Silicon crystal heterojunction solar cell and preparation method thereof
A solar cell and heterojunction technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of limiting the hole transport performance of the film and the limited control of the stoichiometric ratio of oxides, so as to reduce the density of defect states and the surface recombination rate of carriers, Improve the carrier transport capacity of the thin film and improve the effect of short-circuit current of the battery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
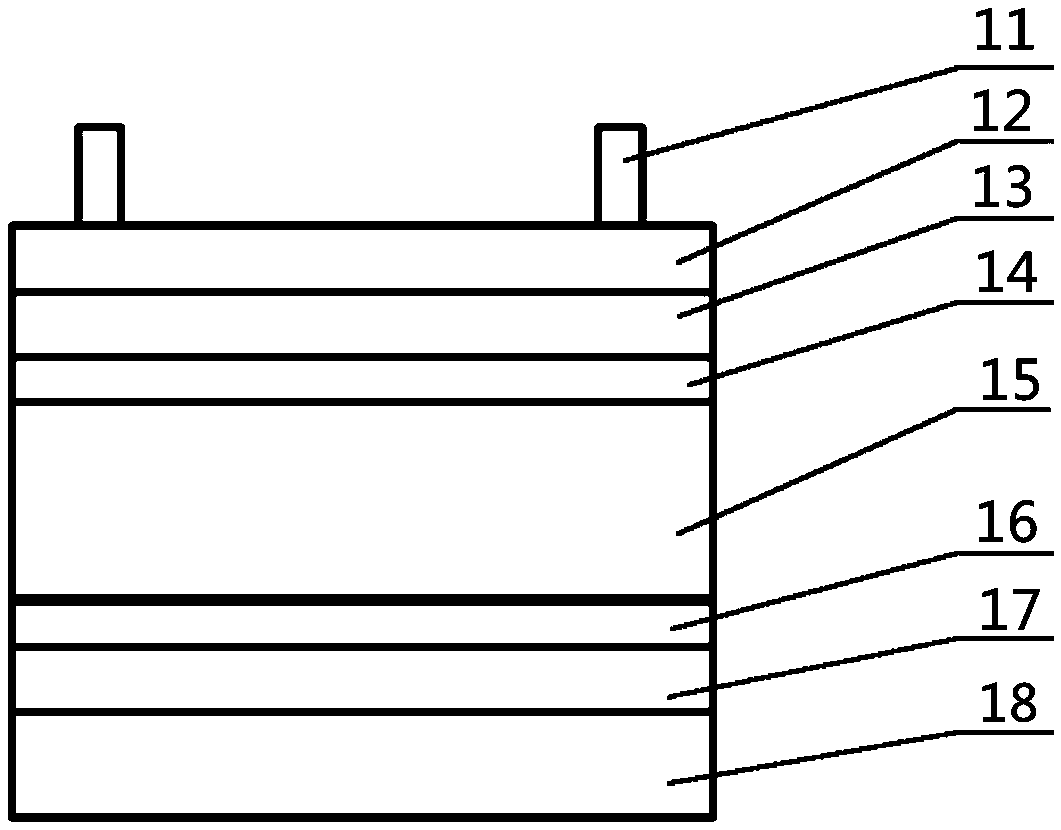
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment is based on the crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cell of the molybdenum oxysulfur hole extraction layer, and its structure is: a first tunneling layer 14, MoO 3-x S x The hole extraction layer 13 , the transparent conductive electrode 12 and the metal grid line 11 are sequentially prepared on the back of the n-type silicon wafer 15 with a second tunneling layer 16 , an electron extraction layer 17 and a metal back electrode 18 .
[0026] This embodiment specifically gives the preparation method of crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells, as follows:
[0027] (1) The n-type CZ 180 micron (1~10 Ω·cm) silicon wafer was cleaned by RCA, and then the silicon wafer was immersed in diluted hydrofluoric acid (5%, 3 minutes) to remove the natural oxide layer on the surface. Put the cleaned silicon wafer into 70wt% nitric acid for 15 minutes (at room temperature) to form a tunnel oxide layer with a thickness of abo...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the molybdenum oxysulfur monolayer film structure is prepared in step (4) of Example 1, and the molybdenum oxysulfur / molybdenum oxide double layer is prepared in step (4) in this example structure, the two-layer structure together serves as a hole-extracting layer.
[0034] The preparation process of the molybdenum oxysulfide / molybdenum oxide double-layer structure is as follows: first evaporate molybdenum oxide with a thickness of 0.5nm to 5nm, and then deposit a molybdenum oxysulfide thin film by co-evaporating molybdenum sulfide and molybdenum oxide according to the method in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Same as Example 1, the molybdenum oxysulfur monolayer thin film structure is also prepared in step (4) in this example, but the preparation method of the molybdenum oxysulfur single layer thin film structure in this example is as follows: molybdenum sulfide and molybdenum oxide are alternately Deposition, the evaporation rate of molybdenum oxide is 0.01~0.05nm / s, the evaporation rate of molybdenum sulfide is 0.01~0.1nm / s, and finally annealed, the annealing temperature is 100~300°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com