High-strength and heat-resistant concrete
A heat-resistant concrete and high-strength technology, which is applied in the field of concrete, can solve problems such as the decrease of compressive strength, the increase of temperature variation and deformation difference between aggregate and cement slurry, etc., so as to improve the early strength, reduce the material shrinkage rate, improve and easy The effect of fluidity and self-resisting strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
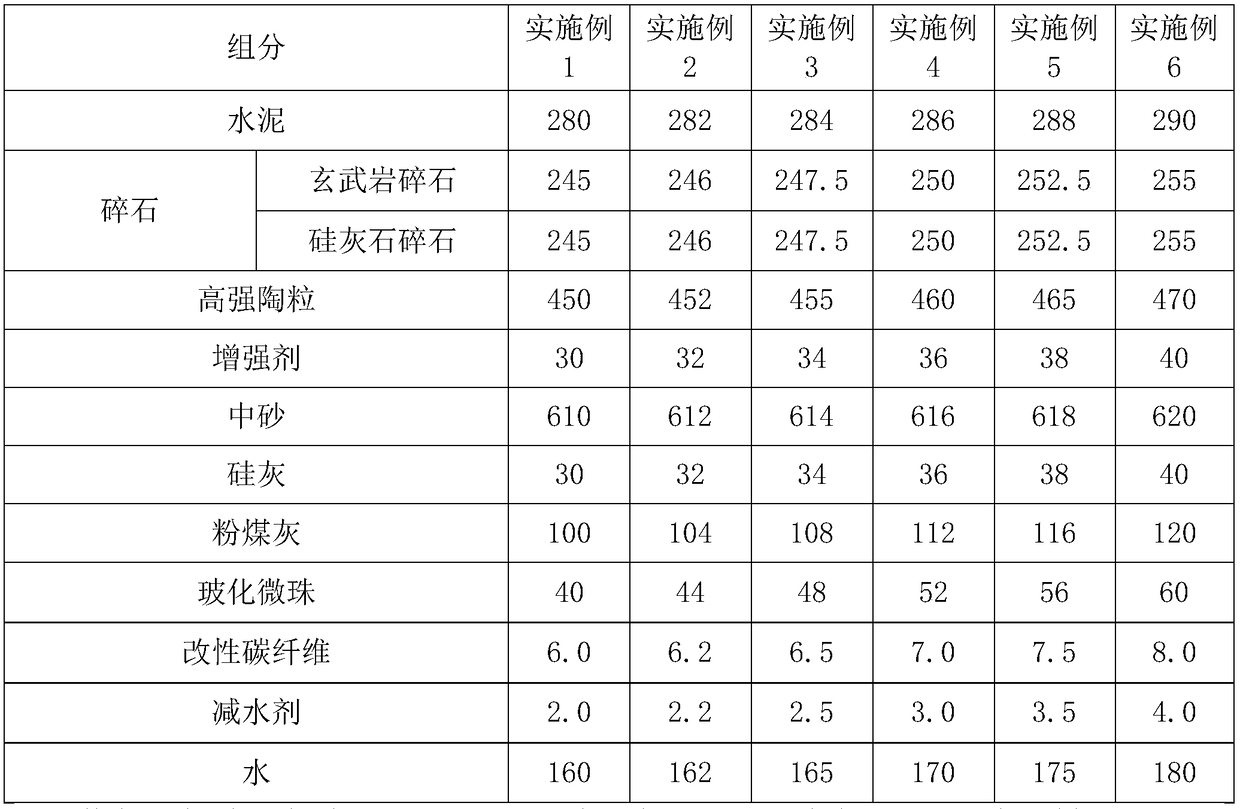
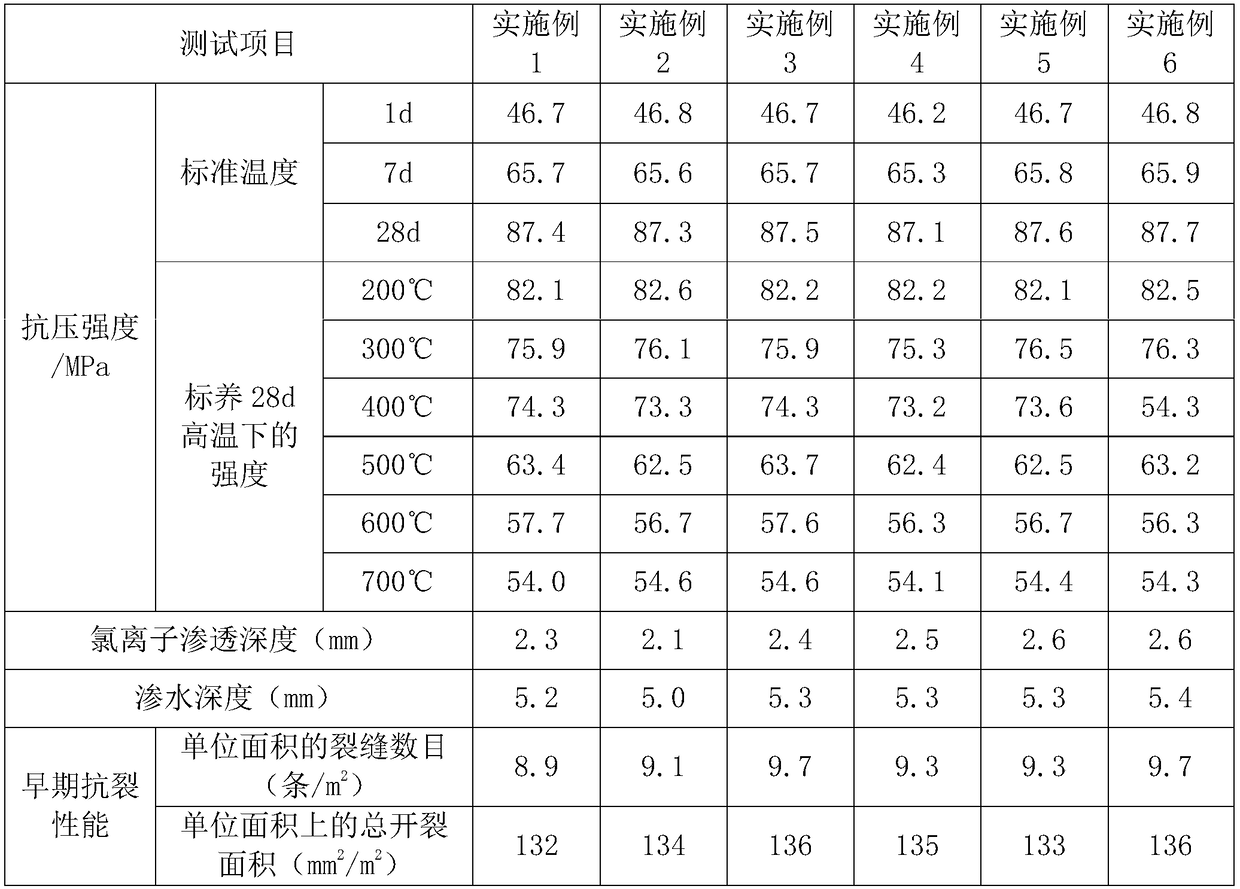
Examples
preparation example 1
[0052] Preparation example 1: Modified carbon fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0053] (1) Dispersion treatment: Soak the carbon fiber in acetone for 60 minutes, then clean it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 60 minutes, and dry it in a vacuum oven for 3 hours;
[0054] (2) Radiation grafting: After immersing the carbon fibers in step (1) in N-methylolacrylamide solution for 4 hours, carry out plasma treatment under the condition of an inert atmosphere and a pressure of 45 Pa, and the treatment time is 30 minutes;
[0055] (3) Post-treatment: wash the carbon fiber in step (2) three times with dichloromethane, and dry for 2 hours to obtain the modified carbon fiber.
preparation example 2
[0056] Preparation example 2: Modified carbon fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0057] (1) Dispersion treatment: Soak the carbon fiber in acetone for 75 minutes, then clean it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 50 minutes, and dry it in a vacuum oven for 3.5 hours;
[0058] (2) Radiation grafting: After soaking the carbon fibers in step (1) in N-methylolacrylamide solution and methacrylic acid solution for 4.5h, plasma treatment was carried out under the condition of an inert atmosphere and a pressure of 45Pa. The time is 25 minutes;
[0059] (3) Post-treatment: wash the carbon fiber in step (2) four times with dichloromethane, and dry for 2.5 hours to obtain the modified carbon fiber.
preparation example 3
[0060] Preparation example 3: Modified carbon fiber is prepared by the following method:
[0061] (1) Dispersion treatment: soak the carbon fiber in acetone for 90 minutes, then clean it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 40 minutes, and dry it in a vacuum oven for 3 hours;
[0062] (2) Radiation grafting: After soaking the carbon fiber in step (1) in N-methylolacrylamide solution and methacrylic acid solution for 5h, plasma treatment was carried out under the condition of an inert atmosphere and a pressure of 45Pa. 30min;
[0063] (3) Post-treatment: the carbon fiber in step (2) was washed 5 times with dichloromethane, and dried for 3 hours to obtain the modified carbon fiber.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com