River-bottom in-situ remediation agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of in-situ remediation agent and bioremediation agent, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological sludge treatment, fixed/solidified sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as sediment solidification, achieve fast solidification speed and improve decomposition ability , the effect of strong environmental adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A method for preparing an in-situ ecological restoration agent for bottom mud comprises the following steps:
[0049] 1) Weigh 350 parts of ceramsite, 250 parts of fly ash, 20 parts of polyacrylamide, 100 parts of magnesium oxide, and 80 parts of iron filings; put the above powder into a high-speed powder mixer at a speed of 650 rpm, and stir for 60 minutes. Mix evenly to obtain the precursor of the sediment in-situ solidification bioremediation agent;
[0050] 2) Mix 200 parts of the bottom mud material with the precursor of the bottom mud in-situ solidification bioremediation agent prepared in the previous step, and then soak and stir for 200 seconds at 30°C in a bacterial culture medium with a pH of 7-8 , and mix well; every two days, replace the fresh bacterial culture medium and mix well, after cultivating for 7 days, filter and complete;
[0051] The microbial abundances of photosynthetic bacteria, nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, Ps...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A method for preparing an in-situ ecological restoration agent for bottom mud comprises the following steps:
[0054] 1) Weigh 300 parts of ceramsite, 300 parts of fly ash, 30 parts of polyacrylamide, 120 parts of magnesium oxide, and 100 parts of iron filings; put the above powder into a high-speed powder mixer at a speed of 1000 rpm, and stir for 50 minutes. Mix evenly to obtain the precursor of the sediment in-situ solidified bioremediation agent.
[0055] 2) Mix 300 parts of the bottom mud material with the precursor of the bottom mud in-situ solidification bioremediation agent prepared in the previous step, and then soak and stir in a bacterial culture medium with a pH of 7 to 8 at 35°C for 150 seconds. , and mix well; every two days, replace the fresh bacterial culture medium and mix well, after cultivating for 7 days, filter and complete.
Embodiment 3
[0057] In order to verify the improvement effect of the remediation agent prepared in the above examples on the polluted bottom mud, an experiment was carried out on the polluted bottom mud of a river course that often has domestic sewage and industrial wastewater discharged into both sides of a certain place and has a foul smell.
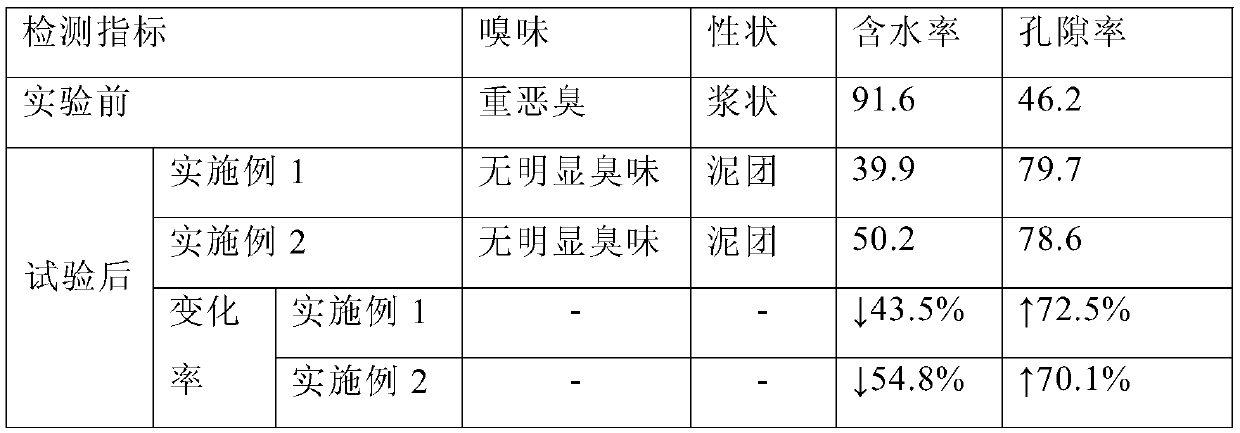
[0058] Get mud sample 1Kg, each get 0.5Kg and place in two large beakers respectively, add appropriate amount of deionized water, stir into slurry, then to one of the beakers, add the ecological restoration agent prepared in Examples 1 and 2 2.5g each, stir quickly to mix evenly, observe the effect of the mud sample after 2 minutes, and the results of sampling and detection indicators after the test are shown in Table 1. Another beaker served as a control group.
[0059] Table 1
[0060]
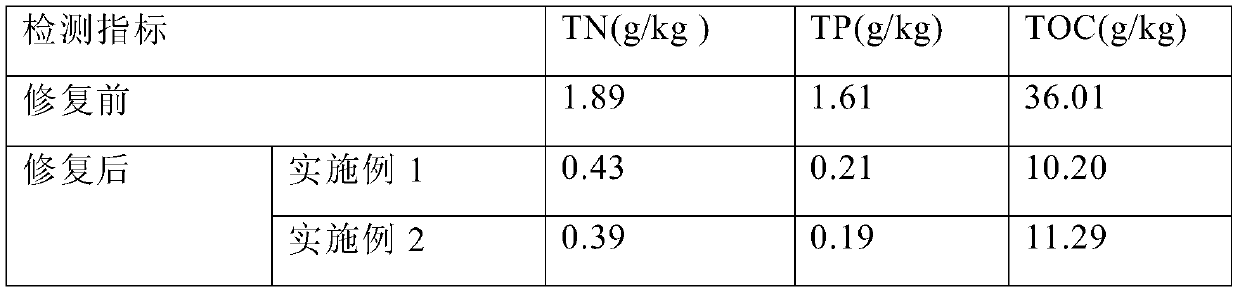
[0061] The carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus indicators in the sediment before and after the above experiment were detected, and the results of the detection i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com