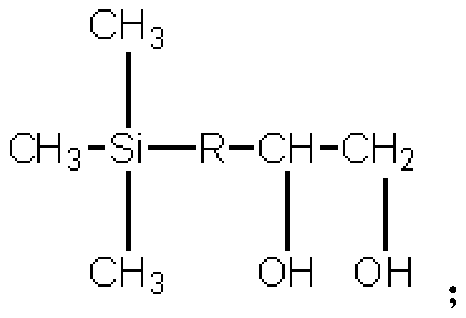
Dihydric alcohol modified polyester fibers with trimethylsilyl lateral groups and preparation method thereof
A technology of trimethylsilyl and modified polyester, which is applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, single-component polyester rayon, rayon manufacturing, etc., which can solve the problems of inability to catalyze, high cost, graying of polyester color and brightness reduction, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of increasing the free volume of space and changing the interaction force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] A preparation method of glycol-modified polyester fibers with trimethylsilyl side groups, the steps are as follows:
[0081] (1) Preparation of doped modified Sb 2 o 3 ;
[0082] (1.1) Mg(NO 3 ) 2 aqueous solution with a concentration of 8 mol% Sb 2 o 3 The solution is mixed evenly, Sb 2 o 3 The solvent of the solution is oxalic acid, the Mg in the mixture 2+ with Sb 3+ The molar ratio is 2:100;
[0083] (1.2) Add dropwise ammonia water with a concentration of 2 mol / L until the pH value of the mixed solution is 9 to obtain a precipitated product, and then wash and dry the precipitated product at a temperature of 105° C. for 2.5 hours;
[0084] (1.3) The dried product was first heated to 400°C and then kept for 2.5h, then heated to 900°C and kept for 1.5h, and finally cooled in air and pulverized to obtain doped modified Sb with an average particle size of 0.4 microns 2 o 3 Powder;
[0085] (2) Preparation of doped modified Bi 2 o 3 Powder;
[0086] (2.1)...
Embodiment 2
[0104] A preparation method of glycol-modified polyester fibers with trimethylsilyl side groups, the steps are as follows:
[0105] (1) Preparation of doped modified Sb 2 o 3 ;
[0106] (1.1) The concentration of 0.5mol% Ca(NO 3 ) 2 Aqueous solution with a concentration of 5 mol% Sb 2 o 3 The solution is mixed evenly, Sb 2 o 3 The solvent of the solution is oxalic acid, the Ca in the mixture 2+ with Sb 3+ The molar ratio is 1:100;
[0107] (1.2) Add dropwise ammonia water with a concentration of 2 mol / L until the pH value of the mixed solution is 10 to obtain a precipitated product, and then wash and dry the precipitated product at a temperature of 110° C. for 2 hours;
[0108] (1.3) The dried product was first heated to 400°C and then kept for 2h, then heated to 900°C and kept for 1h, and finally cooled in air and pulverized to obtain doped modified Sb with an average particle size of 0.4 microns 2 o 3 Powder;
[0109] (2) Preparation of doped modified Bi 2 o 3...
Embodiment 3
[0124] A preparation method of glycol-modified polyester fibers with trimethylsilyl side groups, the steps are as follows:
[0125] (1) Preparation of doped modified Sb 2 o 3 ;
[0126] (1.1) Ba(NO 3 ) 2 Aqueous solution with a concentration of 10 mol% Sb 2 o 3 The solution is mixed evenly, Sb 2 o 3 The solvent of the solution is oxalic acid, Ba in the mixture 2+ with Sb 3+ The molar ratio is 3:100;
[0127] (1.2) Add dropwise ammonia water with a concentration of 2 mol / L until the pH of the mixed solution is 9.5 to obtain a precipitated product, and then wash and dry the precipitated product at a temperature of 105° C. for 3 hours;
[0128] (1.3) The dried product was first heated to 400°C and kept for 3 hours, then heated to 900°C and kept for 2 hours, and finally cooled in air and pulverized to obtain doped modified Sb with an average particle size of 0.5 microns 2 o 3 Powder;
[0129] (2) Preparation of doped modified Bi 2 o 3 Powder;
[0130] (2.1) The con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Monofilament denier | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Monofilament denier | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com