Method for producing biosurfactant through strain fermentation
A biological surface and active agent technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as the loss of bacteria and nutrients, affect the conversion efficiency, and reduce the production of surfactants, and achieve the effects of reducing separation costs, simple fermentation methods, and increased product concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1 This example illustrates the rhamnolipid fermentation process in a conventional stirred fermenter.
[0016] Strain: Pseudomonas aeruginosa YM4.
[0017] Seed medium: xylose 15g / L; nitrogen source (sodium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, urea or yeast powder); KH 2 PO 4 4g / L; K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 4g / L; NaCl 1g / L; KCl 1g / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L; CaCl 2 0.1g / L.
[0018] Fermentation medium: soybean oil 30g / L; NaNO 3 6g / L; KH 2 PO 4 4g / L; K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 4g / L; NaCl 1g / L; KCl 1g / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L; CaCl 2 0.1g / L; trace elements 2.5mL / L (FeCl 3 0.16g / L; CuSO 4 0.15g / L; ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.5g / L; MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 1.5g / L).
[0019] Shake flask seed culture: Take a loop of bacteria from the slant medium, inoculate it into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed medium, and incubate in a shaking incubator at 37°C and 200rpm for 20h.
[0020] 5L fermenter culture: inoculate the seed culture solution in...
Embodiment 2
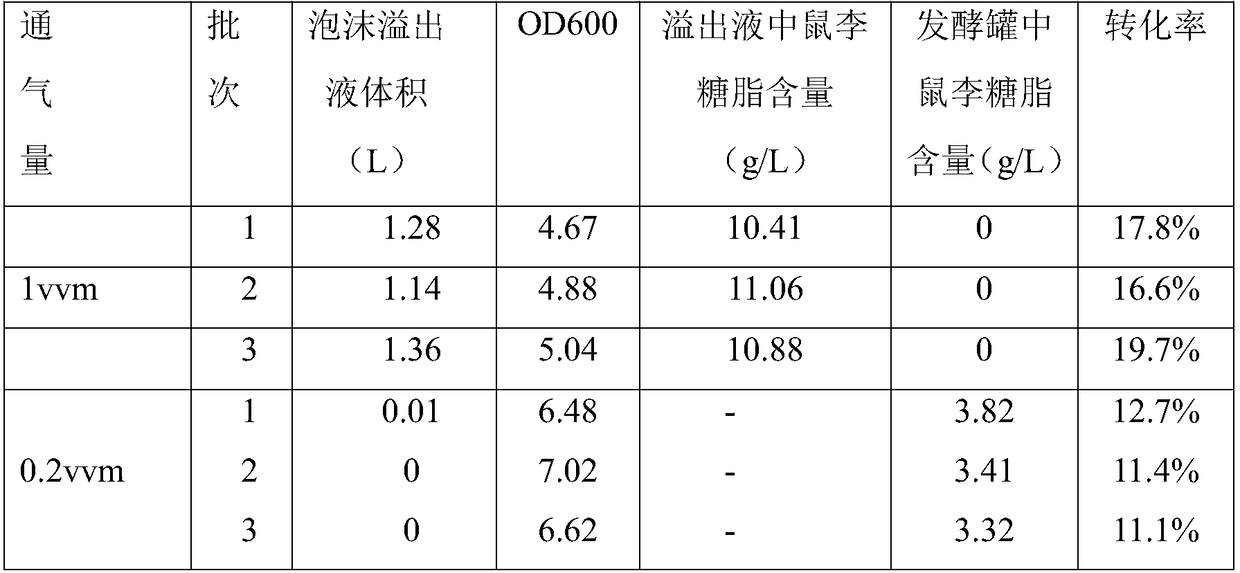
[0024] Example 2 This example illustrates the production of rhamnolipids by fermentation in a high-oxygen air medium.
[0025] Strain: Pseudomonas aeruginosa YM4.
[0026] Seed medium: xylose 15g / L; nitrogen source (sodium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, urea or yeast powder); KH 2 PO 4 4g / L; K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 4g / L; NaCl 1g / L; KCl 1g / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L; CaCl 2 0.1g / L.
[0027] Fermentation medium: soybean oil 30g / L; NaNO 3 6g / L; KH 2 PO 4 4g / L; K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 4g / L; NaCl 1g / L; KCl 1g / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L; CaCl 2 0.1g / L; trace elements 2.5mL / L (FeCl 3 0.16g / L; CuSO 4 0.15g / L; ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.5g / L; MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 1.5g / L).
[0028] Shake flask seed culture: Take a loop of bacteria from the slant medium, inoculate it into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed medium, and incubate in a shaking incubator at 37°C and 200rpm for 20h.
[0029] Gas medium with high concentration of oxygen: Use an oxyge...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 This example illustrates the use of foam separation to concentrate rhamnolipids in the late stage of bacterial strain fermentation to produce rhamnolipids
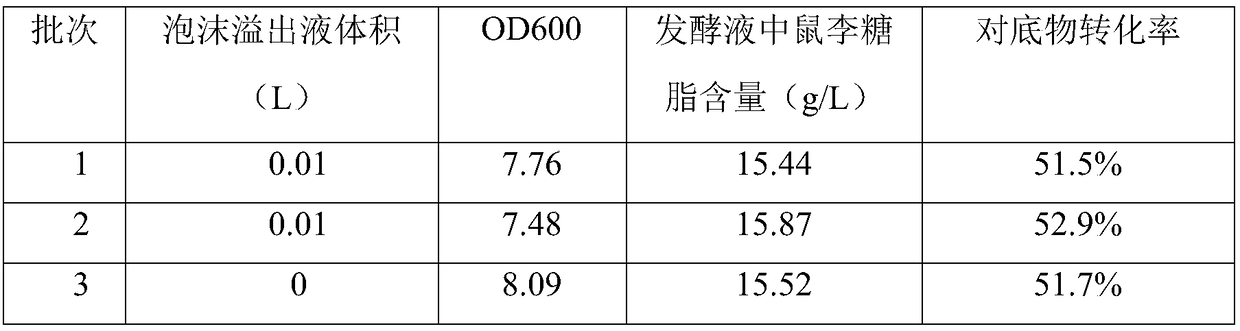
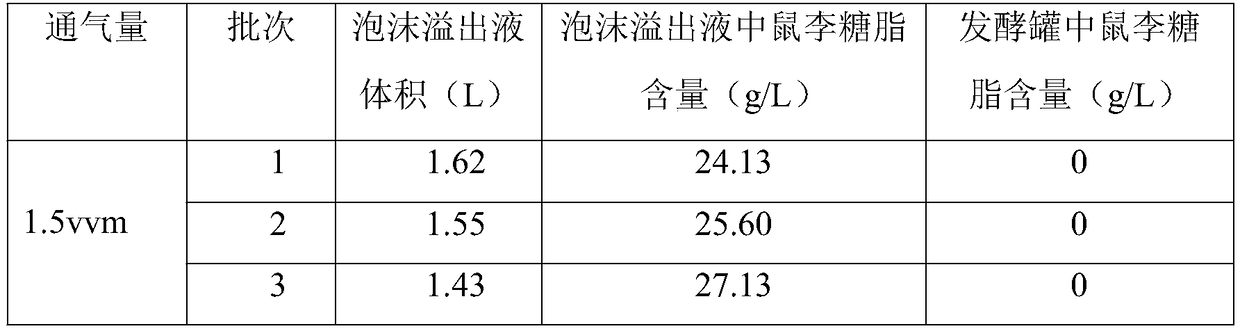
[0035] Replace the high-oxygen gas in the fermentation system fermented for 48 hours in Example 2 with ordinary air, connect a hose and a collection device to the exhaust port, adjust the ventilation to 1.5vvm, stir at 200rpm, and maintain for 1.5h-2h Until there is no more foam overflow at the vent of the fermenter, collect the foam overflow, measure the volume and analyze the rhamnolipid content. The results are shown in Table 3. Before the end of fermentation, ordinary air medium is used for foam separation. The rhamnolipid content in the foam overflow liquid reaches about 25g / L, and there is no more rhamnolipid in the raffinate in the fermenter, realizing the rhamnolipid separation. concentrate.
[0036] Table 3 uses foam separation technology to the concentration effect of rhamnolipid fermentation brot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com