Low-energy nuclear reactor capable of enhancing thermal excitation by using carbon material, energy production method of low-energy nuclear reactor and energy device
A nuclear reactor and thermal excitation technology, applied in the field of condensed matter nuclear science and nuclear engineering, can solve problems such as questioning scientificity and failure, and achieve the effect of reversible hydrogen release, good kinetics of hydrogen release, and increased reaction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
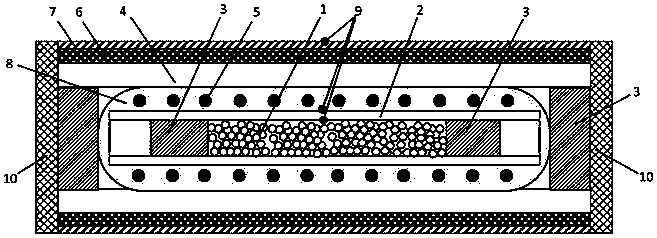
[0055] The low-energy nuclear reactor provided by this embodiment is as figure 1 As shown, implement thermal excitation, adopt an external electric heater, and have a sealed end cover 10 and a reactor outer seal shell 7 (1-10mm) of materials such as a refractory alloy or stainless steel that can withstand high temperatures above 1400°C. The two contact thermocouple junctions 9 are sealed with high temperature resistant cement, and there is a heat insulating material layer 6 (such as Al 2 o 3 Corundum, yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) single crystal, Sc 2 o 3 , MgO, etc.), which contains high temperature resistant (over 1500c) corundum Al 2 o 3 , yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) single crystal, Sc 2 o 3 Or the outer protective tube 4 of molybdenum disilicide, etc., the outer protective tube 4 is provided with an external electric heater 5 sealed with high temperature resistant cement 8, and is made of carbon material (including carbon fiber, silicon carbide, silicon carbide ro...
Embodiment 2
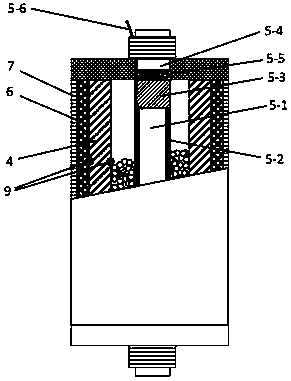
[0061] Reactor such as figure 2 As shown, the main difference with Embodiment 1 is that the electric heating element 5-1 with a diameter of 1-10mm is covered with a high temperature resistant electrically insulating ceramic tube 5-2 (Al 2 o 3 , yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) single crystal, Sc 2 o 3 ), placed in the center of the reaction zone to replace the external electric heater in Example 1 to implement thermal excitation. The two ends of the electric heating element 5-1 are provided with Al 2 o 3 , yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) single crystal, Sc 2 o 3 A ceramic material plug 5-3, and a high temperature and high pressure resistant sealing end cap 5-4, the plug 5-3 can reduce the temperature at the sealing end cap 5-4. The electric heating element 5-1 is connected to the wire 5-6, the wire 5-6 passes through the ceramic material plug and the end cover, and is sealed with high temperature resistant cement 5-5, and the outer protection tube 4 and the thermal insulati...
Embodiment 3
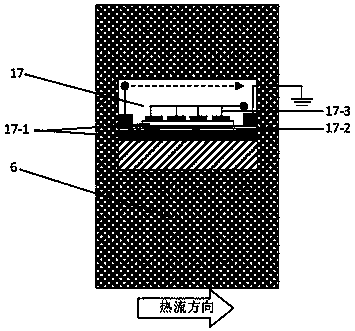
[0063] Compared with the above-mentioned embodiment, the main difference is that the thermoelectric direct conversion unit 17 of graphene is embedded in the heat insulating material layer 6 corresponding to the reaction zone, such as Figure 4 As shown, the thermoelectric direct conversion unit 17 includes a graphene layer 17-2, and the top and bottom of the graphene layer are SiO 2 Layer 17-1, on upper SiO 2 An electrode array 17-3 is provided on the layer. Cooling units of carbon nanotubes and graphene or heat pipe devices can be used to cool waste heat. The cooling units of carbon nanotubes and graphene and heat pipe devices themselves are prior art and will not be described here. In a specific application, one end (hot end) of the cooling unit or the heat pipe can be arranged in the heat insulating material layer 6 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com