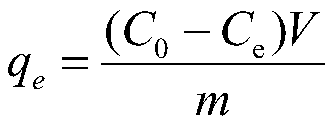A method for preparing aminated magnetic chitosan
A technology of chitosan and amination, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of limited hydrophilicity, uneven adhesion, blocking material pores, etc., and achieve strong adsorption performance and Effects of adsorption selectivity, rich porous structure, and rapid magnetic separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A preparation method of aminated magnetic chitosan, comprising the following steps;
[0030] 1) Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles: add 25mL water into a 50mL three-neck flask, stir mechanically, pass argon gas to remove oxygen for about 30min, add 4mmol FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 2.4 mmol FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, continue to stir for 10min, the stirring speed is 500r / min, the solution is orange-red, the water bath is heated to 60°C, slowly add 2.5mL concentrated ammonia water dropwise, and the addition is completed in about 1min. The orange red turns black, continue to stir for 40 minutes, raise the temperature to 80°C, stop stirring, and age for 30 minutes, in order to prevent Fe 2+ was oxidized, and the solution was kept under the protection of argon during the whole reaction process. The magnetic nanoparticles were separated by an external magnetic field, then washed three times alternately with deionized water and alcohol, and the product was freeze-dried and stored for late...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A preparation method of aminated magnetic chitosan, comprising the following steps;
[0036] 1) Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles: add 25mL water into a 50mL three-neck flask, stir mechanically, pass argon gas to remove oxygen for about 30min, add 5mmol FeCl3 6H2O and 2.1mmol FeSO4 7H2O, continue stirring for 10min, the stirring speed is 500r / min, the solution is Orange red, heat the water bath to 60°C, slowly add 2.5mL of concentrated ammonia water dropwise, and finish adding in about 1 minute. The pH value of the solution is between 9-10, and the solution quickly changes from orange red to black. ℃, stop stirring, and age for 30 minutes, in order to prevent Fe 2+ was oxidized, and the solution was kept under the protection of argon during the whole reaction process. The magnetic nanoparticles were separated by an external magnetic field, then washed three times alternately with deionized water and alcohol, and the product was freeze-dried and stored for later use...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The aminated magnetic chitosan prepared in Example 1 is the test group, and the magnetic chitosan prepared in Example 2, Comparative Example 1, and Comparative Example 2 is a control group 1, a control group 2, and a control group 3, and each group is tested The adsorption time and adsorption capacity when the adsorption of Cd(II) solution reaches adsorption equilibrium are shown in Table 1.
[0046] Test method: take Cd(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O was dissolved in 500mL deionized water to prepare a mother solution with a concentration of Cd(II) of 1000mg / L. The Cd(II) solutions of various concentrations required in the experiment were obtained by diluting the mother solution. 20 mL of Cd(II) solution with a concentration of 200 mg / L was placed in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and each group of samples with a dose of 5-20 mg was added respectively.
[0047] The Erlenmeyer flask containing the test solution was placed in a shaker at a rotational speed of 150 rpm. After the adsorptio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com