Molecular marker method for detecting high oleic acid content of peanuts and application
A molecular marker, high oleic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of limiting the wide and efficient application of new high-oleic acid peanut mutants, avoid phenotypic identification, Improve breeding efficiency and avoid time-consuming and labor-intensive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Example 1, Peanut high oleic acid-related CAPS marker primer design and PCR amplification to obtain homologous gene fragments
[0059] 1.1 Sequence analysis and specific primer design of homologous genes AhFAD2A and FAD2B related to oleic acid content in peanut seeds
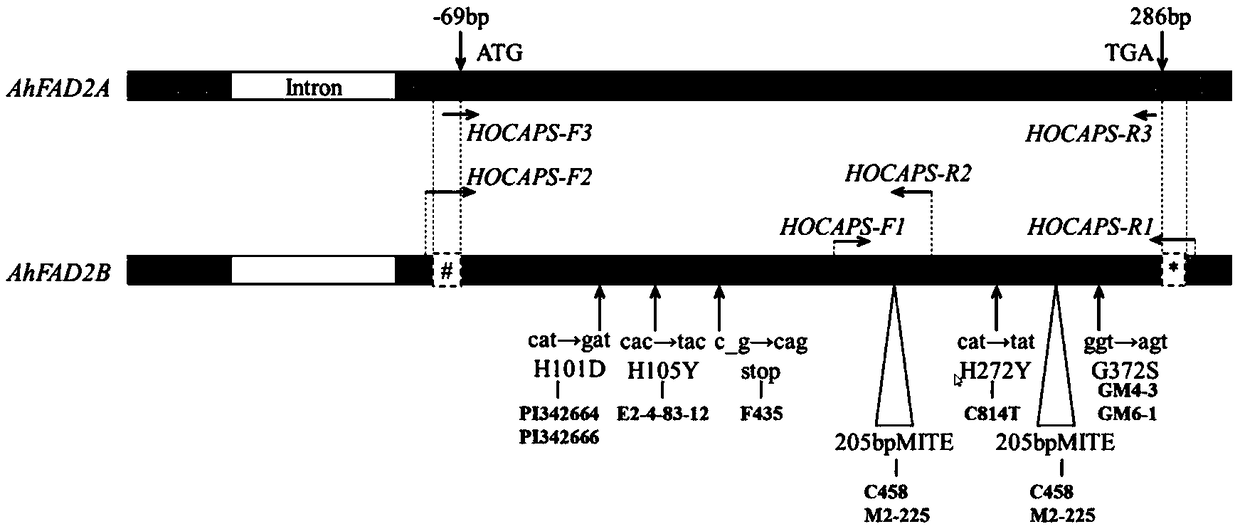
[0060] The sequence information of the peanut AhFAD2 gene was retrieved from the NCBI database (National Center for Biotechnology Information, https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ), and the obtained sequences were compared and analyzed using GeneiousPro R11 software, and it was found that these sequences Clearly divided into 2 categories, namely AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B. The nucleotide sequences of the two types of genes are highly similar, but there are multiple SNP difference sites in the coding region, and there are also obvious sequence differences at the 5' and 3' ends, such as figure 1 As shown, the AhFAD2B gene has a 19 bp missing base sequence at 69 bp upstream of the start codon and a 15 bp missing base seq...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment 2, enzyme digestion analysis of mutation site
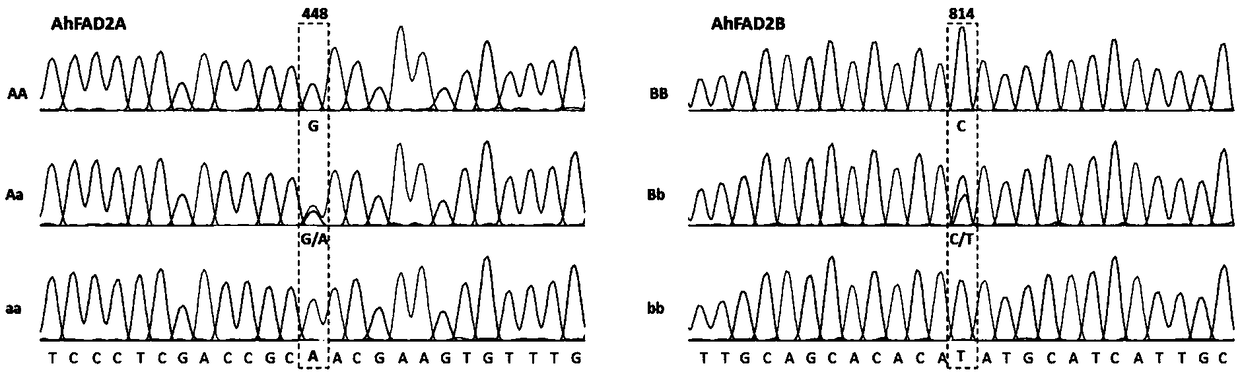
[0090]Find the appropriate endonuclease for the wild type or mutant genotype at the mutation site. It was found that two different enzyme cutting strategies can be adopted for different mutation sites, that is, the C814T and G1111A mutations can find suitable restriction enzymes at the mutation site of the mutant genotype, and the expected result will be that of the wild-type single plant. The amplified product cannot be digested by enzymes, and the amplified product of a mutant individual plant can be digested by enzymes, while the heterozygous genotype presents two band patterns; C301G and C313T mutations can find suitable endonucleases at the mutation site of the wild genotype Enzyme, the expected result is that the amplified product of the wild-type individual plant can be digested, the amplified product of the mutant individual plant cannot be digested, and the heterozygous genotype presents two band patter...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Example 3: Application of CAPS markers in genotype identification of individual plants of high oleic peanut breeding progeny population
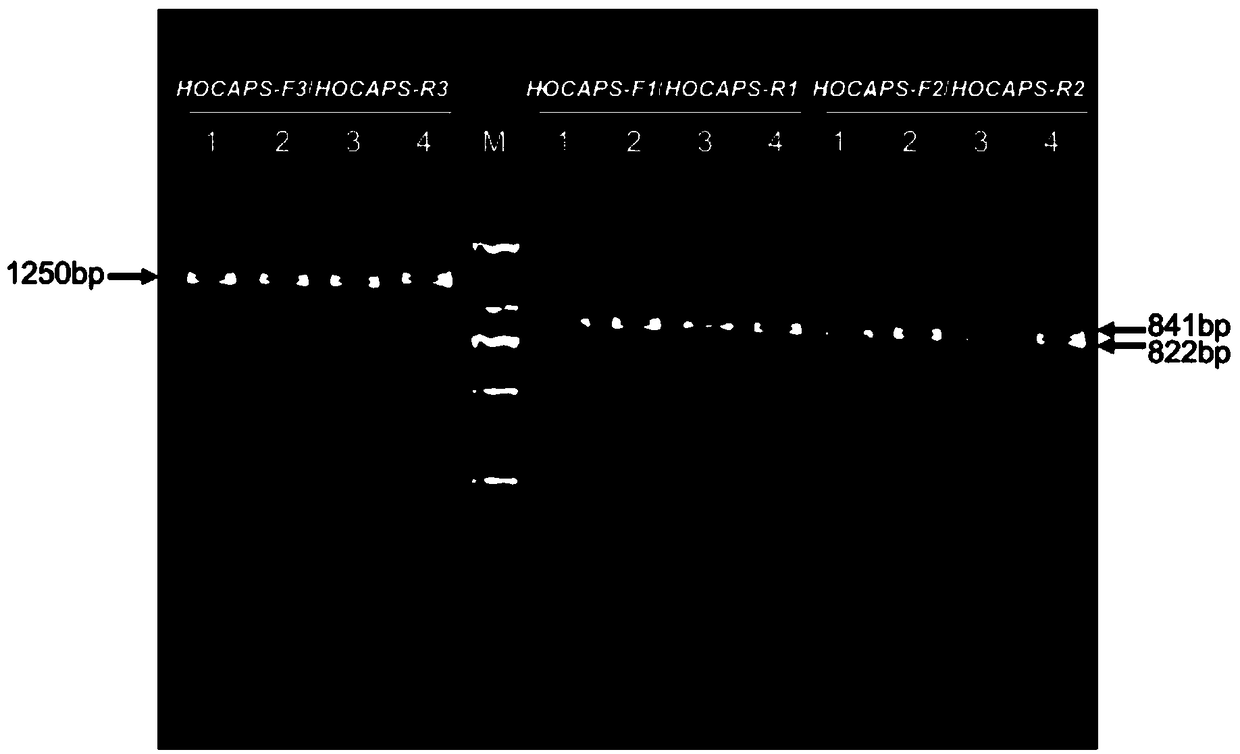
[0097] The research materials are 200 F2 single plants of the hybrid progeny of "Jihua No. 6 × C814T" selected randomly. NdeI endonuclease, and the primer pair HOCAPS-F3 / HOCAPS-R3 and Hpy99I endonuclease constituted the CPAS marker system respectively, using the above-mentioned F2 generation single plant genomic DNA as a template for specific PCR amplification, followed by enzyme digestion reaction to obtain bands After genotyping, single-plant genotype analysis and judgment were carried out. The technical parameters and methods used were all carried out in accordance with the above-mentioned operations.
[0098] The results are shown in Table 2, the mutation sites of the AhFAD2A or AhFAD2B genes in the F2 population genetic law alone present a segregation ratio of 1:2:1, which is in line with the Mendelian single gene inheritance law...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com