Chip and kit for detecting non-deletion alpha-thalassemia
A thalassemia, non-deletion technology, applied in the field of alpha thalassemia kits, can solve the problems of tedious DNA extraction and easy cross-contamination, and achieve the effects of saving manpower and reagent costs, reducing pollution, and shortening detection time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
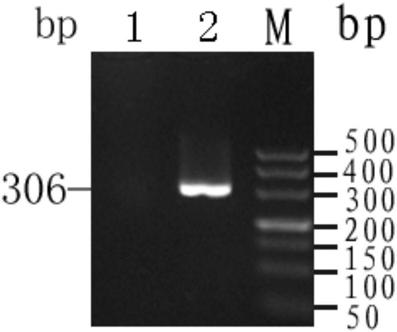
[0069] Embodiment 1: Using the kit specimen source and PCR template type of the present invention
[0070] 1.1 Sample collection and preparation of PCR templates: a) Sample collection: Specimens are derived from anticoagulated peripheral blood, DBS samples, embryonic villus tissue, amniotic fluid, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood, etc.; b) Preparation of PCR templates: The above samples are directly used as templates , DNA extracted from the above-mentioned specimens can also be used as a template.
[0071] 1.2 DBS sample preparation
[0072] The above 1.1 filter paper dry blood spot sample (DBS) collection and preparation are as follows:
[0073] ①. Use Whatman903 filter paper (or ordinary filter paper). Mark the subject number and date of collection on the filter paper.
[0074] ② Both peripheral blood and anticoagulated blood can be used to make dried blood spot samples on filter paper. If a filter paper disc dried blood spot is prepared from peripheral blood, t...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2. Design of specific primers for PCR amplification and determination of PCR reaction system
[0077] 1.1 Primer design
[0078] The α-globin gene sequence was obtained from the GenBank database, and a pair of primers were designed according to the point mutation of the α-thalassemia gene for PCR amplification of the α-thalassemia gene. Primers were synthesized by a professional biological company. Primer sequences are listed in Table 1.
[0079] Table 1 Detection of non-deleted α-thalassemia gene primers and specific oligonucleotide probe sets
[0080]
[0081]
[0082] 1.2 Determination of multiplex PCR reaction system
[0083] Using the orthogonal test method, through a large number of experimental comparisons, the optimal PCR reaction solution formula and system are finally determined as shown in Table 2: PCR reaction solution 18 μ l, peripheral blood (chilli, amniotic fluid or umbilical cord blood) sample volume 2μl, 1-3 pieces of DBS samples (dia...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: Design, spotting and immobilization of oligonucleotide probes
[0090] 1. Probe design and screening
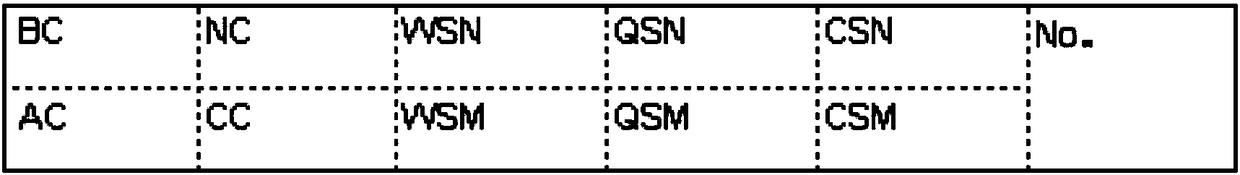
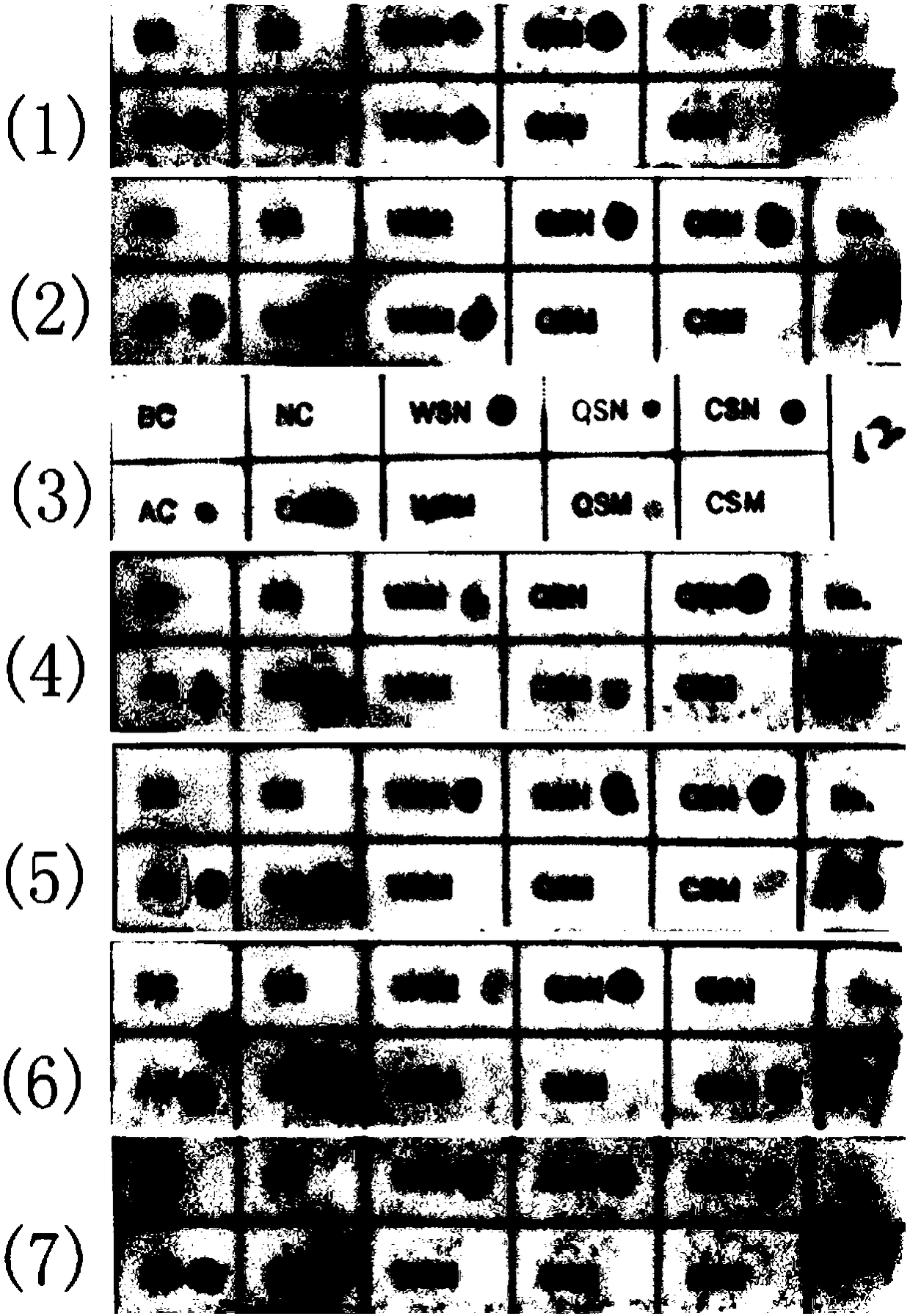
[0091] The α-globin gene sequence was obtained from the GenBank database, and three pairs of mutants (α CS α, α QS α, α WS α) Corresponding probes, design an oligonucleotide probe combination that specifically recognizes a certain genotype; and design negative (NC), positive (AC), chromogenic control probes (CC) (see Table 1) and blank Control (BC). Synthesized by a professional biological company.
[0092] 3.2. Preparation of gene chip.
[0093] The preparation method of the gene chip of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0094] (1) Preparation of the working solution of the oligonucleotide probe: use the probe diluent (0.5M Na 2 CO 3 and 0.5M NaHCO 3 solution) were mixed and diluted into a working solution (10 μM) for sample application.
[0095] (2) Immobilizing the probe: the nylon membrane was activated by soaking in 10% ED...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com