Polystyrene nano zero-valent iron composite material and preparation method and application thereof
A polystyrene nano-composite material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal compounds, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of easy agglomeration and deactivation, poor stability, difficult separation, etc., and achieve large adsorption capacity and stability. Good sex, not easy to agglomerate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
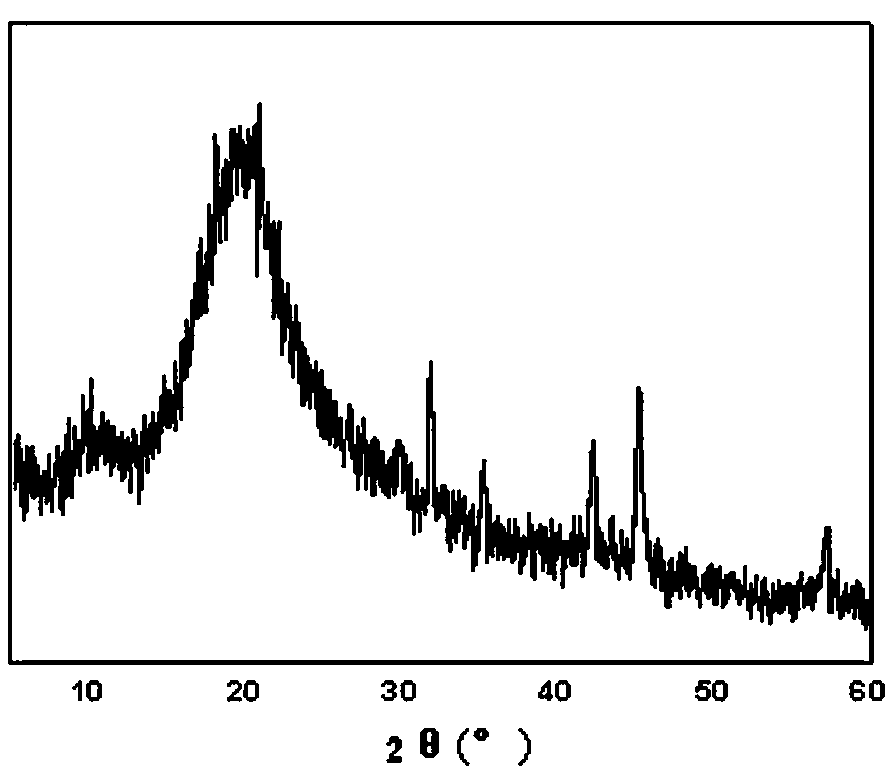
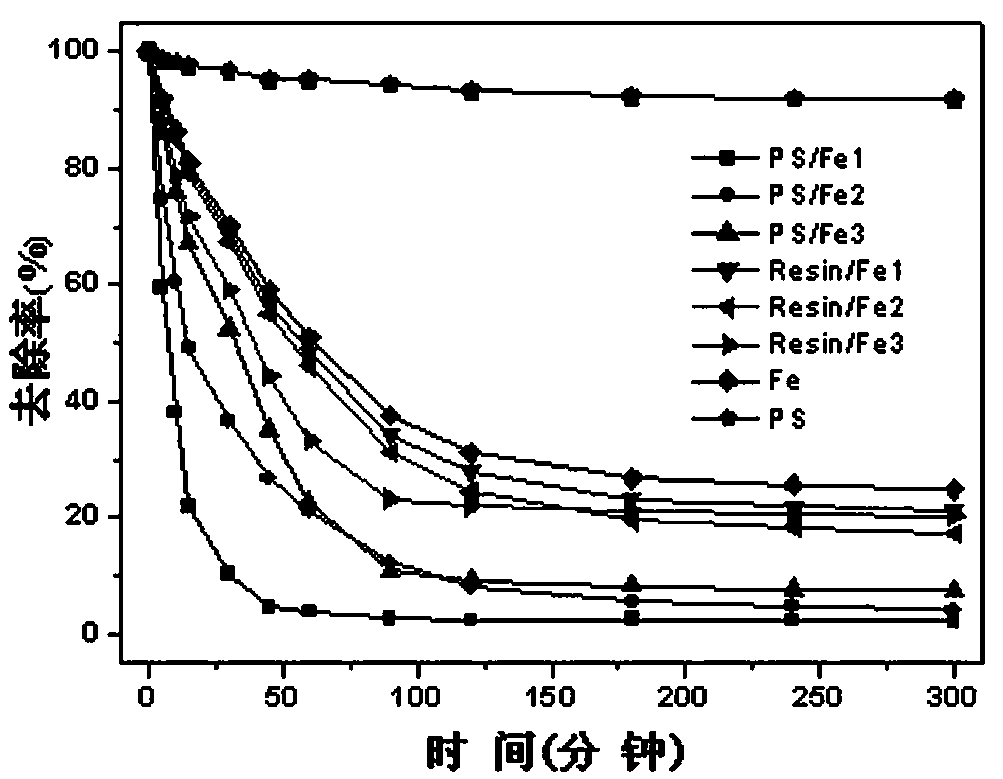
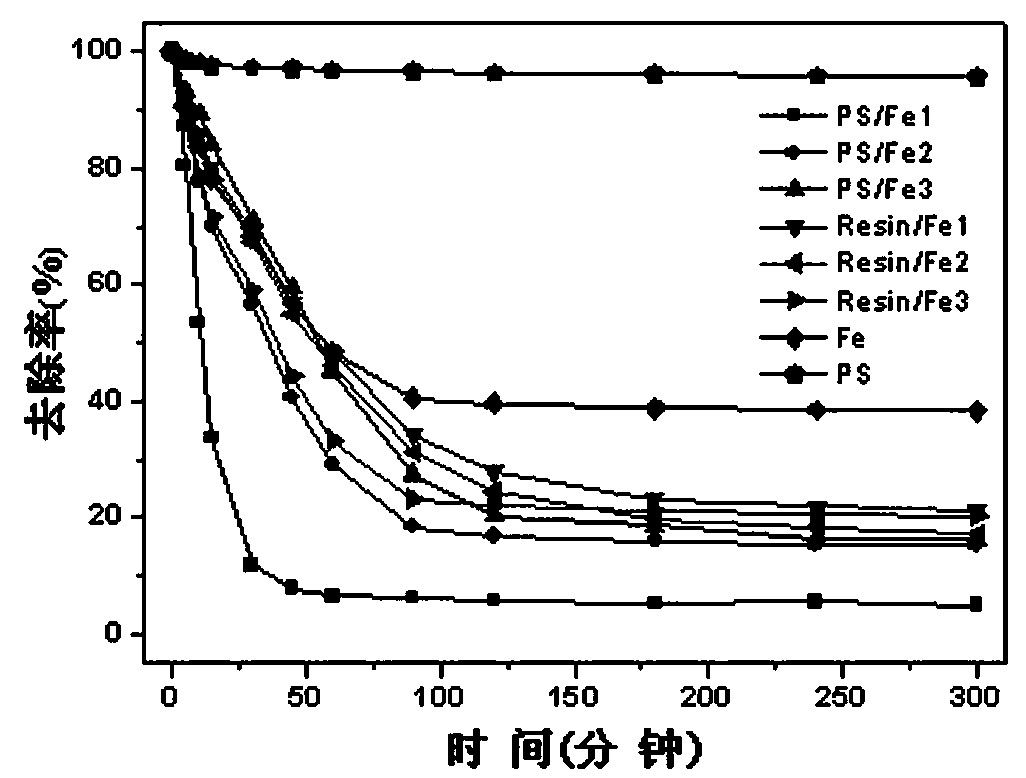
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Dissolve polystyrene in N,N-dimethylformamide at a mass ratio of 1:4 to obtain a polystyrene solution with a mass concentration of 20%, and add methanol 10 times that of N,N-dimethylformamide Under liquid nitrogen freezing conditions, freeze into a solid, place in liquid nitrogen that is twice as large as the solution, wait until the system is stable and the boiling degree of liquid nitrogen slows down, slowly drop 20 wt.% polystyrene solution into the solution containing solid methanol through a peristaltic pump Polystyrene microspheres were obtained in liquid nitrogen to prevent droplet aggregation. Let the system stand still, the liquid nitrogen slowly volatilizes, and the methanol slowly melts with the increase of the system temperature to replace the N,N-dimethylformamide in the polystyrene. The obtained microspheres are washed in methanol for 2-3 times, and then put into a vacuum oven to dry at room temperature.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Dissolve polystyrene in toluene at a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a polystyrene solution with a mass concentration of 50%. Freeze methanol 20 times that of toluene into a solid under liquid nitrogen freezing conditions and place it in three times the solution When the system is stable and the boiling degree of liquid nitrogen slows down, 50 wt.% polystyrene solution is slowly dropped into liquid nitrogen containing solid methanol through a peristaltic pump to obtain polystyrene microspheres to prevent droplet polymerization. Let the system stand still, the liquid nitrogen slowly volatilizes, and the methanol melts slowly with the increase of the system temperature, displacing the toluene in the polystyrene. The obtained microspheres are washed in methanol for 2-3 times, and then put into a vacuum oven to dry at room temperature.
[0045] Dissolve ferrous sulfate in water at a mass ratio of 1:7, immerse the microspheres obtained above in a methanol solution of ferrous sul...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Dissolve polystyrene in carbon tetrachloride at a mass ratio of 1:3 to obtain a polystyrene solution with a mass concentration of 25%, and freeze methanol 15 times that of carbon tetrachloride into a solid under liquid nitrogen freezing conditions , placed in liquid nitrogen five times that of the solution, and when the system was stable and the boiling degree of liquid nitrogen slowed down, 25 wt.% polystyrene solution was slowly dropped into liquid nitrogen containing solid methanol through a peristaltic pump to obtain polystyrene microspheres , to prevent droplet aggregation. Let the system stand still, the liquid nitrogen volatilizes slowly, and the methanol melts slowly with the increase of the system temperature, displacing the carbon tetrachloride in the polystyrene. The obtained microspheres are washed in methanol for 2-3 times, and then put into a vacuum oven to dry at room temperature.
[0051] Dissolve ferrous nitrate in water at a mass ratio of 1:10, immers...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com