Method for preparing antioxidant tripeptide from rice polypeptide and application
A technology of rice peptides and peptides, applied in the field of peptides, can solve problems such as destructive activity, adverse effects on product safety, and structural damage, and achieve the effects of simple preparation methods, good antioxidant activity, and product safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The enzymolysis of embodiment 1 rice protein
[0050] 1. Enzyme hydrolysis:
[0051] 1. Enzymatic hydrolysis of flavored protein: rice protein was prepared into a solution with a concentration of 100mg / mL with distilled water as a solvent, added flavored protease to 0.75wt%, temperature 50°C, pH 6.0, after enzymolysis for 4 hours, use a boiling water bath to inactivate the enzyme, and centrifuge at 8000rpm After 20 minutes, the supernatant was concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain polypeptide A.
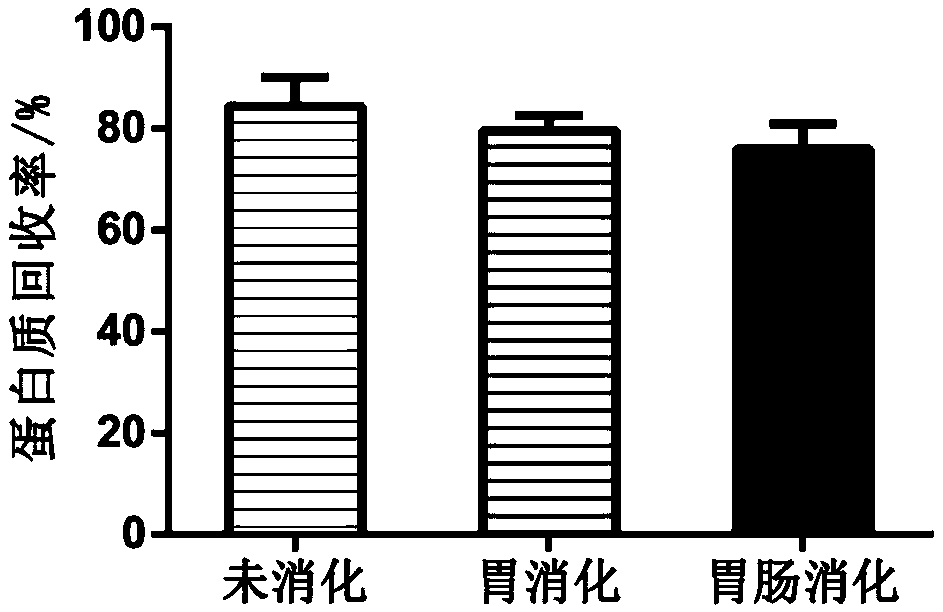
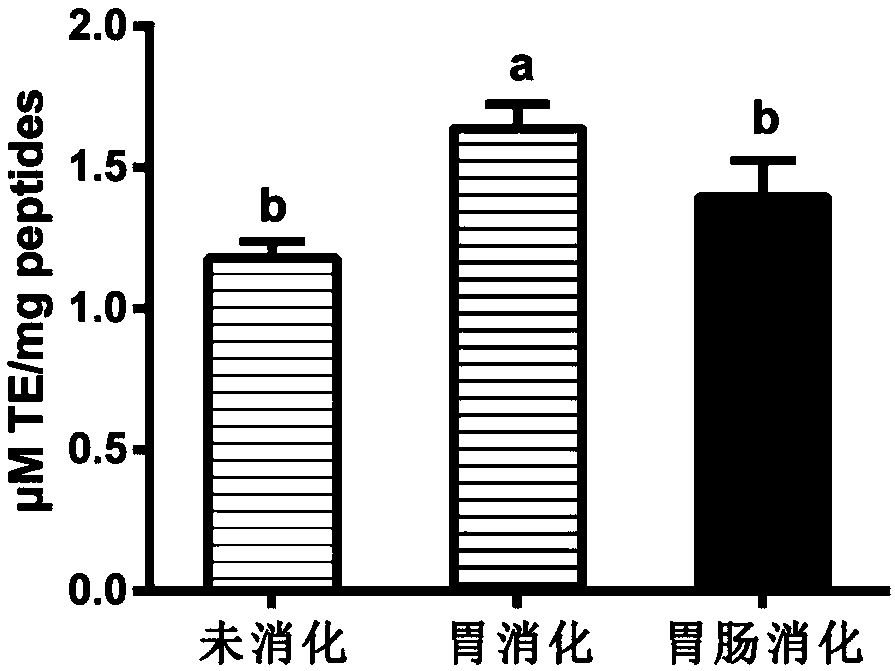
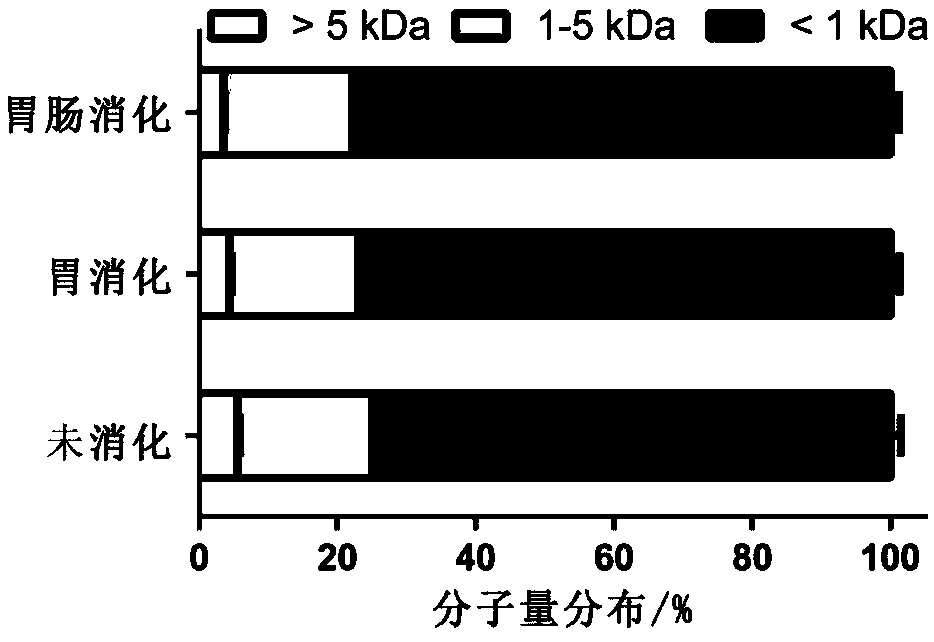
[0052] 2. Simulated gastric digestion: Polypeptide A was prepared into a solution with a concentration of 100 mg / mL by using distilled water as a solvent, adding pepsin to 1.7% wt%, temperature 37°C, pH 1.5, enzymatic hydrolysis for 1.5 hours, and using a boiling water bath to inactivate the enzyme. Centrifuge at 8000rpm for 20min, and the supernatant is concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain polypeptide B.
[0053] 3. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion: After enzymatic...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2 cellulose glass column purification
[0065] A DEAE-52 cellulose glass column (1.6×30 cm) was pre-equilibrated with distilled water. The rice polypeptide prepared in Example 1 was prepared into a solution with a concentration of 50 mg / mL in distilled water, and loaded on the DEAE-52 column.
[0066] Take 200 mL of distilled water and 200 mL of NaCl solutions with concentrations of 0.05 mol / L, 0.1 mol / L, 0.2 mol / L and 0.4 mol / L for gradient elution at a flow rate of 0.5 mL / min. Collect each fraction eluted and monitor at 214nm, collect the purified product as Figure 2a shown.
[0067] The six fractions obtained (F1, F2, F3, F4, F5 and F6) were collected, each fraction was freeze-dried, and their ORAC antioxidant activity was measured. The ORAC test results of each component are as follows Figure 2b As shown, the ORAC value of component F1 was 4.412±0.161, which was significantly higher than other components, so F1 was further purified.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 Sephadex column purification
[0069] A Sephadex G-15 column (1.6 x 60 cm) was pre-equilibrated with distilled water. The polypeptide F1 prepared in Example 3 was prepared into a solution with a concentration of 30 mg / mL with distilled water, and loaded onto a well-balanced Sephadex G-15 column for further purification. Fractions were eluted with distilled water at a flow rate of 0.5 mL / min, and each eluted fraction was collected and then detected at 214 nm.
[0070] The results of the secondary purification are as follows Figure 2c As shown, F1 obtained three fractions (F1-a, F1-b, F1-c) through secondary purification, and this purification method can effectively separate the components of rice polypeptide; the ORAC detection results of each component are as follows: Figure 2d As shown, the ORAC value of wherein component F1-a is 6.815 ± 0.298, is significantly higher than other other components, and the rice polypeptide oxygen free radical absorption ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com