Application of corn gene ZmABCG20 in regulating male fertility of crops
A technology of male fertility and male sterility, which is applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, and plant genetic improvement, and can solve problems such as unstable fertility of sterile lines, affecting the purity of hybrids, and the withdrawal of cytoplasmic male sterility technology from the market.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2 M 2 Substitute Planting and Character Observation
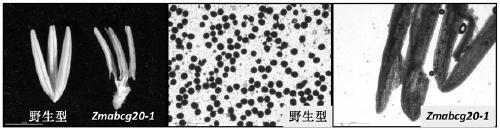
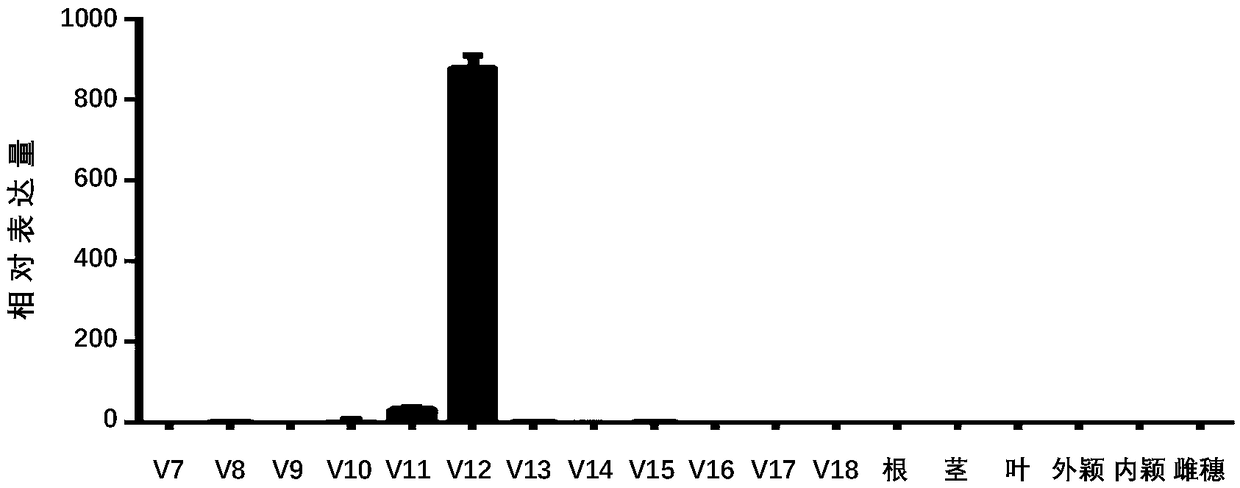
[0088] in M 2 During the heading and flowering period of the first generation, the morphology of anthers was observed in the field, and anthers with abnormalities such as light white color, small shape, and small pollen amount were selected for further microscopic examination under a microscope. In the family numbered 3326, 9 plants with abnormal fertility were found, which could not loose powder normally, but had normal fruiting ( figure 1 ). The anthers of the mutant are smaller than the wild type, light yellow in color, and have no visible pollen, but there is no obvious difference from the wild type in vegetative growth, heading stage, and panicle type, so it is selected as a candidate mutant material for further research. According to the finally identified mutated gene (see Examples 6, 7, 8), the mutant was named zmabcg20-1.
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 Sterile Mutant Pollen Microscopic Examination and Genetic Analysis
[0090] The pollen fertility was counted by the ratio of iodine-stained pollen to non-colored pollen. Observing the morphology of zmabcg20-1 male flowers under a stereomicroscope, the anthers were smaller and lighter in color than the wild type ( figure 2 ). Collect florets at the flowering stage in the field, take out the anthers with tweezers, and put them in iodine-potassium iodide solution (0.6% KI, 0.3% I 2 , w / w), gently squeeze the anthers, drop them on a glass slide, cover with a cover glass, observe the pollen iodine staining under a microscope and take pictures. The wild type has more pollen and is stained blue-black, while the mutant cannot see the pollen grains ( figure 2 ).
[0091] Mutants can bear fruit normally under open pollination ( figure 1 ), indicating that the mutant is a male sterile mutant, and ear fertility is not affected. Harvest zmabcg20-1 open-pollinated s...
Embodiment 4
[0092] Example 4 Leaf Sampling and DNA Extraction
[0093] In this study, the CTAB method was used to extract DNA from maize leaves. The specific method is as follows: Weigh about 0.1g leaves, put them into a centrifuge tube, add 600 μL CTAB extraction buffer, 5 μL RNase A, shake to disperse, put in a water bath at 65°C for 0.5hr, and shake gently in between 2-3 times; add an equal volume of chloroform / Tris-saturated phenol (1:1, v / v), mix well, and shake gently for 10 min; centrifuge at 10000 rpm at 4°C for 20 min; transfer the supernatant to a new tube, and add 1 / 10 volume of 3M sodium acetate (pH 5.2), 0.6-1 times the volume of cold isopropanol; gently shake and mix until flocculent precipitates appear; centrifuge at 10000rpm at 4°C for 10min; discard the supernatant, and use 70% ethanol by volume Wash the precipitate twice; air dry, add 50 μL 1×TE to dissolve the precipitate, and store at -20°C. The DNA concentration was detected by Nanodrop2000 and diluted to 10ng / L for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com