Preparation method of hydroxyapatite/modified polylactic acid composite microspheres
A technology of hydroxyapatite and composite microspheres, which is applied in pharmaceutical formulations, microcapsules, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of easy agglomeration of hydroxyapatite particles and uneven performance of composite materials, and achieves improved hydrophilicity, Improved biological activity and good interface compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
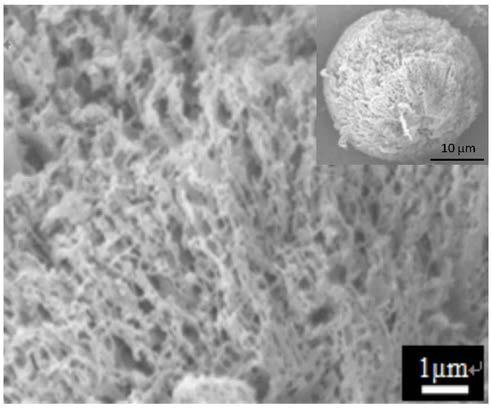
[0017] Polylactic acid was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane solvent at 60 °C to prepare 20 g of a 1.0 wt% homogeneous solution, and a 1.2% mass percent ethylenediamine aqueous solution was added, and 40 g of glycerin, stirred evenly to form a stable emulsion. The emulsified system was placed in a refrigerator at -15°C for 4 h to solidify the polylactic acid droplets into microspheres. After filtering, washing and freeze-drying, the modified polylactic acid microspheres with amino active groups were obtained. The shape of the microspheres was The appearance and structure are as shown in the accompanying drawings of the description figure 1 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the obtained microspheres are round in shape, about 30 μm in size, and have a uniform and fine network nanofiber structure.
[0018] The concentration in 10 mL is 1.0 mol·L -1 Ca(NO 3 ) 2 20 mg of amino-modified polylactic acid nanofiber microspheres were put into the solution, and the mixed system of t...
Embodiment 2
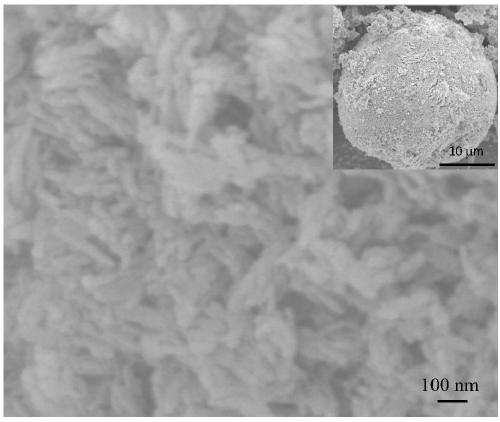
[0020] Dissolve polylactic acid in 1,4-dioxane solvent at 70 °C to prepare 20 g of 1.5 wt% homogeneous solution, add ethylenediamine aqueous solution with a mass percentage of 1.5%, react for 30 min, and then add 60 g of glycerin, stirred evenly to form a stable emulsion. The emulsified system was placed in a refrigerator at -15°C for 4 h to solidify the polylactic acid droplets into microspheres. After filtering, washing and freeze-drying, the modified polylactic acid microspheres with amino active groups were obtained. Microspheres were observed by scanning electron microscope. The balls have a network of nanofiber structures.
[0021] The concentration in 10 mL is 1.5 mol·L -1 Ca(NO 3 ) 2 20 mg of amino-modified polylactic acid nanofiber microspheres were put into the solution, and the mixed system of the microspheres and the solution was placed in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 37 °C for oscillating adsorption for 4 days, and then filtered and separated. T...
Embodiment 3
[0023] Dissolve polylactic acid in 1,4-dioxane solvent at 60 °C to prepare 20 g of 0.5 wt% homogeneous solution, add ethylenediamine aqueous solution with a mass percentage of 1.0 %, react for 30 min, and then add 40 g of glycerin, stirred evenly to form a stable emulsion. The emulsified system was placed in a refrigerator at -15°C for 4 h to solidify the polylactic acid droplets into microspheres. After filtering, washing and freeze-drying, the modified polylactic acid microspheres with amino active groups were obtained. Microspheres were observed by scanning electron microscope. The balls have a network of nanofiber structures.
[0024] 0.5 mol·L in 10 mL -1 Ca(NO 3 ) 2 20 mg of amino-modified polylactic acid nanofiber microspheres were put into the solution, and the mixed system of the microspheres and the solution was placed in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 37 °C for oscillating adsorption for 5 days, and then filtered and separated. The concentration of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com