Macrostructure and microstructure controllable hydroxyapatite porous ceramic, preparation method thereof and application of ceramic
A technology of hydroxyapatite and porous ceramics, used in ceramic products, applications, other household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of inability to intervene and design the internal microstructure of deposited materials, and difficult to meet the control and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
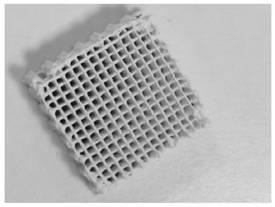
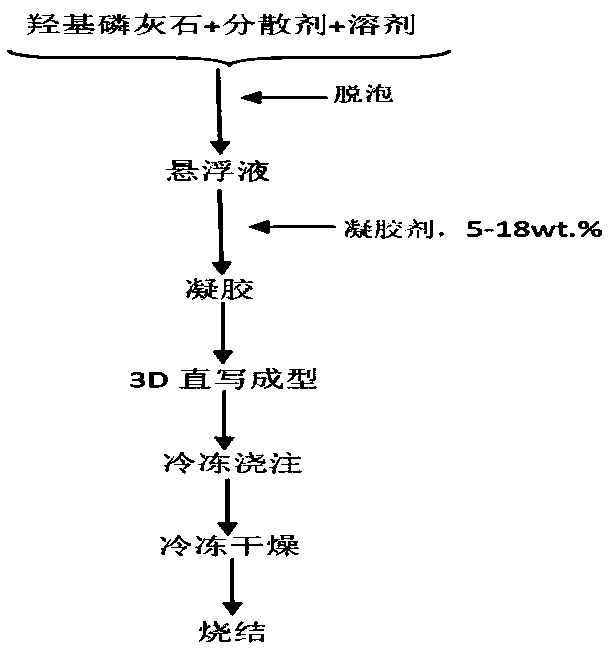
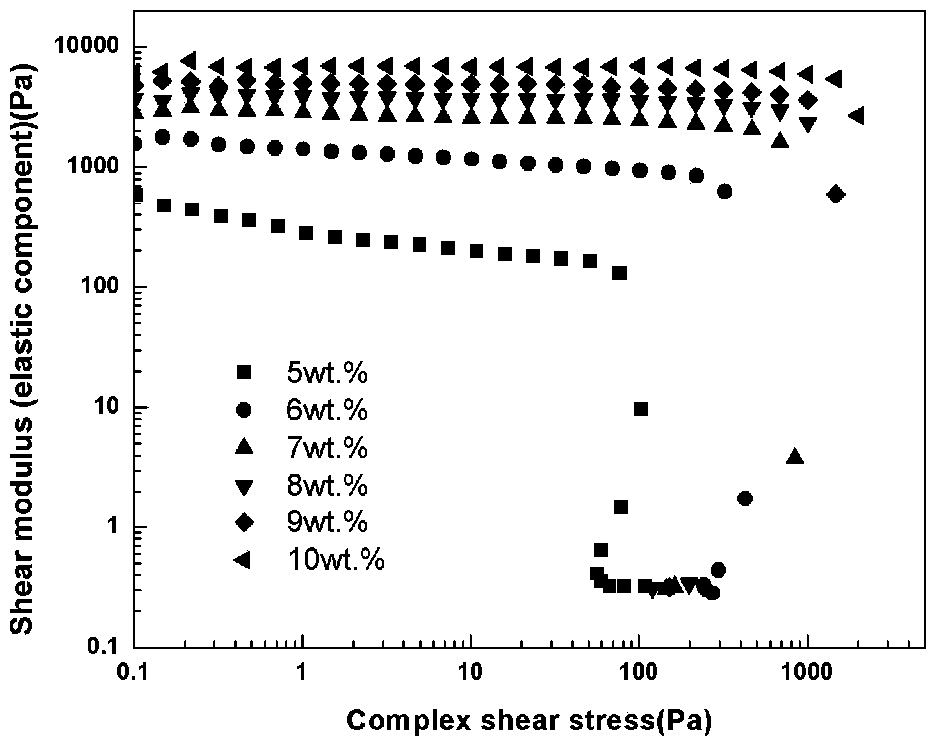
[0089] In the slurry, the solid content (solid phase volume fraction) of hydroxyapatite is 10vol.%, the gelling agent is gelatin, and the content is 5wt.% of the solvent mass, and the solvent is water; the dispersant is ammonium polyacrylate , the addition amount is 0.6wt.% of the mass of hydroxyapatite. Firstly, the hydroxyapatite powder, water and dispersant are mixed and ball milled at 30 rpm for 12 hours to form a suspension, and zirconia balls are added as grinding Medium, while adding 1-2 drops of n-octanol as a defoamer. Subsequently, gelatin, a gelling agent, was added to the hydroxyapatite suspension, followed by ball milling at a temperature of 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a slurry, which was then poured into a syringe of a 3D direct writing device and left to stand at 0°C. Set aside for 5 minutes to promote the transformation of the suspension into a gel, then put the syringe loaded with hydroxyapatite gel into a 210 μm needle nozzle, and perform direct writing moldin...
Embodiment 2
[0091] In the slurry, the solid content of hydroxyapatite is 40vol.%, the gelling agent is gelatin, and the content is 15wt.% of the solvent mass, and the solvent is water; the dispersant is ammonium polyacrylate, and the addition amount is hydroxyphosphorus 1.2wt.% of the mass of limestone, first mix hydroxyapatite powder, water and dispersant, form a suspension after ball milling in a ball mill at 60rpm for 8 hours, add zirconia balls as grinding media, and simultaneously add 1- 2 drops of n-octanol as a defoamer. Subsequently, gelatin gelatin was added to the hydroxyapatite suspension, followed by ball milling at a temperature of 80°C for 2 hours to obtain a slurry, which was then poured into the syringe of a 3D direct writing device and left to stand at 0°C. Place for 2 minutes to promote the transformation of the suspension into a gel, then put the syringe loaded with hydroxyapatite gel into a 160 μm needle nozzle, and perform direct writing molding on the thermally condu...
Embodiment 3
[0093] In the slurry, the solid content of hydroxyapatite is 20vol.%, the gelling agent is gelatin, and the content is 10wt.% of the solvent mass, and the solvent is water; the dispersant is ammonium polyacrylate, and the addition amount is hydroxyapatite 1.2wt.% of the stone mass, first mix the hydroxyapatite powder, water and dispersant, and then ball mill at 60rpm for 8 hours to form a suspension, add zirconia balls as grinding media, and add 1-2 Drops of n-octanol were used as defoamers. Subsequently, gelatin gelatin was added to the hydroxyapatite suspension, followed by ball milling at a temperature of 80°C for 2 hours to obtain a slurry, and then the suspension was poured into the syringe of a 3D direct writing device and left at 0°C Leave it for 3 minutes to promote the transformation of the suspension into a gel, then put the syringe loaded with hydroxyapatite gel into a 400 μm needle nozzle, and perform direct writing molding of the slurry on the thermally conductive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com