Genetic engineering application of rice gene ORYsa;SQD1
A rice and gene technology, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, application, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the undisclosed Arabidopsis growth and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of gene sequence
[0024] AtSQD1 is a gene located on the fifth chromosome, encoding the synthesis of thioisorhamnose diglyceride synthase SQD1. The essence of SQD1 enzyme is a member of the uridine diphosphate thioisorhamnose synthase family (UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase family; SDR52E) in the short-chain dehydrogenase superfamily (Short-Chain Dehydrogenase superfamily; SDR), with NAD + The binding site can bind to ferredoxin glutamine synthase and accept sulfite (SO 3 2- ). According to the sequence of Arabidopsis SQD1 gene in NCBI, the homologous gene OsSQD1 in rice was obtained from the NCBI database, and the gene number is (same as RAB_DB) Os05g0387200. Blast and GenomeScan analysis showed that: OsSQD1 is located on the fifth chromosome of rice, the specific position is Chr5:18738602..18741791. The rice SQD1 gene contains 2 exons and 1 intron. The protein coding region of the gene is 1440bp, encoding 479 amino acids.
Embodiment 2
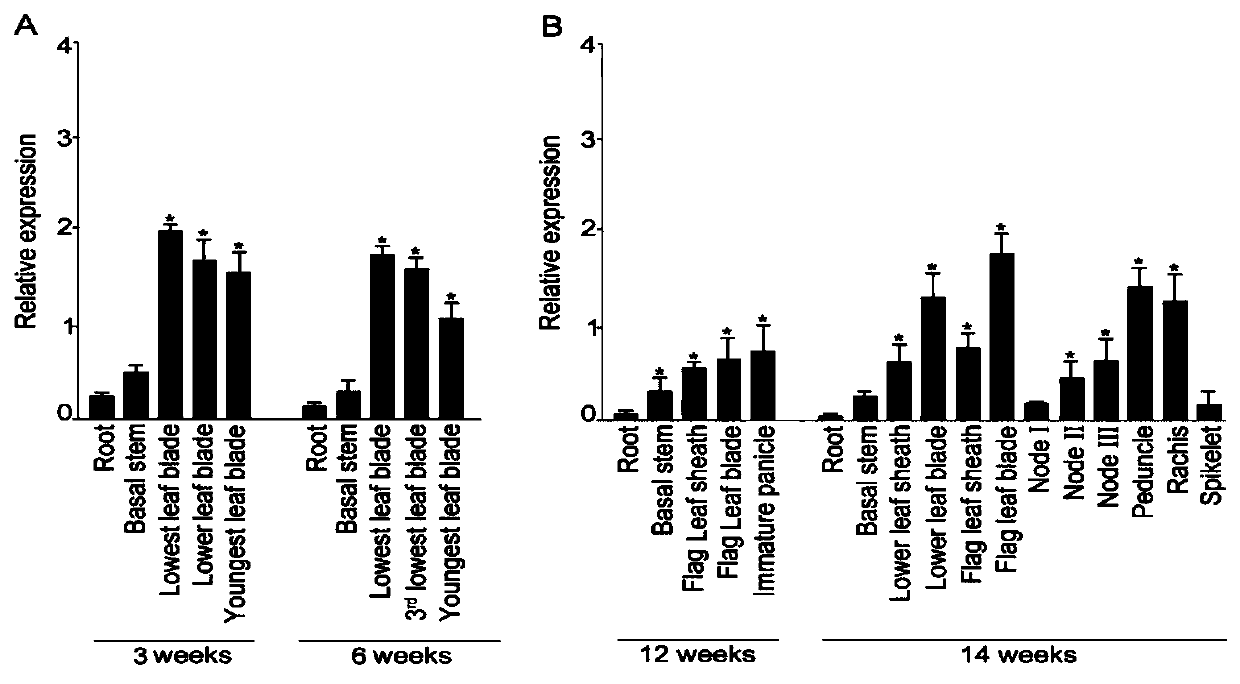
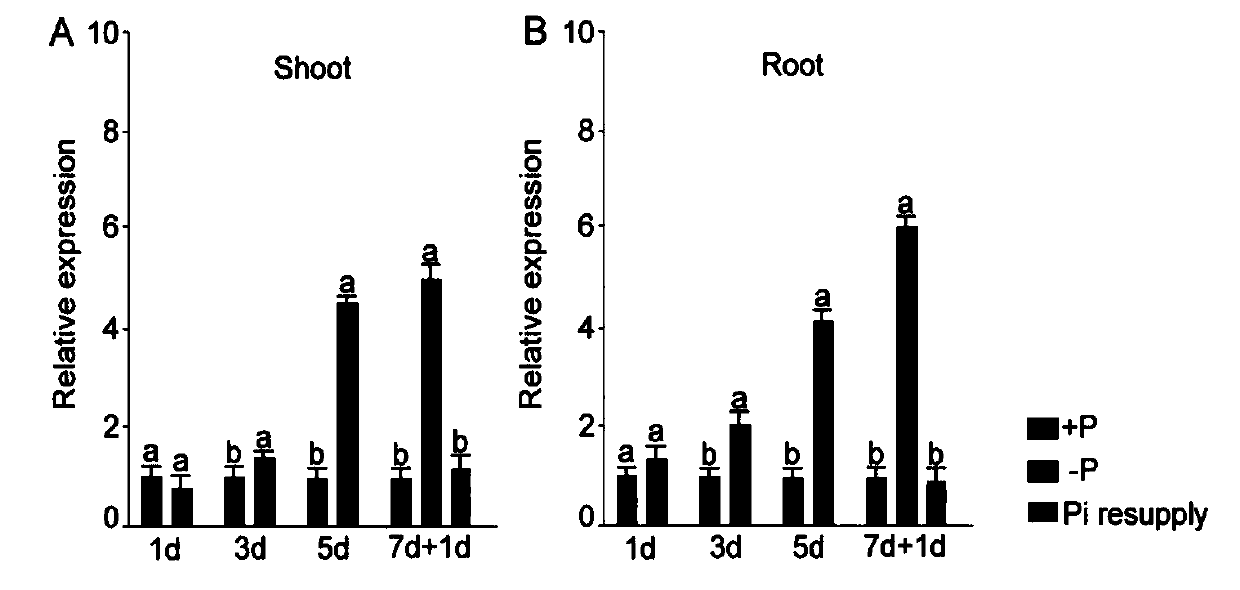
[0025] Embodiment 2, ORYsa; Expression pattern identification of SQD1 gene
[0026] 2.1. Extraction and transcription of total RNA to synthesize the first strand of cDNA
[0027] The rice variety "Nihonbare" was selected. After the rice seedlings grew to 10 days, they were cultured in complete nutrient solution for 1 week and then sampled (inverted one leaf, inverted two leaves, inverted four leaves, inverted second leaf sheath, inverted four leaf sheath, rhizome junction, root tip, root elongation zone and maturation zone). Rice seedlings were transplanted to potted pots when they were 30 days old, and samples were taken when the seedlings were 60 days old (flag leaves, inverted clover leaves, flag leaf sheaths, inverted clover leaf sheaths, stalks, stem knots and panicles). The total RNA was extracted with TriZol reagent, and the quality of the total RNA was identified by agarose gel electrophoresis, and then the RNA content was determined on a spectrophotometer. The obtai...
Embodiment 3
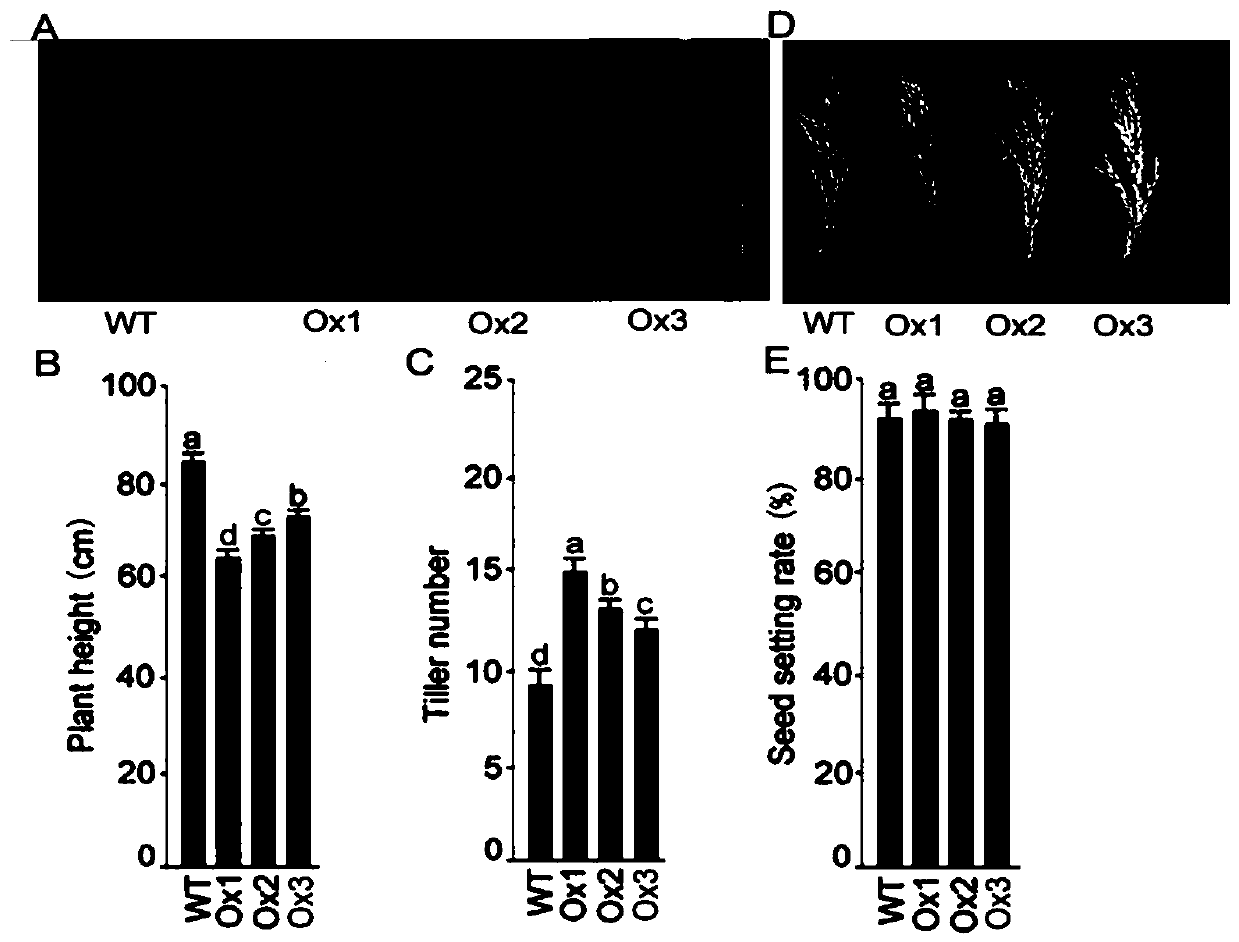
[0036] Example 3, ORYsa; SQD1 overexpression material acquisition and functional identification
[0037] 3.1 Construction of OsSQD1 overexpression vector
[0038] In order to construct the overexpression material of OsSQD1, we chose the vector pTCK303 commonly used in our laboratory as the expression vector ( Figure 9 ). According to the cDNA sequence of OsSQD1 published on the NCBI website, use DNAMAN to perform restriction enzyme analysis, and select KpnI and SpeI that are not in the cDNA and have multiple cloning restriction sites in the vector, and the target fragment can be directly combined with the pTCK303 vector. Enzyme cleavage and enzyme ligation. The primers are shown in the table (Table 1). The full-length cDNA sequence fragment of OsSQD1 was obtained by PCR amplification using high-fidelity PCR Mix using the cDNA of Nipponbare leaves as a template. Purify and recover the PCR product, and connect it into the cloning vector pEASY-Blunt. After sequencing to con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com