A thin-sheet heat-conducting wave-absorbing composite material and its preparation method
A composite material and sheet technology, which is applied in the field of sheet-type thermally conductive and wave-absorbing composite materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of low magnetic permeability and lack of wave-absorbing properties, and achieves excellent thermal conductivity and wave-absorbing properties, and easy and precise control. , the preparation method is simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
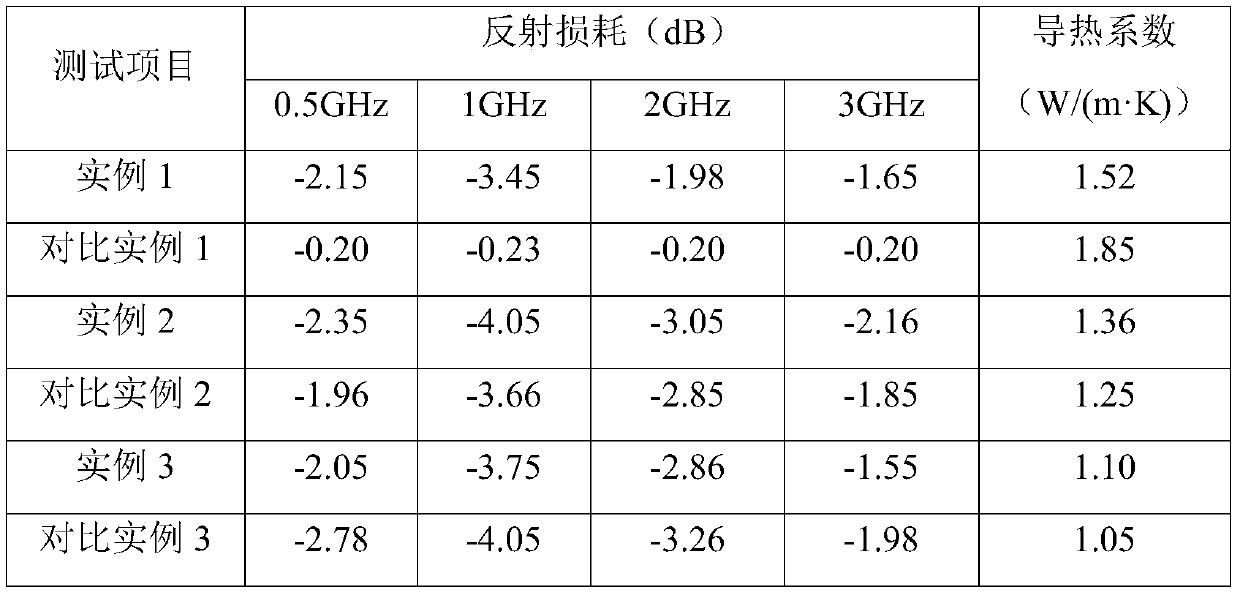
Examples
Embodiment 1
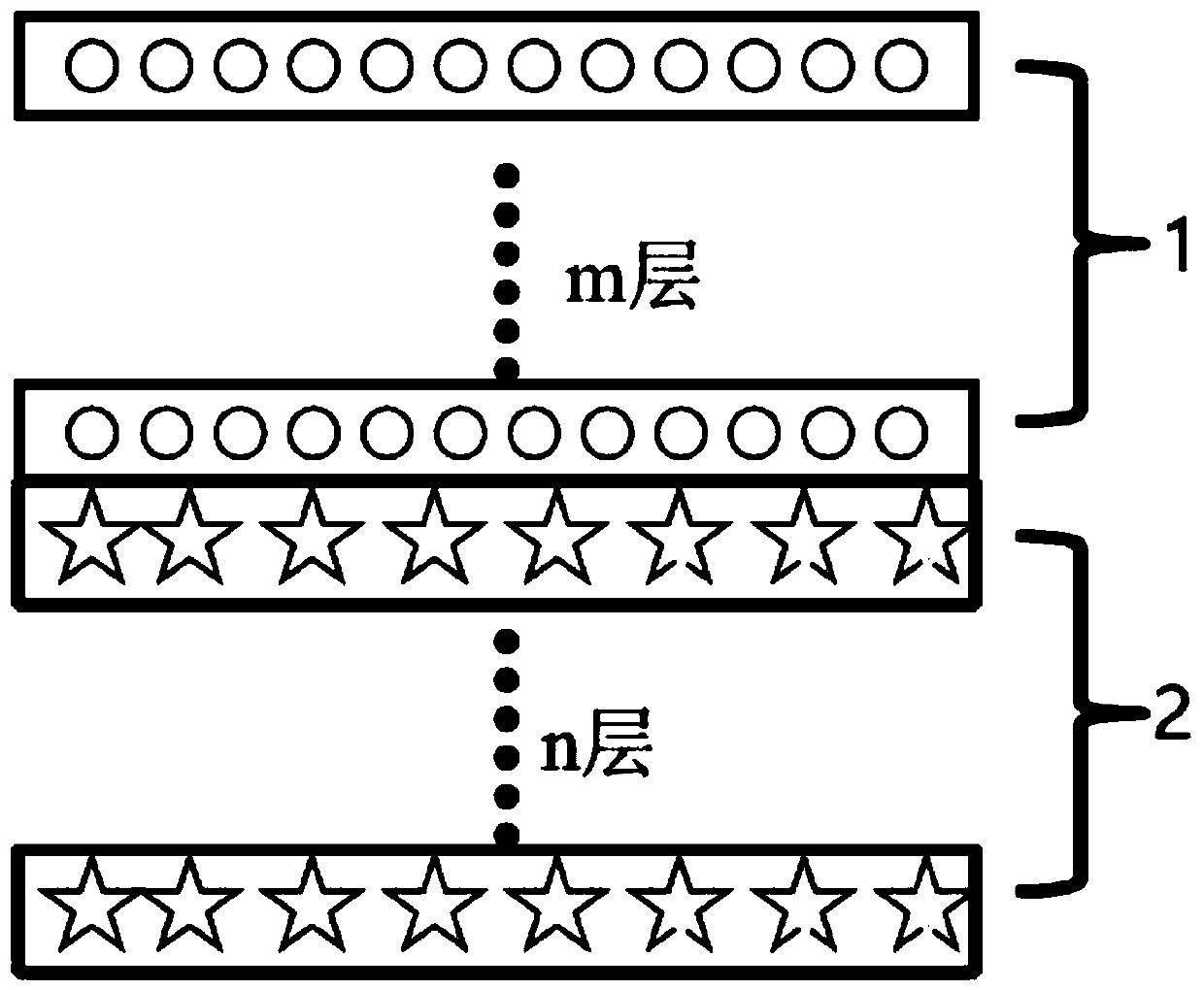
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the sheet-type heat-conducting and wave-absorbing composite material has a double-layer structure of a heat-conducting layer and a wave-absorbing layer. The performance of the composite material can be regulated by adjusting the number, thickness, formula and process of the heat conducting layer and the wave absorbing layer in the composite absorbing material.
[0040] (1) The composition and weight percentage of the heat conducting layer are:
[0041] Polymer binder: 10%
[0042] Heat conduction agent: 86%
[0043] Auxiliary: 4%
[0044] The polymer binder is polyurethane, which is required to meet the requirements of the heat-conducting material casting process.
[0045] The heat conducting agent is spherical silicon carbide with a diameter of 0.8-3 μm.
[0046] The auxiliary agent includes a dispersant, a polyurethane curing agent and a curing catalyst, and the mass ratio of the three is 1:8:1.
[0047] The single-layer thickness of t...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, the sheet-type heat-conducting and wave-absorbing composite material has a double-layer structure of a heat-conducting layer and a wave-absorbing layer. The performance of the composite material can be regulated by adjusting the number, thickness, formula and process of the heat conducting layer and the wave absorbing layer in the composite absorbing material.
[0064] (1) The composition and weight percentage of the heat conducting layer are:
[0065] Polymer binder: 12%
[0066] Heat conduction agent: 84%
[0067] Auxiliary: 4%
[0068] The polymer binder is polymethyl methacrylate, which is required to meet the requirements of the heat-conducting material casting process.
[0069] The heat conducting agent is spherical aluminum oxide with a diameter of 1-3 μm.
[0070] The auxiliary agent includes a dispersant, a polymethyl methacrylate curing agent and a curing catalyst, and the mass ratio of the three is 3:6:1.
[0071] The single-l...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Such as figure 1 As shown, the sheet-type heat-conducting and wave-absorbing composite material has a double-layer structure of a heat-conducting layer and a wave-absorbing layer. The performance of the composite material can be regulated by adjusting the number, thickness, formula and process of the heat conducting layer and the wave absorbing layer in the composite absorbing material.
[0088] (1) The composition and weight percentage of the heat conducting layer are:
[0089] Polymer binder: 14%
[0090] Heat conduction agent: 82%
[0091] Auxiliary: 4%
[0092] The polymer binder is ethyl cellulose, which is required to meet the requirements of the heat-conducting material casting process.
[0093] The heat conducting agent is spherical zinc oxide with a diameter of 0.5-2 μm.
[0094] The auxiliary agent includes a dispersant, an ethyl cellulose curing agent and a curing catalyst, and the mass ratio of the three is 3:6:1.
[0095] The single-layer thickness of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com