Method for preparing biological-bacteria fertilizer by utilizing tobacco leaf residues
A technology of residue and tobacco leaves, which is used in the preparation of compound biological bacterial fertilizer and the comprehensive utilization of waste tobacco leaf residues, can solve the problem of unclear changes in microbial interactions, species and bacterial species, and it is difficult to effectively control the number and proportion of bacterial species. , complex formula and other problems, to achieve the effect of a wide range of cheap raw materials, low price, good sensory smell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Preparation of microbial seed solution
[0049] (1) Take 1 mL of Bacillus subtilis cultured in LB medium for 20 hours and inoculate it into 100 mL of Bacillus subtilis seed culture medium for expansion culture, 200 r / min, 37 ° C shaker culture for 20 hours, OD 620 When it reaches 4-6, it is Bacillus subtilis seed liquid.
[0050] (2) Take 1 mL of Bacillus colioids cultured in LB medium for 20 hours and inoculate it into 100 mL of Bacillus colioids seed culture medium for expansion culture, 200 r / min, 30 °C shaker culture for 20 hours, OD 620 When it reaches 4-6, it is the seed liquid of Bacillus colloidus.
[0051] (3) Take 1 mL of Paecilomyces lilacinus cultured in PDA medium for 20 hours and inoculate it into 100 mL of Paecilomyces lilacinus seed culture medium for expanded culture, and culture it on a shaker at 200 r / min at 30 °C for 20 hours, OD 620 When it reaches 4-6, it is the seed liquid of Paecilomyces lilacinus.
[0052] (4) The three kinds of seed solution...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Effect of Tobacco Leaf Raw Material on Bacterial Growth
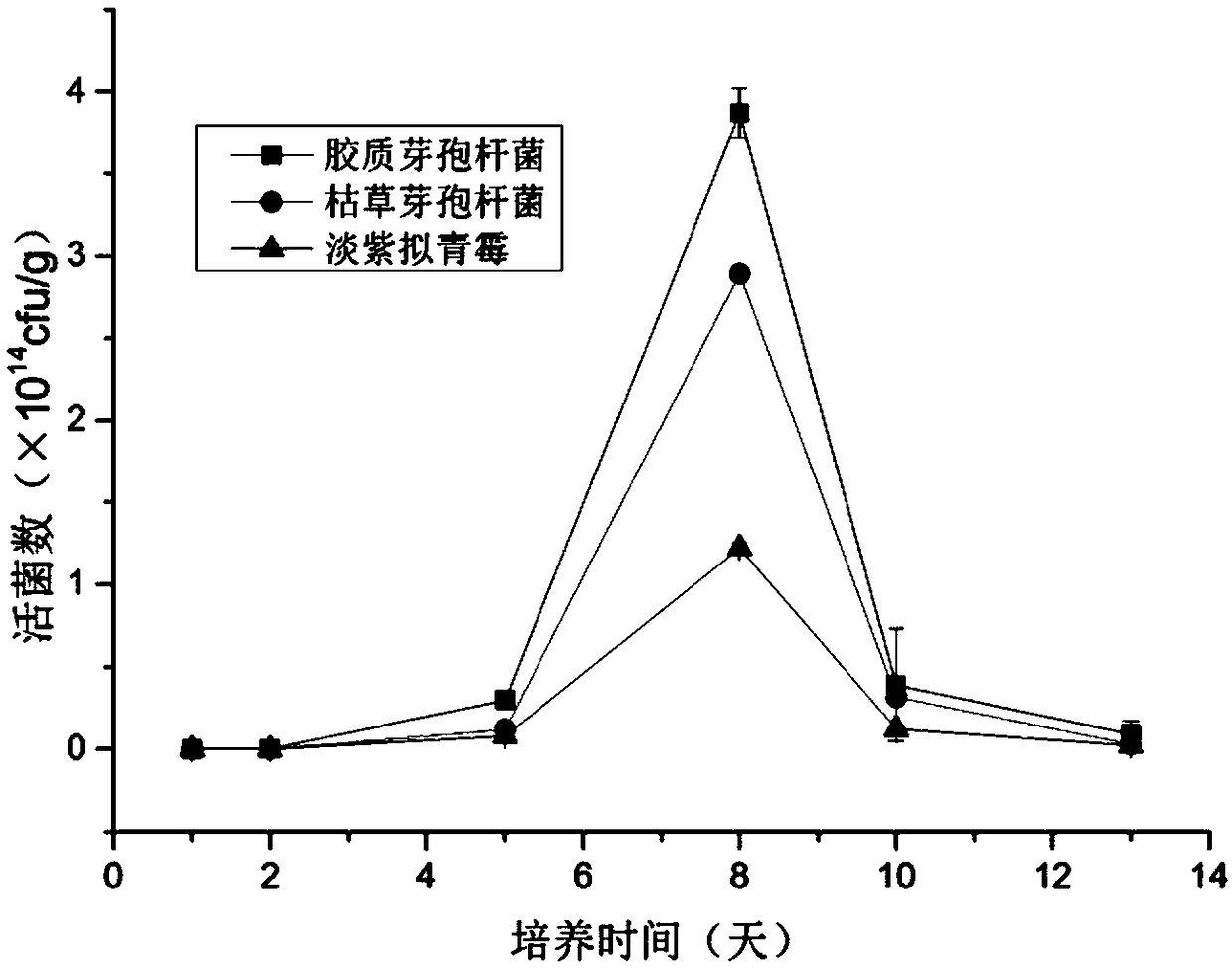
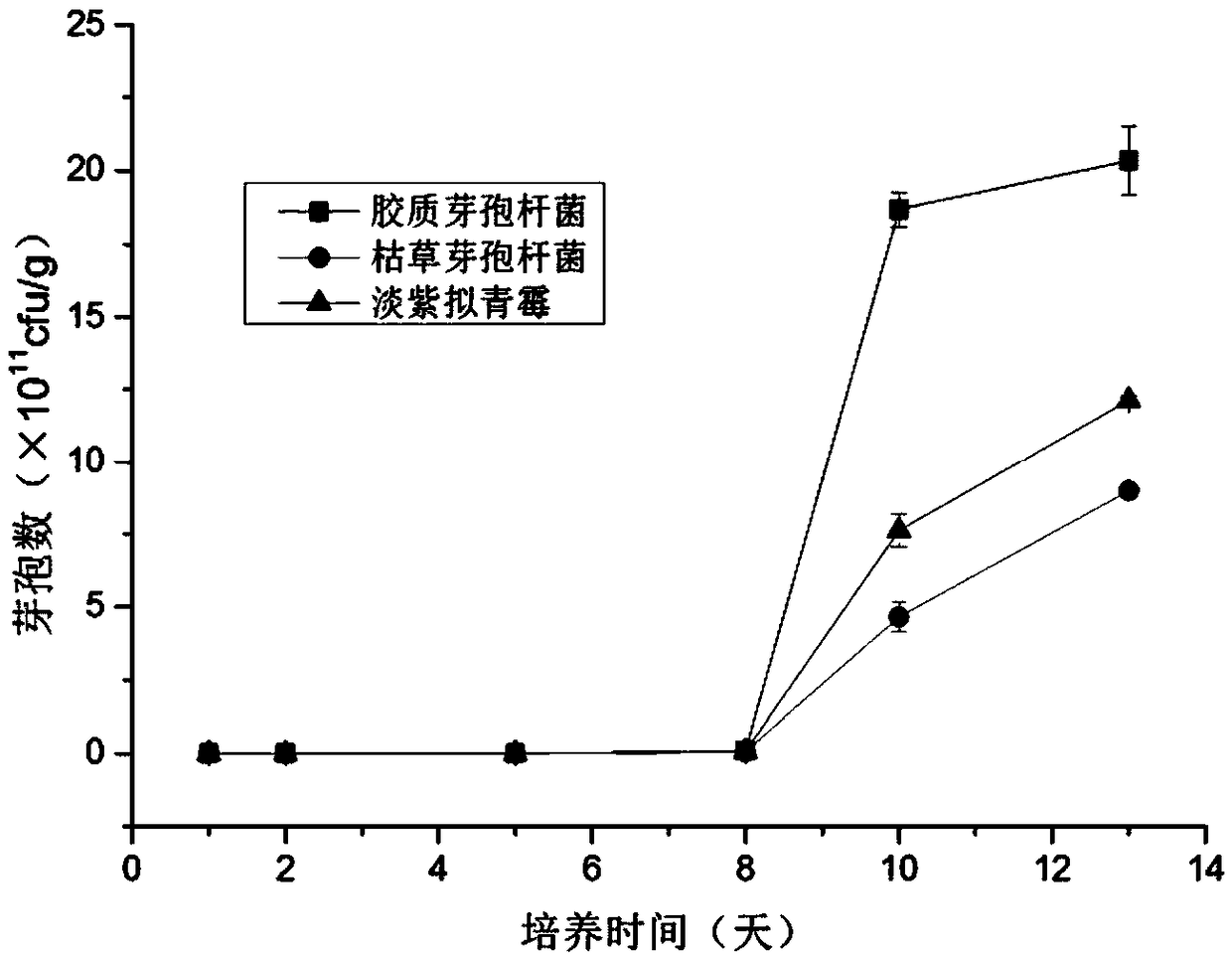
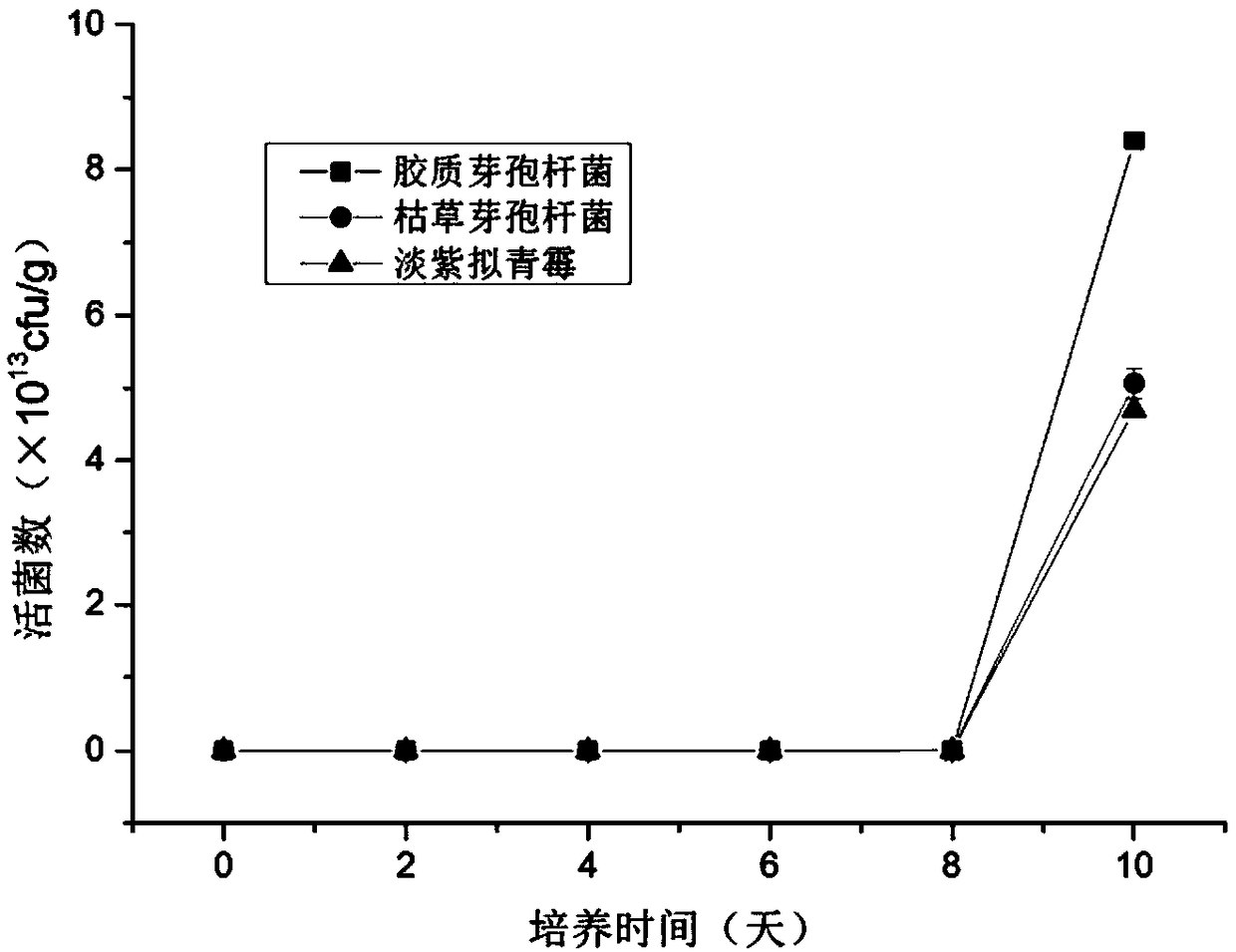
[0055] (1) Take 60g of dried tobacco leaf residue and mix them in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask according to the solid-liquid ratio of residue to water of 1:1.8 (mass ratio) to prepare tobacco leaf culture medium. Insert the Bacillus subtilis seed solution with a total mass of 10%, put it in a 37°C incubator and culture it for 4 days, and turn the material every 48 hours. The number of viable bacteria and the number of spores were counted on the plate culture. The number of viable bacteria and the number of spores were 2.5×10 13 cfu / g and 5×10 10 cfu / g.
[0056] (2) Grinding the untreated dried tobacco leaves as the raw material of the tobacco leaf culture medium, and carrying out the fermentation of Bacillus subtilis according to the above method (1). The culture time was 5 days and 7 days, and the number of viable bacteria obtained was 2.15×10 8 cfu / g and 6.37×10 8 cfu / g, the number of spores were 4.68×10 8 c...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Comparison of single-strain culture and compound-strain culture
[0060] (1) Put 35g of dried tobacco leaf residue and 49mL of water into a 250mL narrow-necked Erlenmeyer flask, and sterilize at 115°C for 20min. Insert the Bacillus subtilis seed solution with a total mass of 10%, and culture it statically in a 30°C incubator, and turn the material once every 48h. Both the number of viable bacteria and the number of spores reached the maximum on the 10th day, and the number of viable bacteria was 7×10 13 cfu / g, the number of spores is 1.5×10 13 cfu / g.
[0061] (2) Put 35 g of dried tobacco leaf residue and 49 mL of water into a 250 mL conical flask, and sterilize at 115° C. for 20 min. Insert 10% of the total mass of Bacillus colioids seed liquid, culture it statically in a 30°C incubator, and turn the material every 48 hours. Both the number of viable bacteria and the number of spores reached the maximum on the 12th day, and the number of viable bacteria was 2×10 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com