Indium gallium bismuth nitride material, laser and detector using the material and preparation method
A technology of indium gallium nitride and lasers, which is applied in the field of semiconductor photoelectric material preparation, can solve the problems of threading dislocations, and achieve the effects of easy growth, easy control, simple structure and operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Example 1: InGaNBi near-infrared laser
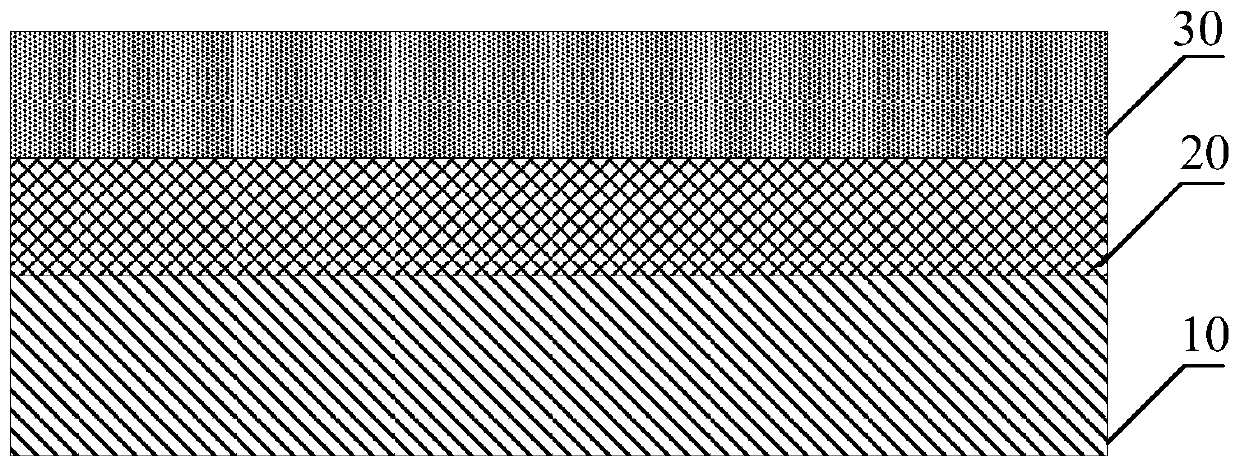
[0075] Using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) or metal organic vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth tools, epitaxially grow the InP buffer layer on the InP substrate (substrate) or auxiliary substrate (template);
[0076] Epitaxial growth of In on the InP buffer layer y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi x Thin films and heterojunction materials.
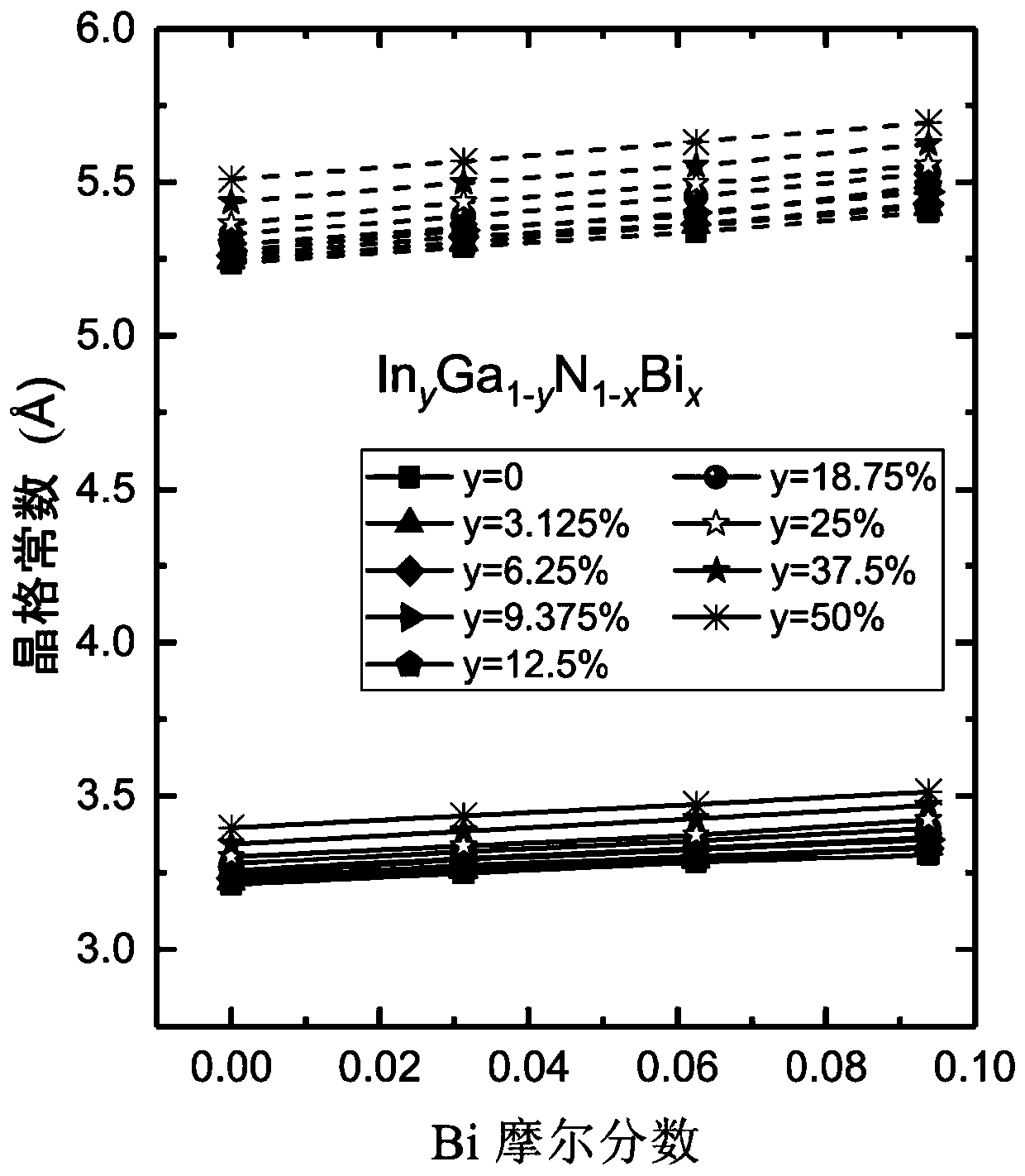
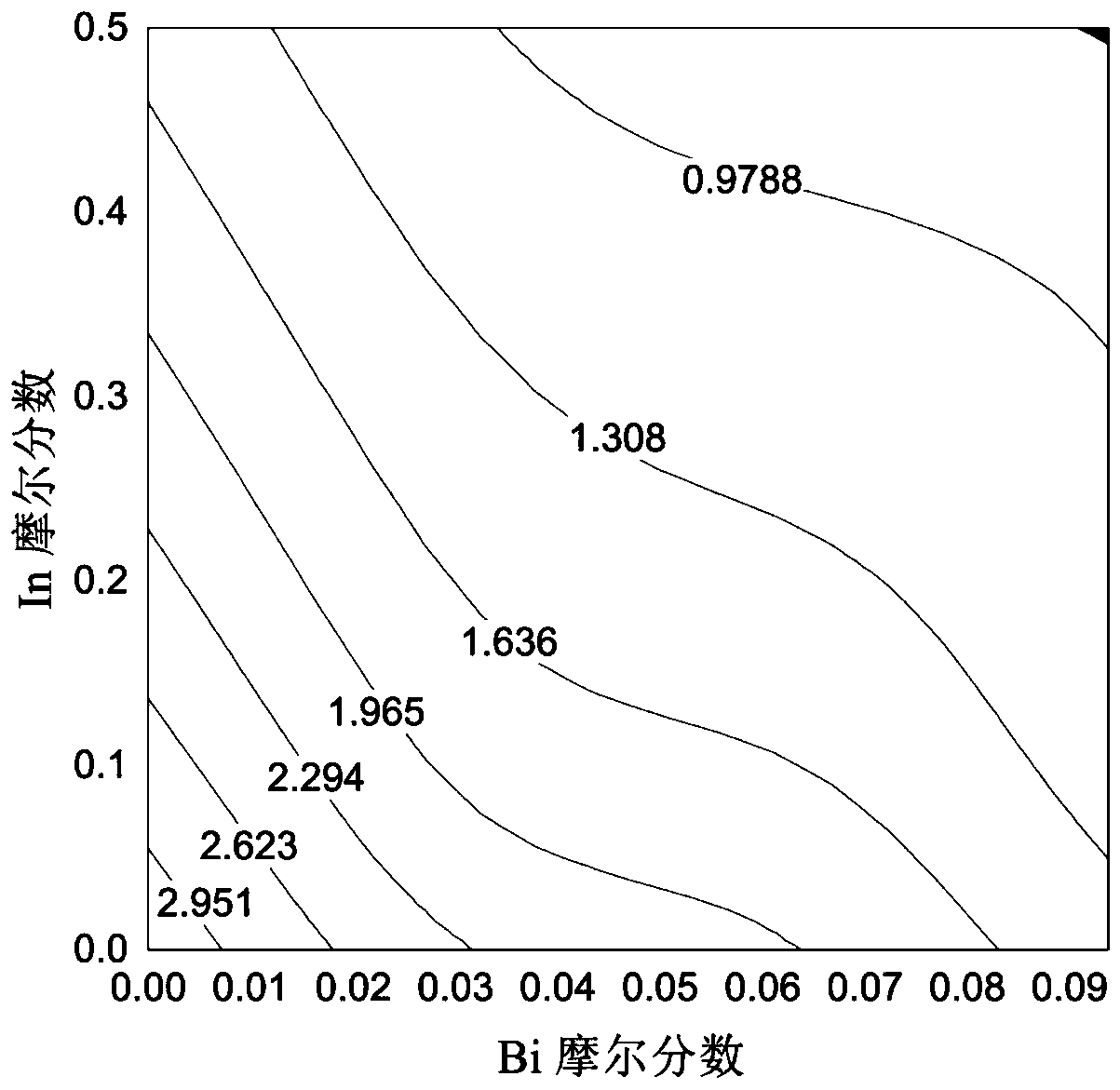
[0077] By controlling the concentration of doped In atoms and Bi atoms, the In y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi x The band gap of the material, the wavelength range can cover visible light to near infrared.
[0078] Figure 4 In the embodiment 1 of the present application contains In y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi x Schematic diagram of the structure of a near-infrared laser. In this example, the In of sphalerite structure y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi xThe material has a forbidden band width of 0.651eV when the In component is 50% and the Bi component is 9.375%, and the corresponding wavelength is 1.9 μm, which is located i...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2: InGaNBi near-infrared detector
[0098] Figure 5 is according to an embodiment of the present application containing In y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi x Schematic diagram of the near-infrared detector structure. In this example, the In of sphalerite structure y Ga 1-y N 1-x Bi x The material has a forbidden band width of 0.651eV when the In component is 50% and the Bi component is 9.375%, and the corresponding wavelength is 1.9 μm, which is located in the near-infrared band. The specific structure of the near-infrared detector prepared with this material is described as follows:
[0099] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the near-infrared detector includes in order from bottom to top: an InP substrate layer, an N-type InP doped layer, a P-type InGaNBi absorption region, and a P-type InP doped layer,
[0100] Wherein, a passivation layer is deposited on the outer surface of the N-type InP doped layer, the P-type InGaNBi absorption region, and the P-type InP doped lay...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com