Thin-film transistor, display device, and preparation method of thin-film transistor
A technology of thin-film transistors and semiconductors, which is applied in the preparation of display devices and thin-film transistors. In the field of thin-film transistors, it can solve problems such as poor uniformity, restrictions on the application of large-size and flexible display devices, and difficult manufacturing processes, and achieve display performance improvement and driving. Effects of performance improvement and shutdown performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
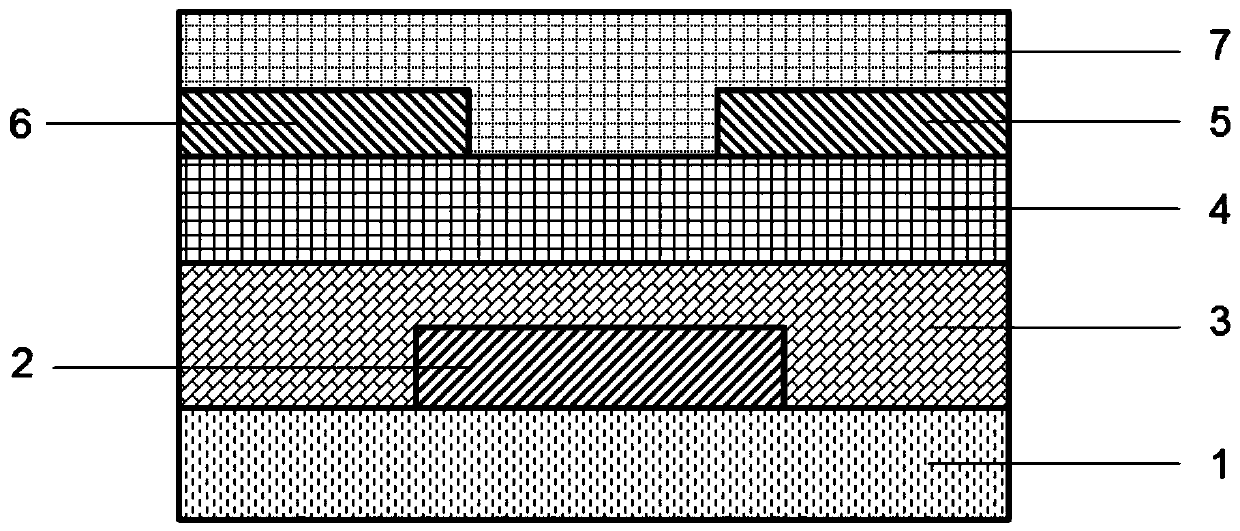
[0042] This embodiment provides a thin film transistor, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes: a gate electrode 2 formed on the substrate 1, an insulating layer 3 formed on the gate electrode 2 and extending to cover the top surface of the substrate 1, an active layer 4 formed on the insulating layer 3, and an active layer formed on the active layer The source electrode 6 and the drain electrode 5 on the source layer 4 are formed on the source and drain electrodes and partially cover the passivation layer 7 on the top surface of the active layer 4 .
[0043] The gate electrode 2 is made of metal molybdenum (Mo) doped with B + Forming, through ion doping, the gate electrode 2 is conductorized to increase the conductivity of the gate electrode 2 . The material of the insulating layer 3 is silicon oxide (SiOx), and the material of the source electrode 6 and the drain electrode 5 is titanium-aluminum-titanium lamination. The active layer 4 is an indium gallium zinc oxide film, ...
Embodiment 2
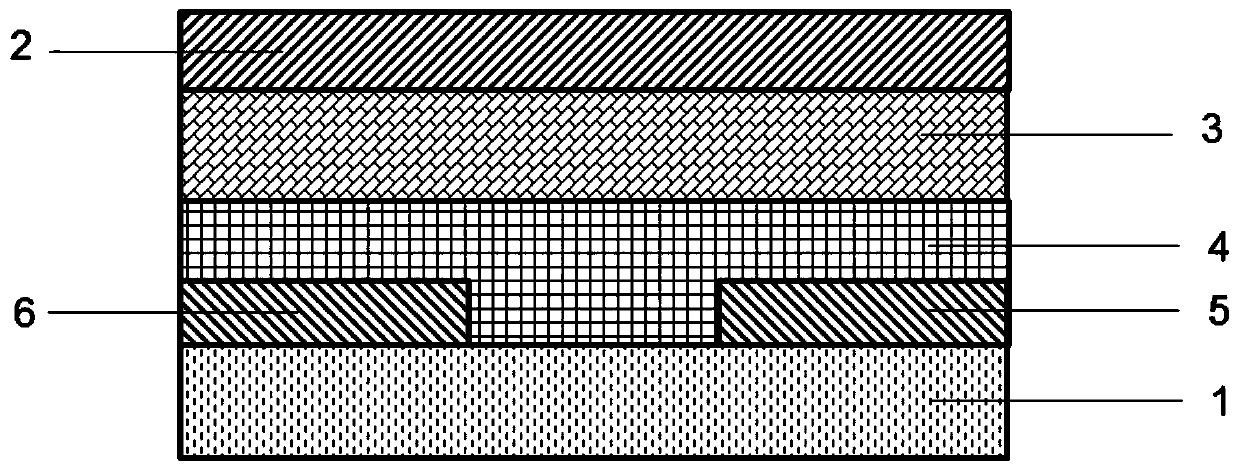
[0066] This embodiment provides a thin film transistor, which differs from the thin film transistor provided in Embodiment 1 in that: figure 2 As shown, the thin film transistor includes a gate electrode 2 formed on a substrate 1, an insulating layer 3 formed on the gate electrode 2 and extending to cover the top surface of the substrate 1, an active layer 4 formed on the insulating layer 3, and an active layer 4 formed on the active layer. A source electrode 6 and a drain electrode 5 on the layer 4 , a passivation layer 7 formed on the source and drain electrodes and partially covering the top surface of the active layer 4 .
[0067] Wherein, the active layer 4 is an indium gallium zinc oxide film, and the indium gallium zinc oxide film is doped with acetylacetone as a photosensitive active agent. The molar ratio of indium atoms: gallium atoms: zinc atoms: acetylacetone in the indium gallium zinc oxide film is 2:10:10:50.
[0068] The preparation method of the above-mention...
Embodiment 3
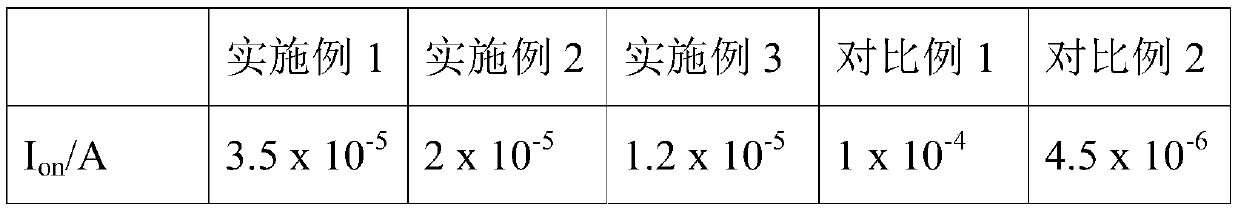
[0074] This embodiment provides a thin film transistor, which differs from the thin film transistor provided in Embodiment 1 in that in the thin film transistor as the active layer 4, the molar ratio of indium atoms: gallium atoms: zinc atoms: acetylacetone is 8:3 :3:5.
[0075] The difference between the preparation method of the above thin film transistor and the preparation method provided in Example 1 is that in step S32, In 3+ : Ga 3+ : Zn 2+ : The molar ratio of acetylacetone is 8:3:3:5, wherein, In 3+ The molar concentration is 10M.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com