High-yield coenzyme Q10 rhodobacter sphaeroides and mutation breeding and application thereof
A technology of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and coenzyme, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, enzymes, and electric/wave energy treatment enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective performance improvement of selected strains, fatigue, and restrictions on the fermentation level of coenzyme Q10 strains, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] The ARTP mutagenesis of embodiment 1 Rhodobacter sphaeroides
[0078] (1) Preparation of bacterial strain seed suspension:
[0079] Take 100 μl of Rhodobacter sphaeroides bacteria CF02 (preservation number: CGMCC NO.2458) stored in a glycerol tube at -80°C, spread evenly on medium A, and culture at 32°C for 5 days. After the colonies grow out, use an inoculation shovel to pick up 6 single colonies, inoculate them into a 50mL / 250mL seed bottle containing medium B, seal with a cotton plug and 2 layers of gauze, and culture at 32°C and 220rpm for 24 hours to obtain a seed suspension.
[0080] (2) Preparation of bacterial suspension slides:
[0081] Put the metal slide in the ultra-clean bench Put it in the outer flame of an alcohol lamp and burn for 30s, and put it into a disposable petri dish or a sterilized glass petri dish after cooling. Take 2mL of the cultured seed bacteria suspension, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 2min, remove the supernatant, add 0.8% normal saline,...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The screening of embodiment 2 ARTP optimal mutagenesis conditions
[0085] Experiments were designed on four parameters including mutagenesis power, mutagenesis time, mutagenesis distance and protective agent concentration, and the optimal mutagenesis conditions for ARTP to mutate Rhodobacter sphaeroids were determined by strain lethality index. When the lethal rate is 85%-95%, the mutagenesis conditions are better, and the next step of screening can be carried out. The closer the lethal rate is to 90%, the better the mutagenesis conditions.
[0086] (1) The influence of different mutagenesis powers on the lethality rate: the mutagenesis time is 20s, the mutagenesis distance is 2mm, and the protective agent is glycerol with a volume percent concentration of 5%. Mutagenesis was carried out at 130W and 140W, and the results are shown in Table 1;
[0087] (2) The influence of different mutagenesis time on the lethality rate: the mutagenesis power is 120W, the mutagenesis ...
Embodiment 3
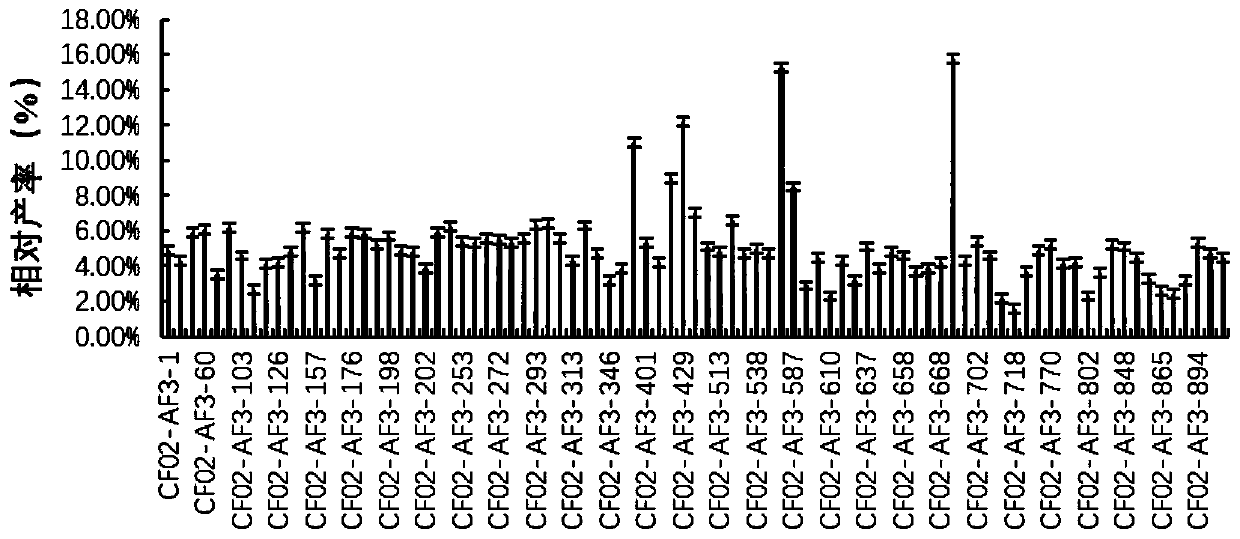
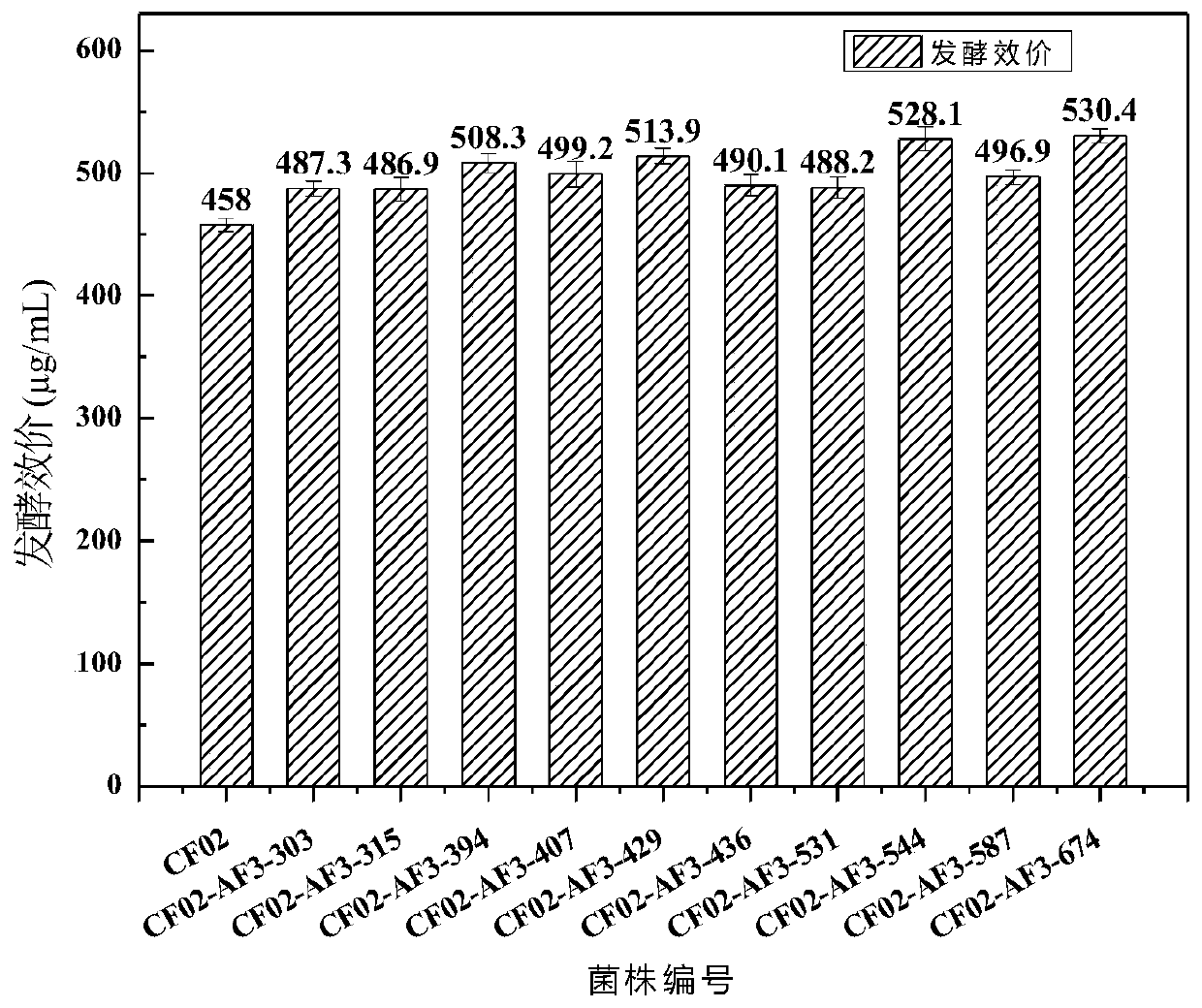
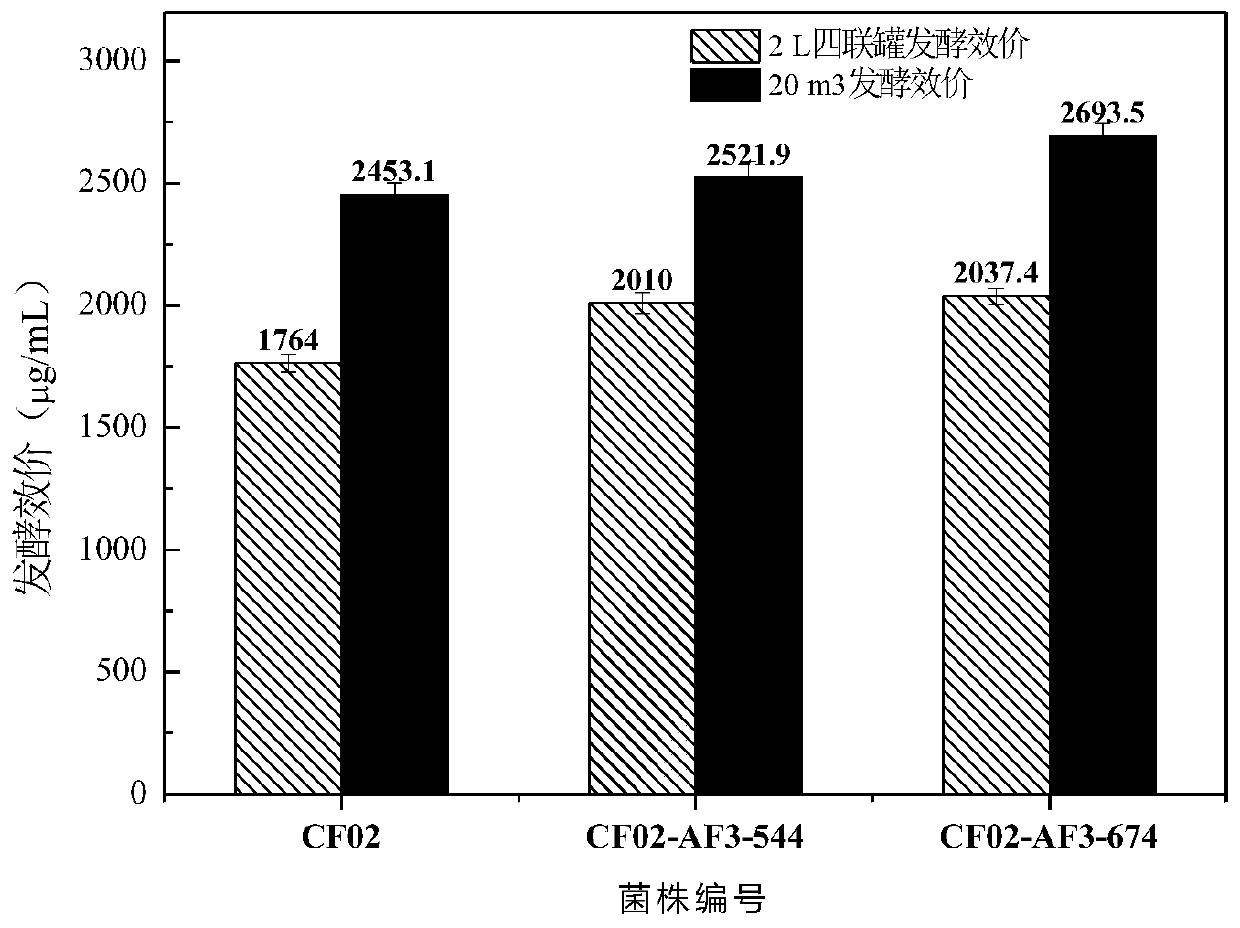
[0094] The screening of embodiment 3 multi-resistant bacterial strains
[0095] (1) Determination of optimal inhibitory concentrations of different resistant substances
[0096] In order to overcome the blindness and non-directionality of mutagenesis breeding and improve the screening efficiency, most of the strains that do not meet the production traits were removed through the resistance screening. The inhibitory effects of 10 antibiotics in 4 categories on the starting strain were verified, and the minimum inhibitory concentrations of different antibiotics were determined.
[0097] The antibiotics used are menaquinone, kanamycin, roxithromycin, vitamin K3, doxorubicin, Na 3 N, Na 2 S, actinomycin D, benzoic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
[0098] Taking the starting strain CF02 as the test object, set different concentration gradients of 10 resistant substances. When medium A is cooled to 55-60°C, add different concentrations of antibiotics into the solid medium, mix well,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fermentation titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com