Method for preparing reverse osmosis membrane by utilizing ethyl silicate as oil-phase cosolvent
A technology of ethyl silicate and reverse osmosis membrane, which is applied in the direction of semi-permeable membrane separation, chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, etc., can solve problems such as unsafe, strong pungent odor, and volatile ethyl acetate, and achieve the process Simple, easy-to-implement, low-cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Immerse the surface of the support membrane in the aqueous phase solution for 20 s so that the support membrane is fully infiltrated by the aqueous phase solution. Subsequently, the solution was poured off. Next, after ensuring that there was no visible liquid on the membrane surface, the membrane surface was immersed in a solution containing 0.04% benzoyl chloride, 2% ethyl silicate and 97.96% Isopar G to initiate interfacial polymerization. Finally, the membrane was heat-treated at 70° C. for 4 minutes to prepare an aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane, which was fully cleaned with deionized water.
[0022] Filtration of 2000ppm sodium chloride aqueous solution at 15.5bar and 25°C shows that the flux and rejection rate of the composite reverse osmosis membrane are respectively 2.45L m -2 h -1 · bar -1 and 99.25%.
Embodiment 2
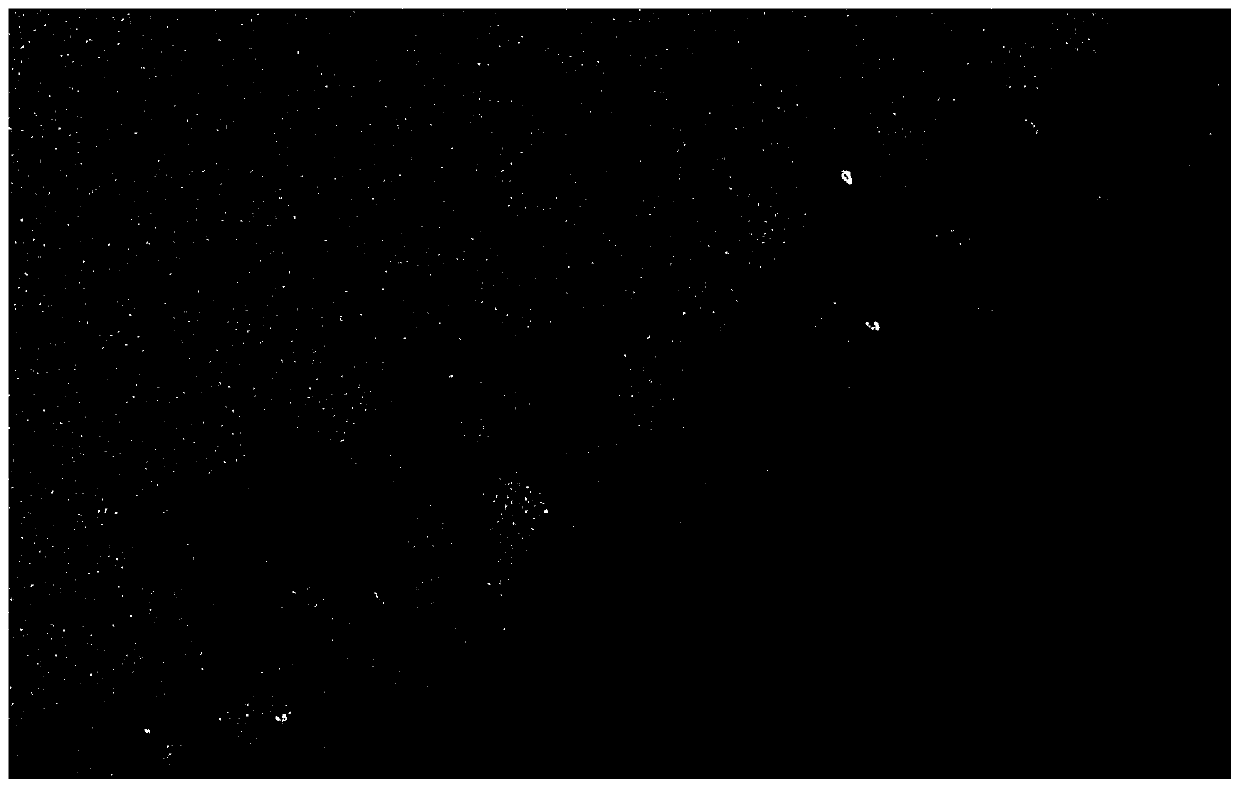
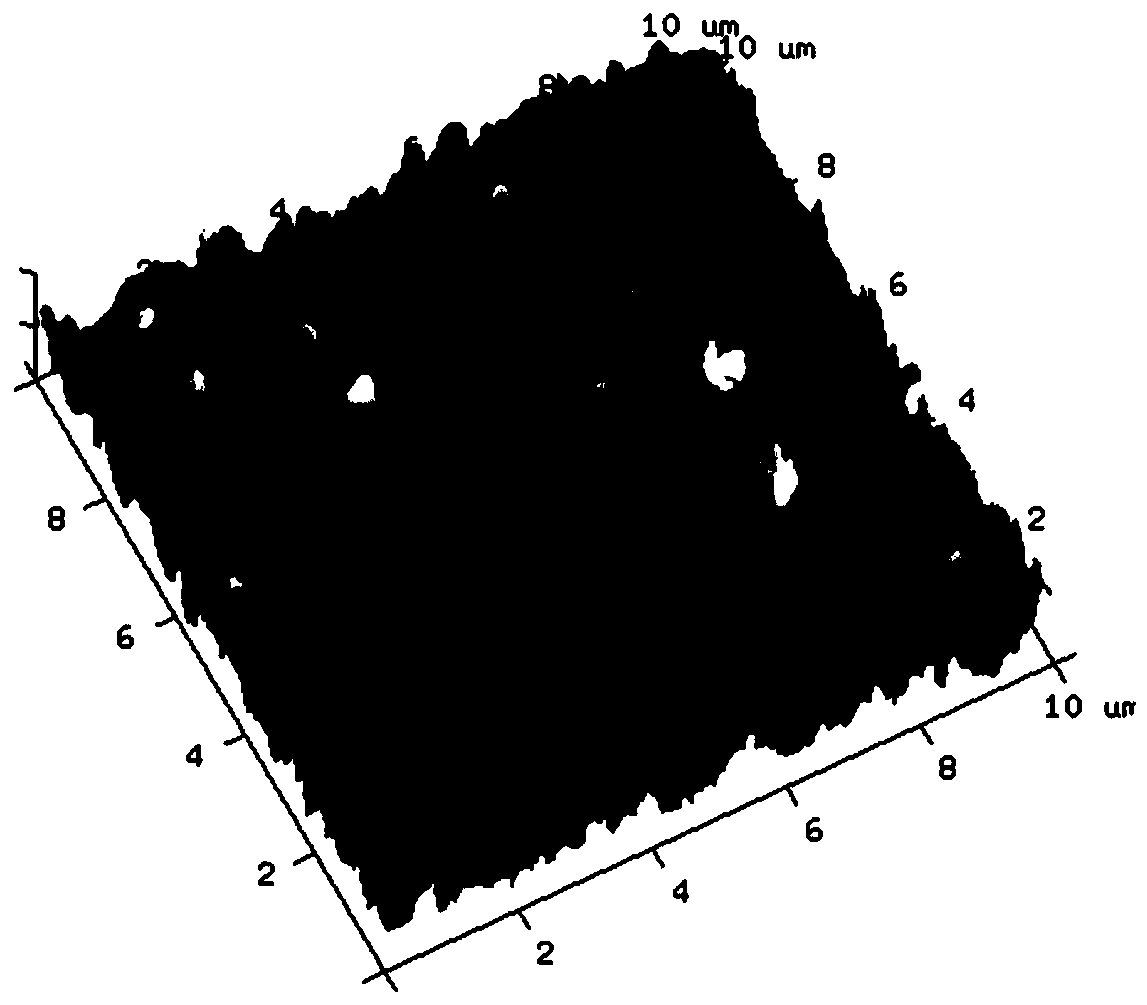
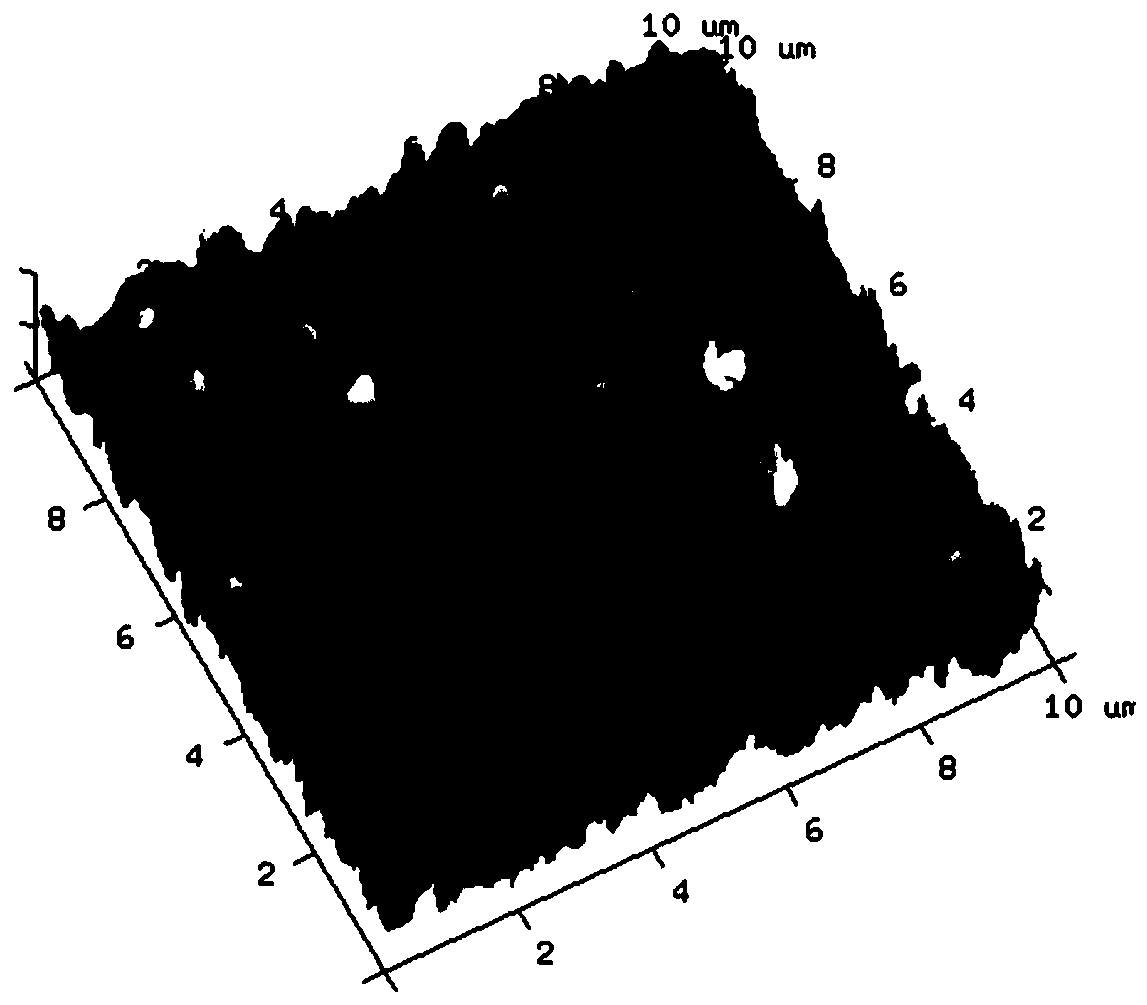
[0024] Immerse the surface of the support membrane in the aqueous phase solution for 30s so that the support membrane is fully infiltrated by the aqueous phase solution. Subsequently, the solution was poured off. Next, after ensuring that there was no visible liquid on the membrane surface, the membrane surface was immersed in a solution containing 0.12% benzoyl chloride, 8% ethyl silicate and 91.88% Isopar G to initiate interfacial polymerization. Finally, the membrane was heat-treated at 80° C. for 5 minutes to prepare an aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane, which was fully cleaned with deionized water. The atomic force microscope image of the aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane prepared in this embodiment shows that the surface of the prepared reverse osmosis membrane is rough, and the roughness is as high as 104.9nm (attached figure 1 ); the prepared aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane transmission electron microscope ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] The surface of the support membrane was soaked in the aqueous phase solution for 40s so that the support membrane was fully infiltrated by the aqueous phase solution. Subsequently, the solution was poured off. Next, after ensuring that there was no visible liquid on the membrane surface, the membrane surface was soaked in a solution containing 0.20% benzoyl chloride, 14% ethyl silicate and 85.80% Isopar G to initiate interfacial polymerization. Finally, the membrane was heat-treated at 90° C. for 6 minutes to prepare an aromatic polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane, which was fully cleaned with deionized water.
[0028] Filtration of 2000ppm sodium chloride aqueous solution at 15.5bar and 25°C shows that the flux and rejection rate of the composite reverse osmosis membrane are respectively 2.84L m -2 h -1 · bar -1 and 97.94%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com