Uric acid-lowering molecules and screening method and application thereof
A technology for reducing uric acid and molecules, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of lack of immune effector Fc segment structure, small molecular weight, etc., and achieve the effects of easy to expand production, small molecular weight, and strong penetrating power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Construction of Random Mutation Library
[0053] By self-design, artificially synthesized oligonucleotide fragments encoding random cyclic octapeptides, and amplifying the gene fragments encoding random cyclic octapeptides by extending primers; passing the coding gene fragments and M13KE phage vector through EagI and KpnI restriction endonucleases Ligation was performed after double enzyme digestion, and the recombinant product was electrotransformed into Escherichia coli ER2738 competent cells to obtain a phage display random cyclic octapeptide library, and the capacity and diversity of the library were detected by plaque and sequencing;
[0054] The oligonucleotide fragments include;
[0055] 5'-GCT TGT (NNK) 8 TGC GGT GGA GGT-3′ positive strand
[0056] That is, SEQ ID NO.3: GCT TGT NNK NNK NNK NNK NNK NNK NNK NNK NNK TGC GGT GGA GGT
[0057] 3’-CGA ACA(NNM) 8 ACG CCA CCT CCA-5′ negative strand
[0058] That is, SEQ ID NO.4: CGA ACA NNM NNM NNM NNM NNM...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 Screening of Random Mutation Library
[0063] The uric acid molecule is coupled with BSA, and the coupled uric acid molecule is used as the target molecule. Based on the principle of affinity adsorption, the phage mutant library is subjected to multiple rounds of "adsorption-elution-amplification" with a support ELISA plate. Enrich and amplify phages with specific binding activity to target molecules.
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3 identifies the phage obtained by screening
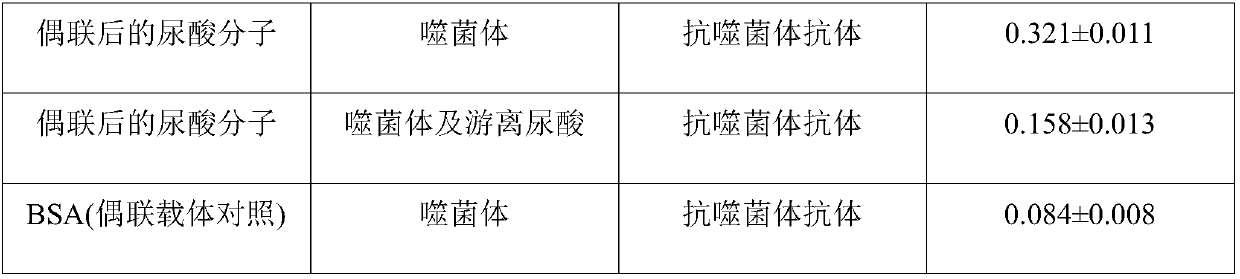
[0065] The phages that can specifically bind uric acid were identified by ELISA and competition ELISA, and the results are shown in Table 1;
[0066] Table 1
[0067]
[0068]
[0069] It can be seen from Table 1 that the screened phages have good binding ability to the coupled uric acid molecules.
[0070] The screened phages were sequenced by sequencing method, and the obtained coding nucleotide sequence and corresponding amino acid sequence were as follows:
[0071] SEQ ID NO.2: GCT TGT CCT TCT ACT ACT CTT ATT TTT GCT ACT TGC GGT GGA GGTTCG (nucleotide sequence)
[0072] SEQ ID NO.1: ACPSTLIFATCGGGS. (amino acid sequence)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com