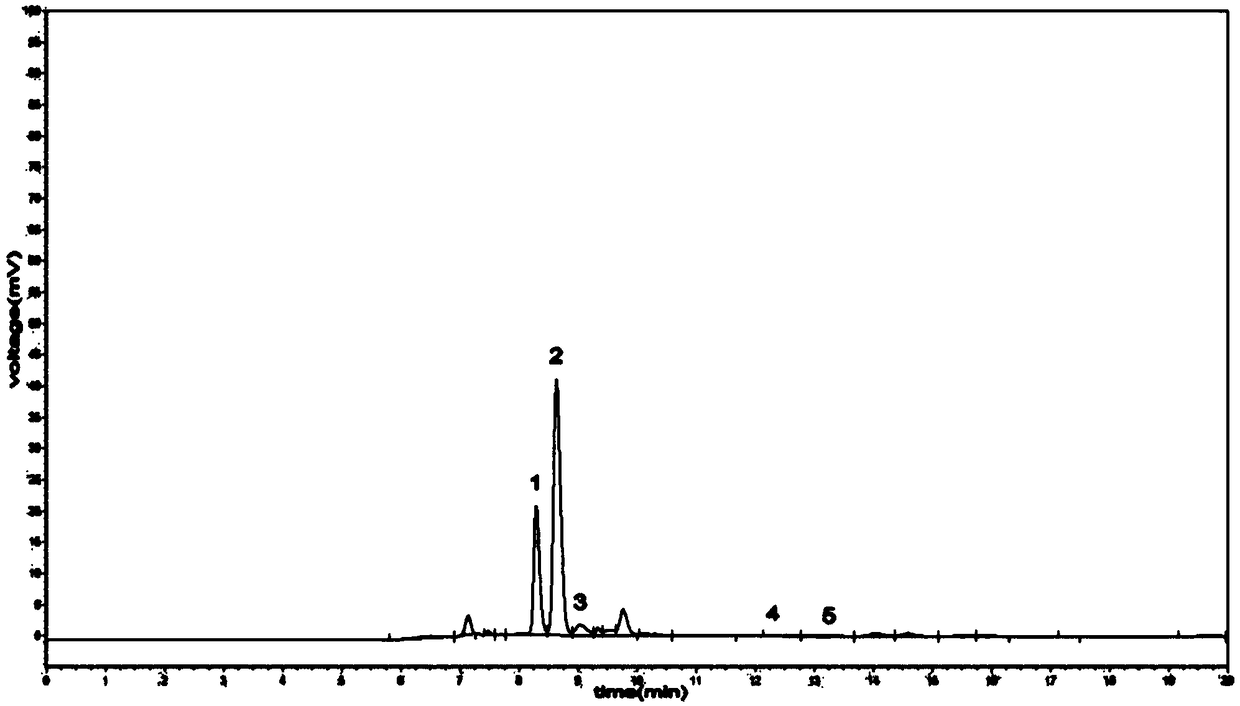
[0045] The same conditions as in Example 1 were adopted, but the sequential detoxification of laccase and Phanerochaete chrysosporium was changed to simultaneous detoxification for 24 hours. After detoxification, the content of phenolic inhibitors was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The results showed that the degradation rates of vanillin, p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, ferulic acid, 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol and salicylic acid were respectively 58.37%, 64.61%, 83.67%, 30.70%, 20.42%. The peak diagram of phenolic substances in the liquid components is shown in the appendix Figure 5 . It can be seen from the figure that the three main phenolic substances have been transformed to a greater extent; the detoxification of laccase and Phanerochaete chrysosporium has a certain synergistic effect.
[0046] The fungal fermentation conditions were the same as Example 1, and the true protein content increased by 1.93 times after Neurospora fermentation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com